Abstract
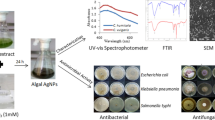
This study describes phycocompounds of the non-N2-fixing filamentous cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp., which has potential bio-reducing and stabilizing heavy metal–accumulating properties for synthesizing silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), whose formation was confirmed by the colour change of the Lyngbya sp.-AgNP solution from pale green to deep brown. The reduction of ‘Lyngbya sp.-AgNPs’, called Lsp-AgNPs, was proved by UV-visible photo-spectrometry analysis with an obtained peak value at 426 nm. Lsp-AgNPs were characterised by analytical techniques, XRD, FESEM, DLS and FTIR. The XRD analysis with 5–70 theta was obtained at 2ϴ angles ranging from 38.79º with intensity, indicating the crystal structure of Lsp-AgNPs. The FESEM analysis indicated the area size at 20–50 µm; in the DLS analysis, the peak at 400 d nm indicated the size and distribution of Lsp-AgNPs. In FTIR analysis, the peaks were obtained at wavenumbers 3338, 1639, and 542 cm−1, which indicated the presence of N–H, –OH and C=O functional groups in Lsp-AgNPs. Those had in vitro antibacterial activities against Gram-negative Escherichia coli (MTCC 443) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MTCC 1688) and Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus (MTCC 7443) bacterial strains with zone of inhibitions (ZOI) of 16, 12 and 14 mm, respectively, with comparing the antibiotic gentamycin as a positive control, as was monitored with agar-well diffusion method. Furthermore, the MIC value was 50 mg/ml, and MBC values of 65 mg/ml of Lsp-AgNPs were effective against those bacteria. Thus, Lsp-AgNPs had potential antibacterial activities against MDR pathogenic S. aureus, E. coli and P. aeruginosa. In conclusion, MDR pathogenic bacteria could be controlled as prodrugs in the future.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
References
Adebayo-Tayo B, Salaam A, Ajibade A (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticle using Oscillatoria sp extract, its antibacterial, antibiofilm potential and cytotoxicity activity. Heliyon 5:e02502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019
Ahamad I, Aziz N, Zaki A, Fatma T (2021) Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Anabaena variabilis as a potential antimicrobial agent. J Appl Phycol 33:829–841. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-020-02323-w
Aly BE, Mona BH, Higazy AM (2023) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by cyanobacterial extracts: an approach guarantees potential bioactivity and proper cereal seed germination. Egypt Pharm J 22:613–631. https://doi.org/10.4103/epj.epj_101_23
Ameen F, Abdullah MM, Al-Homaidan AA, Al-Lohedan HA, Al-Ghanayem AA, Almansob A (2020) Fabrication of silver nanoparticles employing the cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis and its bactericidal effect against opportunistic nosocomial pathogens of the respiratory tract. J Mol Struct 1217:128392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128392
Attallah NG, Elekhnawy E, Negm WA, Hussein IA, Mokhtar FA, Al-Fakhrany OM (2022) In vivo and in vitro antimicrobial activity of biogenic silver nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates. Pharmaceuticals 15:194. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020194
Bharani RA, Namasivayam SK (2017) Biogenic silver nanoparticles mediated stress on developmental period and gut physiology of major lepidopteran pest Spodoptera litura (Fab.)(Lepidoptera: Noctuidae)—an eco-friendly approach of insect pest control. J Environ Chem Eng 5:453–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.12.023
Bishoyi AK, Sahoo CR, Sahoo AP, Padhy RN (2021) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles with the brackish water blue-green alga Oscillatoria princeps and antibacterial assessment. Appl Nanosci 11:389–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01593-7
Bishoyi AK, Sahoo CR, Padhy RN (2023) Recent progression of cyanobacteria and their pharmaceutical utility: an update. J Biomol Struct Dyn 41:4219–4252. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2022.2062051
Borah D, Das N, Das N, Bhattacharjee A, Sarmah P, Ghosh K, Chandel M, Rout J, Pandey P, Ghosh NN, Bhattacharjee CR (2020) Alga-mediated facile green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Photophysical, catalytic and antibacterial activity. Appl Organomet Chem 34:e5597. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.5597
Ghasemi S, Dabirian S, Kariminejad F, Koohi DE, Nemattalab M, Majidimoghadam S, Zamani E, Yousefbeyk F (2024) Process optimization for green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Rubus discolor leaves extract and its biological activities against multi-drug resistant bacteria and cancer cells. Sci Rep 14:4130. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-54702-9
Husain S, Verma SK, Azam M, Sardar M, Haq QM, Fatma T (2021) Antibacterial efficacy of facile cyanobacterial silver nanoparticles inferred by antioxidant mechanism. Mater Sci Eng C 122:111888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2021.111888
Ismail GA, El-Sheekh MM, Samy RM, Gheda SF (2021) Antimicrobial, antioxidant, and antiviral activities of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles by phycobiliprotein crude extract of the cyanobacteria Spirulina platensis and Nostoc linckia. Bionanoscience 11:355–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-021-00828-3
Jang J, Hur HG, Sadowsky MJ, Byappanahalli MN, Yan T, Ishii S (2017) Environmental Escherichia coli: ecology and public health implications—a review. J Appl Microbiol 123:570–581. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13468
Karageorgou D, Zygouri P, Tsakiridis T, Hammami MA, Chalmpes N, Subrati M, Sainis I, Spyrou K, Katapodis P, Gournis D, Stamatis H (2022) Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles with high antibacterial activity using cell extracts of cyanobacterium Pseudanabaena/ Limnothrix sp. Nanomater 12:2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12132296
Kumpitsch C, Koskinen K, Schöpf V, Moissl-Eichinger C (2019) The microbiome of the upper respiratory tract in health and disease. BMC Biol 17:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-019-0703-z
Mandhata CP, Sahoo CR, Padhy RN (2022) Biomedical applications of biosynthesized gold nanoparticles from cyanobacteria: an overview. Biol Trace Elem Res 200:5307–5327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-03078-2
Mandhata CP, Bishoyi AK, Sahoo CR, Swain S, Bej S, Jali BR, Meher RK, Dubey D, Padhy RN (2023) Investigation of in vitro antimicrobial, antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of Nostoc calcicola biosynthesized gold nanoparticles. Bioproc Biosyst Eng 46:1341–1350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-023-02905-1
Moraes LC, Figueiredo RC, Ribeiro-Andrade R, Pontes-Silva AV, Arantes ML, Giani A, Figueredo CC (2021) High diversity of microalgae as a tool for the synthesis of different silver nanoparticles: a species-specific green synthesis. Colloid Interfac Sci Com 42:100420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2021.100420
Mora-Godínez S, Abril-Martínez F, Pacheco A (2022) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using microalgae acclimated to high CO2. Mater Today Proc 48:5–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.04.761
Namasivayam S, Bharani RS (2021) Biocompatible silver nanoparticles-loaded fungal metabolites nanoconjugate (AgNP–FM) preparation for the noteworthy pesticidal activity. Natl Acad Sci Lett 44:511–517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40009-021-01044-z
Namasivayam SK (2024) Eco friendly, green route method for the preparation of poly ethylene glycol (PEG) mediated surface modified iron oxide nanoparticles (PEG-IONps) with potential biological activities. Environ Qual Manag. https://doi.org/10.1002/tqem.22172
Namasivayam SK, Pattukumar V, Samrat K, Kumar JA, Bharani RA, Alothman AA, Osman SM, Tran VA, Rajasimman M (2022) Evaluation of methyl orange adsorption potential of green synthesized chitosan-silver nanocomposite (CS–AgNC) and its notable biocompatibility on freshwater Tilapia (Oreochromis nitoticus). Chemosphere 308:135950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135950
Namasivayam SK, Francis AL, Kavisri M, Alharbi NS, Thiruvengadam M, Moovendhan M (2023) Biocompatible nanoscale silica particles fabricated from aminopropyltriethoxysilane functionalized brick ash induced versatile pesticidal activity. Environ Res 238:117090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.117090
Namasivayam SK, Aroma R, Samrat K, Bharani RA, Kavisri M, Kadaikunnan S, Thiruvengadam M, Moovendhan M (2024) Heat shock proteins capped biocompatible silver nanoparticles and their notable organic waste pollutants removal efficacy. J Environ Chem Eng 12:111753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.111753
Pandurangan P, Dinesh RA, MohanaSundaram A, Samrat AV, Meenambika SS, Vedanarayanan V, Meena R, Namasivayam SK, Moovendhan M (2023) Integrating cutting-edge technologies: AI, IoT, blockchain and nanotechnology for enhanced diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer-A review. J Drug Deliv Technol 29:105197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2023.105197
Ramasamy T, Nooruddin T (2023) Antibacterial potential of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using phycocyanin of freshwater cyanobacterium Oscillatoria pseudogeminata. Appl Nanosci 13:1277–1283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01973-7
Rosman NS, Harun NA, Idris I, Ismail WI (2020) Eco-friendly silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) fabricated by green synthesis using the crude extract of marine polychaete, Marphysa moribidii: biosynthesis, characterisation, and antibacterial applications. Heliyon 6:e05462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05462
Sahoo CR, Maharana S, Mandhata CP, Bishoyi AK, Paidesetty SK, Padhy RN (2020) Biogenic silver nanoparticle synthesis with cyanobacterium Chroococcus minutus isolated from Baliharachandi sea-mouth, Odisha, and in vitro antibacterial activity. Saudi J Biol Sci 27:1580–1586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.03.020
Sahoo CR, Swain S, Luke AM, Paidesetty SK, Padhy RN (2021) Biogenic synthesis of silver-nanoparticles with the brackish water cyanobacterium Nostoc sphaeroides and assessment of antibacterial activity against urinary tract infecting bacteria. J Taibah Univ SCI 15:805–813. https://doi.org/10.1080/16583655.2021.2005909
Sathishkumar RS, Sundaramanickam A, Srinath R, Ramesh T, Saranya K, Meena M, Surya P (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by bloom forming marine microalgae Trichodesmium erythraeum and its applications in antioxidant, drug-resistant bacteria, and cytotoxicity activity. J Saudi Chem Soc 23:1180–1191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2019.07.008
Sharma D, Kanchi S, Bisetty K (2019) Biogenic synthesis of nanoparticles: a review Arab. J Chem 12:3576–3600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.11.002
Sowmya R, Karthick Raja Namasivayam S, Krithika Shree S (2024) A critical review on nano-selenium based materials: synthesis, biomedicine applications and biocompatibility assessment. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 11:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02959-4
Swain S, Bej S, Bishoyi AK, Mandhata CP, Sahoo CR, Padhy RN (2023) Recent progression on phytochemicals and pharmacological properties of the filamentous cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. N-S Arch Ph 396:2197–2216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02488-4
Syam Kumar VN, Sunkar S, Selvaraj KR, Nellore J (2023) Nano drug delivery systems: a mini-review. Nanosci Nanotechnol Asia 13:68–81. https://doi.org/10.2174/2210681213666230504115152
Tripathi N, Goshisht MK (2022) Recent advances and mechanistic insights into antibacterial activity, antibiofilm activity, and cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. ACS Appl Bio Mater 5:1391–1463. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.2c00014
Vishwanath R, Negi B (2021) Conventional and green methods of synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their antimicrobial properties. Curr Res Green Sustain Chem 4:100205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crgsc.2021.100205
Yalçın D, Erkaya İA, Erdem B (2022) Antimicrobial, antibiofilm potential, and anti-quorum sensing activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized from cyanobacteria Oscillatoria princeps. Environ Sci Pollut R 29:89738–89752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22068-y
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Prof. Dr. S. Mishra, Dean, Institute of Medical Sciences and Sum Hospital, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, for encouragement.
Funding
This work, along with S. Swain, received funding through a PhD fellowship (University Registration Number 2181611011/2021) in Biotechnology from SOA Deemed to be University in Bhubaneswar, Odisha.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SS: Writing an original work, collecting the reference materials, reviewing and editing. SB: AKB: BRJ: reviewing and editing RNP: Conceptualisation, reviewing, editing, and supervision. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Biosynthesis of silver oxide with cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp.
• Spectral characterisations of biosynthesised L sp-AgNPs.
• In vitro antibacterial assessment of L sp-AgNPs.
• L sp-AgNPs may play a role as future antibacterial druggable agents.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Swain, S., Bej, S., Bishoyi, A.K. et al. Biosynthesis and characterisations of silver nanoparticles with filamentous cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. with in vitro antibacterial properties against MDR pathogenic bacteria. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-024-03235-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-024-03235-z