Abstract
Purpose
Chemotherapy-induced neutropenia (CIN) is a common side effect of chemotherapy and an important dose-limiting factor. However, an association between CIN development and longer survival was recently reported in several solid cancers. In the present study, we aimed to assess whether CIN could be a prognostic factor and clarify other prognostic factors for patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed the medical records of 84 patients who received gemcitabine monotherapy as first-line chemotherapy for metastatic pancreatic cancer to assess whether CIN could be a prognostic factor. Potential prognostic factors of survival were examined by univariate and multivariate analyses using the log-rank test and Cox proportional hazard model, respectively.
Results
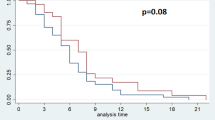
Median survival time was 170 days [95% confidence interval (CI), 147–193] in patients without CIN (grade 0), 301 days (95% CI, 152–450) in patients with grade 1–2 CIN, and 406 days (95% CI, 271–541) in patients with grade 3 CIN. The multivariate analysis revealed that a pretreatment C-reactive protein level of <0.50 mg/dL [hazard ratio (HR), 0.534; 95% CI, 0.323–0.758, P = 0.015] and grade 3 CIN (HR, 0.447; 95% CI, 0.228–0.875, P = 0.019) were independent favorable prognostic factors in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer treated with gemcitabine.
Conclusions
Neutropenia during chemotherapy was associated with increased survival of patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer. Monitoring of CIN could be used to predict treatment responsiveness.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ito Y, Miyashiro I, Ito H, Hosono S, Chihara D, Nakata-Yamada K, Nakayama M, Matsuzaka M, Hattori M, Sugiyama H, Oze I, Tanaka R, Nomura E, Nishino Y, Matsuda T, Ioka A, Tsukuma H, Nakayama T, the J-CANSIS Research Group (2014) Long-term survival and conditional survival of cancer patients in Japan using population-based cancer registry data. Cancer Sci 105(11):1480–1486. doi:10.1111/cas.12525
Monitoring of cancer incidence in Japan—Survival 2003–2005 Report (Center for Cancer Control and Information Services, National Cancer Center, 2013). http://ganjoho.jp/professional/statistics/statistics.html
Matsuda T, Ajiki W, Marugame T, Ioka A, Tsukuma H, Sobue T, Research Group of Population-Based Cancer Registries of Japan (2011) Population-based survival of cancer patients diagnosed between 1993 and 1999 in Japan: a chronological and international comparative study. Jpn J Clin Oncol 41(1):40–51. doi:10.1093/jjco/hyq167
Cancer Registry and Statistics. Cancer Information Service, National Cancer Center, Japan. http://ganjoho.jp/reg_stat/statistics/dl/index.html
Cameron DA, Massie C, Kerr G, Leonard RCF (2003) Moderate neutropenia with adjuvant CMF confers improved survival in early breast cancer. Brit J Cancer 89(10):1837–1842. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6601366
Di Maio M, Gridelli C, Gallo C, Shepherd F, Piantedosi FV, Cigolari S, Manzione L, Illiano A, Barbera S, Robbiati SF, Frontini L, Piazza E, Ianniello GP, Veltri E, Castiglione F, Rosetti F, Gebbia V, Seymour L, Chiodini P, Perrone F (2005) Chemotherapy-induced neutropenia and treatment efficacy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a pooled analysis of three randomised trials. Lancet Oncol 6(9):669–677. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(05)70255-2
Kishida Y, Kawahara M, Teramukai S, Kubota K, Komuta K, Minato K, Mio T, Fujita Y, Yonei T, Nakano K, Tsuboi M, Shibata K, Atagi S, Kawaguchi T, Furuse K, Fukushima M (2009) Chemotherapy-induced neutropenia as a prognostic factor in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results from Japan multinational trial organization LC00-03. Brit J Cancer 101(9):1537–1542. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605348
Sunaga T, Suzuki S, Kago M, Kurihara T, Kaji S, Koike N, Harada N, Suzuki M, Kikuchi Y (2014) The association between neutropenia and prognosis in stage III colorectal cancer patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy. Eur J Cancer Care 23(3):394–400. doi:10.1111/ecc.12120
Yamanaka T, Matsumoto S, Teramukai S, Ishiwata R, Nagai Y, Fukushima M (2007) Predictive value of chemotherapy-induced neutropenia for the efficacy of oral fluoropyrimidine S-1 in advanced gastric carcinoma. Brit J Cancer 97(1):37–42. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6603831
Mantovani A, Cassatella MA, Costantini C, Jaillo S (2011) Neutrophils in the activation and regulation of innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 11(8):519–531. doi:10.1038/nri3024
Tanaka T, Ikeda M, Okusaka T, Ueno H, Morizane C, Hagihara A, Iwasa S, Kojima Y (2008) Prognostic factors in Japanese patients with advanced pancreatic cancer treated with single-agent gemcitabine as first-line therapy. Jpn J Clin Oncol 38(11):755–761. doi:10.1093/jjco/hyn098
Szkandera J, Stotz M, Absenger G, Stojakovic T, Samonigg H, Kornprat P, Schaberl-Moser R, AlZoughbi W, Lackner C, Ress AL, Seggewies FS, Gerger A, Hoefler G, Pichler M (2014) Validation of C-reactive protein levels as a prognostic indicator for survival in a large cohort of pancreatic cancer patients. Brit J Cancer 110(1):183–188. doi:10.1038/bjc.2013.701
Inoue D, Ozaka M, Matsuyama M, Yamada I, Takano K, Saiura A, Ishii H (2015) Prognostic value of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and level of C-reactive protein in a large cohort of pancreatic cancer patients: a retrospective study in a single institute in Japan. Jpn J Clin Oncol 45(1):61–66. doi:10.1093/jjco/hyu159
Ohe Y, Ohashi Y, Kubota K, Tamura T, Nakagawa K, Negoro S, Nishiwaki Y, Saijo N, Ariyoshi Y, Fukuoka M (2007) Ann Oncol 18(2):317–323
Kubota K, Kawahara M, Ogawara M, Nishiwaki Y, Komuta K, Minato K, Fujita Y, Teramukai S, Fukushima M, Furuse K, Japan Multi-National Trial Organisation (2008) Lancet Oncol 9(12):1135–1142. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70261-4
Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouché O, Guimbaud R, Bécouarn Y, Adenis A, Raoul JL, Gourgou-Bourgade S, de la Fouchardière C, Bennouna J, Bachet JB, Khemissa-Akouz F, Péré-Vergé D, Delbaldo C, Assenat E, Chauffert B, Michel P, Montoto-Grillot C, Ducreux M, Groupe Tumeurs Digestives of Unicancer; PRODIGE Intergroup (2011) FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med 364(19):1817–1825. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1011923
Von Hoff DD, Ervin T, Arena FP, Chiorean EG, Infante J, Moore M, Seay T, Tjulandin SA, Ma WW, Saleh MN, Harris M, Reni M, Dowden S, Laheru D, Bahary N, Ramanathan RK, Tabernero J, Hidalgo M, Goldstein D, Van Cutsem E, Wei X, Iglesias J, Renschler MF (2013) Increased survival in pancreatic cancer with nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine. N Engl J Med 369(18):1691–1703. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1304369
Rha SY, Jeung HC, Choi YH, Yang WI, Yoo JH, Kim BS, Roh JK, Chung HC (2007) An association between RRM1 haplotype and gemcitabine-induced neutropenia in breast cancer patients. Oncologist 12(6):622–630. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.12-6-622
Tanaka M, Javle M, Dong X, Eng C, Abbruzzese JL, Li D (2010) Gemcitabine metabolic and transporter gene polymorphisms are associated with drug toxicity and efficacy in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Cancer 116(22):5325–5335. doi:10.1002/cncr.25282
Okazaki T, Javle M, Tanaka M, Abbruzzese JL, Li D (2010) Single nucleotide polymorphisms of gemcitabine metabolic genes and pancreatic cancer survival and drug toxicity. Clin Cancer Res 16(1):320–329. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1555
Green H, Hasmats J, Kupershmidt I, Edsgard D, de Petris L, Lewensohn R, Blackhall F, Vikingsson S, Besse B, Lindgren A, Branden E, Koyi H, Peterson C, Lundeberg J (2015) Using whole-exome sequencing to identify genetic markers for carboplatin and gemcitabine-induced toxicities. Clin Cancer Res 22(2):366–373. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0964
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank all patients and medical staff who participated in this study.
Contributions of authors statement
A.O. and D.T. designed the study, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. K.T., M.Y., H.N., M.O., and M.M. collected data. Y.K. analyzed the data. K.I. and K.H. reviewed the study design, protocol, and study report. K.I. approved the version to be published.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Otake, A., Tsuji, D., Taku, K. et al. Chemotherapy-induced neutropenia as a prognostic factor in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer treated with gemcitabine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 73, 1033–1039 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-017-2260-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-017-2260-0