Abstract
A facile and economic colorimetric strategy was designed for ATP detection by rationally using urease, a pH-responsive molecule, and a metal-mediated switchable DNA probe. By utilizing metal ions as a modulator of urease activity, the concentration of ATP is translated into pH change, which can be readily visualized by naked eye. An unmodified single-stranded DNA probe was designed, which consists of a target binding sequence and two flanked cytosine (C)-rich sequences. This C-rich single-stranded DNA can form a hairpin structure triggered by Ag+ ions via C-Ag+-C base mismatch. Upon introduction of ATP, Ag+-coordinated hairpin DNA structure will be broken and release the included Ag+, thus inhibiting the activity of urease. Conversely, urease can hydrolyze urea and raise pH value of the solution, resulting in the color change of the sensing solution. The proposed assay allows determination of ATP as low as 1.6 nM and shows a satisfactory result in human serum. Because of simple operation and low cost of this method, we believe it has a potential in point-of-care (POC) testing in resource-limited areas.
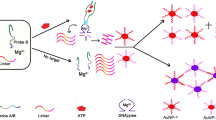
Graphical abstract

Schematic illustration of pH-responsive colorimetric sensor for ATP detection based on switchable DNA aptamer and metal ion–urease interactions





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yokoshiki H, Sunagawa M, Seki T, Sperelakis N. ATP-sensitive K+ channels in pancreatic, cardiac, and vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Phys. 1998;274(1):C25–37.
Zhu S, Wang X, **g C, Yin Y, Zhou N. A colorimetric ATP assay based on the use of a magnesium(II)-dependent DNAzyme. Microchim Acta. 2019;186(3):176.
Ma X, Miao P. Silver nanoparticle@DNA tetrahedron-based colorimetric detection of HIV-related DNA with cascade strand displacement amplification. J Mater Chem B. 2019;7(16):2608–12.
Ma X, Gao L, Tang Y, Miao P. Gold nanoparticles-based DNA logic gate for miRNA inputs analysis coupling strand displacement reaction and hybridization chain reaction. Part Part Syst Charact. 2017;35:1700326.
Chen S-J, Huang Y-F, Huang C-C, Lee K-H, Lin Z-H, Chang H-T. Colorimetric determination of urinary adenosine using aptamer-modified gold nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron. 2008;23(11):1749–53.
Wang J, Wang L, Liu X, Liang Z, Song S, Li W, et al. A gold nanoparticle-based aptamer target binding readout for ATP assay. Adv Mater. 2007;19(22):3943–6.
Li Z, ** R, Mirkin CA, Letsinger RL. Multiple thiol-anchor capped DNA-gold nanoparticle conjugates. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30(7):1558–62.
Liu F, Zhang J, Chen R, Chen L, Deng L. Highly effective colorimetric and visual detection of ATP by a DNAzyme-aptamer sensor. Chem Biodivers. 2011;8(2):311–6.
Xu X, Nan D, Yang H, Pan S, Liu H, Hu X. Quercetin@ZIF-90 as a novel antioxidant for label-free colorimetric ATP sensing at neutral pH. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2020;304:127324.
**ong Y, Zhang J, Yang Z, Mou Q, Ma Y, **ong Y, et al. Functional DNA regulated CRISPR-Cas12a sensors for point-of-care diagnostics of non-nucleic-acid targets. J Am Chem Soc. 2020;142(1):207–13.
Yang Y, Li C, Shi H, Chen T, Wang Z, Li G. A pH-responsive bioassay for paper-based diagnosis of exosomes via mussel-inspired surface chemistry. Talanta. 2019;192:325–30.
Wang L, Chen C, Huang H, Huang D, Luo F, Qiu B, et al. Sensitive detection of telomerase activity in cancer cells using portable pH meter as readout. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;121:153–8.
Liu D, Wang Z, ** A, Huang X, Sun X, Wang F, et al. Acetylcholinesterase-catalyzed hydrolysis allows ultrasensitive detection of pathogens with the naked eye. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2013;52(52):14065–9.
Tram K, Kanda P, Salena BJ, Huan S, Li Y. Translating bacterial detection by DNAzymes into a litmus test. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2014;53(47):12799–802.
Ali MM, Wolfe M, Tram K, Gu J, Filipe CDM, Li Y, et al. A DNAzyme-based colorimetric paper sensor for helicobacter pylori. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2019;58(29):9907–11.
Singh P, Kakkar S, Bharti, Kumar R, Bhalla V. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric detection of pathogens based on silver-urease interactions. Chem Commun. 2019;55(33):4765–8.
He W, Luo L, Liu Q, Chen Z. Colorimetric sensor array for discrimination of heavy metal ions in aqueous solution based on three kinds of thiols as receptors. Anal Chem. 2018;90(7):4770–5.
Joseph J, Schuster GB. Long-distance radical cation hop** in DNA: the effect of thymine−Hg(II)−thymine base pairs. Org Lett. 2007;9(10):1843–6.
Kondo J, Tada Y, Dairaku T, Saneyoshi H, Okamoto I, Tanaka Y, et al. High-resolution crystal structure of a silver(I)-RNA hybrid duplex containing Watson-Crick-like C-silver(I)-C metallo-base pairs. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2015;54(45):13323–6.
Naskar S, Guha R, Müller J. Metal-modified nucleic acids: metal-mediated base pairs, triples, and tetrads. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2020;59(4):1397–406.
Jiang X, Xu W, Chen X, Liang Y. Colorimetric assay for ultrasensitive detection of Ag(I) ions based on the formation of gold nanoparticle oligomers. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411(11):2439–45.
Lee JS, Ulmann PA, Han MS, Mirkin CA. A DNA-gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric competition assay for the detection of cysteine. Nano Lett. 2008;8(2):529–33.
Chen P, Sawyer E, Sun K, Zhang X, Chen C, Ying B, et al. A general strategy for label-free homogeneous bioassays based on selective recognition and silver ion-mediated conformational switch. Talanta. 2019;201:9–15.
Ding J, Qin W, Zhang Y, Wang X. Potentiometric aptasensing based on target-induced conformational switch of a DNA probe using a polymeric membrane silver ion-selective electrode. Biosens Bioelectron. 2013;45:148–51.
Zhang J, Lan T, Lu Y. Translating in vitro diagnostics from centralized laboratories to point-of-care locations using commercially-available handheld meters. Trac-Trend Anal Chem. 2020;124:115782.
Huo Y, Qi L, Lv XJ, Lai T, Zhang J, Zhang ZQ. A sensitive aptasensor for colorimetric detection of adenosine triphosphate based on the protective effect of ATP-aptamer complexes on unmodified gold nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;78:315–20.
Wolfe MG, Ali MM, Brennan JD. Enzymatic litmus test for selective colorimetric detection of C–C single nucleotide polymorphisms. Anal Chem. 2019;91(7):4735–40.
Zheng Y, Yang C, Yang F, Yang X. Real-time study of interactions between cytosine-cytosine pairs in DNA oligonucleotides and silver ions using dual polarization interferometry. Anal Chem. 2014;86(8):3849–55.
Guo Y, Yang K, Sun J, Wu J, Ju H. A pH-responsive colorimetric strategy for DNA detection by acetylcholinesterase catalyzed hydrolysis and cascade amplification. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;94:651–6.
Mazzei L, Cianci M, Gonzalez Vara A, Ciurli S. The structure of urease inactivated by Ag(i): a new paradigm for enzyme inhibition by heavy metals. Dalton Trans. 2018;47(25):8240–7.
Li S, Zhao X, Yu X, Wan Y, Yin M, Zhang W, et al. Fe3O4 nanozymes with aptamer-tuned catalysis for selective colorimetric analysis of ATP in blood. Anal Chem. 2019;91(22):14737–42.
Jiang G, Zhu W, Shen X, Xu L, Li X, Wang R, et al. Colorimetric and visual determination of adenosine triphosphate using a boronic acid as the recognition element, and based on the deaggregation of gold nanoparticles. Microchimi Acta. 2017;184(11):4305–12.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their gratitude to the staff at the Department of Oncology at the First Affiliated Hospital of Nan**g Medical University, Nan**g, China, for providing the human serum samples used for validation purposes. The authors gratefully acknowledge reagent support from Prof. Genxi Li.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81972484), The High-Level Innovation Team of Nan**g Medical University (JX102GSP201727), and The National Key Research and Development Program of China (ZDZX2017ZL-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Statement of ethical approval
All patient samples were acquired from Department of Oncology at the First Affiliated Hospital of Nan**g Medical University. The use of the discarded human serum samples was approved by the First Affiliated Hospital of Nan**g Medical University Institutional Review Board under protocol #2019-SRFA-132.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, S., Yang, Y., Li, M. et al. A pH-responsive bioassay for sensitive colorimetric detection of adenosine triphosphate based on switchable DNA aptamer and metal ion–urease interactions. Anal Bioanal Chem 413, 1533–1540 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-03136-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-03136-z