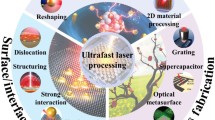
Abstract
Surface functionalization of metallic micro-nanoscale system is an emerging strategy for the realization of multifunctional materials. As a facile one-step process, ultrafast laser micromachining has emerged in recent years as a new technique for micro-nanostructure fabrication. In the past, lots of investigations on ultrafast laser micromachining were focused to understand the complex ablation mechanism, whereas recent works are mostly concerned with the fabrication of various metallic surface structures owing to their numerous potential functions, such as wetting, metallurgical and optical properties. This paper provides a short overview of advances in fabrication of functionalized metallic surfaces by ultrafast laser micromachining. The principles of interaction between ultrafast laser and metallic materials are provided. According to the surface topography, state-of-the-art knowledge on the fabrication of surface functionalization using ultrafast laser are presented. Functionalized properties of laser micro-machined metals are given. In addition, the challenges and outlooks in surface functionalized metals are presented.

































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao X, Jiang L (2004) Water-repellent legs of water striders. Nature 432(7013):36–36. https://doi.org/10.1038/432036a
Gao X, Yan X, Yao X, Xu L, Zhang K, Zhang J, Yang B, Jiang L (2007) The dry‐style antifogging properties of mosquito compound eyes and artificial analogues prepared by soft lithography. Adv Mater 19(17):2213–2217. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200601946
Guo Z, Liu W (2007) Biomimic from the superhydrophobic plant leaves in nature: Binary structure and unitary structure. Plant Sci 172(6)1103–1112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2007.03.005
Wu X, Bai Y, Zhao H, Zhou W, Tao H (2016) Femtosecond Laser Fabricate Wetting Function Micro-and Nanostructure on Aerial Aluminum Alloys Surface. Journal of Changchun University of science and Technology (Natural science Edition) 39(005):25–29,50. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-9870.2016.05.006
Xue L, Yu J, Ma X, Liu Z, Tao H, Lin J (2018) Femtosecond Laser Fabricated Wetting Copper Surfaces and Their Anti-Icing Properties. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology. https://doi.org/10.16080/j.issn1671-833x.2018.12.074
Dimitrakellis P, Gogolides E (2018) Hydrophobic and superhydrophobic surfaces fabricated using atmospheric pressure cold plasma technology: A review. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 254:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2018.03.009
Zhou C, Li H, Lin J, Hou K, Yang Z, Pi P, Xu S, Wen X, Cheng J (2017) Matchstick-Like Cu2S@ CuxO Nanowire Film: Transition of Superhydrophilicity to Superhydrophobicity. J Phys Chem C 121(36):19716–19726. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b03645
Yong J, Yang Q, Chen F, Hou X (2018) Femtosecond laser-induced superwetting surfaces. Chin Sci Bull 64(12):1213–1237
Shan C, Yong J, Yang Q, Chen F, Huo J, Zhuang J, Jiang Z, Hou X (2018) Reversible switch between underwater superaerophilicity and superaerophobicity on the superhydrophobic nanowire-haired mesh for controlling underwater bubble wettability. Aip Advances 8(4):045001. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5018864
Fadeeva E, Chichkov B (2018) Biomimetic Liquid-Repellent Surfaces by Ultrafast Laser Processing. Applied Sciences-Basel 8(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091424
Liu M, Wang S, Wei Z, Song Y, Jiang L (2009) Bioinspired Design of a Superoleophobic and Low Adhesive Water/Solid Interface. Adv Mater 21(6):665–669. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200801782
Parker AR, Lawrence CR (2001) Water capture by a desert beetle. Nature 414(6859):33–34. https://doi.org/10.1038/35102108
Lv J, Song Y, Jiang L, Wang J (2014) Bio-inspired strategies for anti-icing. ACS nano 8(4):3152–3169. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn406522n
Long J, Wu Y, Gong D, Fan P, Jiang D, Zhang H, Zhong M (2015) Femtosecond laser fabricated superhydrophobic copper surfaces and their anti-icing properties. Chin J Lasers 42(7):0706002. https://doi.org/10.3788/CJL201542.0706002
Neinhuis WB (1997) Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta 202(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.2307/23384993
Zheng Y, Gao X, Jiang L (2007) Directional adhesion of superhydrophobic butterfly wings. Soft Matter 3. https://doi.org/10.1039/b612667g
Liang W, Zhu L, Li W, Liu H (2015) Facile fabrication of a flower-like CuO/Cu (OH) 2 nanorod film with tunable wetting transition and excellent stability. RSC Advances 5(48):38100–38110. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra04359j
Rao AV, Latthe SS, Mahadik SA, Kappenstein C (2011) Mechanically stable and corrosion resistant superhydrophobic sol–gel coatings on copper substrate. Appl Surf Sci 257(13):5772–5776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.01.099
Wilkinson M, Kafizas A, Bawaked SM, Obaid AY, Al-Thabaiti SA, Basahel SN, Carmalt CJ, Parkin IP (2013) Combinatorial atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition of graded TiO2–VO2 mixed-phase composites and their dual functional property as self-cleaning and photochromic window coatings. ACS combinatorial science 15(6):309–319. https://doi.org/10.1021/co400027p
Zhu H, Gao L, Yu X, Liang C, Zhang Y (2017) Durability evaluation of superhydrophobic copper foams for long-term oil-water separation. Appl Surf Sci 407:145–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.02.184
Celia E, Darmanin T, de Givenchy ET, Amigoni S, Guittard F (2013) Recent advances in designing superhydrophobic surfaces. J colloid interface sci 402:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.03.041
Su J, Li Y, Yan X, Li R (2016) Fabrication of super-microporous nanocrystalline zirconia with high thermal stability. Chem Phys Lett 650:98–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2016.03.003
Lin C, Zhong M, Fan P, Long J, Gong D, Zhang H (2014) Picosecond laser fabrication of large-area surface micro-nano lotus-leaf structures and replication of superhydrophobic silicone rubber surfaces. Chin J Lasers 41(9):0903007. https://doi.org/10.3788/CJL201441.0903007
Zhang L, Sun Y, Wang G, Li T (2020) Progress in Research and Application of Femtosecond Laser in Industry. Hot Working Technology v.49;No.536(10):27–31. https://doi.org/10.14158/j.cnki.1001.3814.20190729
Küper S, Stuke M (1989) Ablation of polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon) with femtosecond UV excimer laser pulses. Appl Phys Lett 54(1):4–6. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.100831
Küper S, Stuke M (1988) Ablation of UV-transparent materials with femtosecond UV excimer laser pulses. Microelectron Eng 129(1–4):475–480. https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-129-375
Davis KM, Miura K, Sugimoto N, Hirao K (1996) Writing waveguides in glass with a femtosecond laser. Optics letters 21(21):1729–1731. https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.21.001729
Glezer E, Milosavljevic M, Huang L, Finlay R, Her T-H, Callan JP, Mazur E (1996) Three-dimensional optical storage inside transparent materials. Optics letters 21(24):2023–2025. https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.21.002023
Watanabe W, Sowa S, Tamaki T, Itoh K, Nishii J (2006) Three-dimensional waveguides fabricated in poly (methyl methacrylate) by a femtosecond laser. Jpn J Appl Phys 45(29/32):L765-L767. https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.45.L765
Hanada Y, Sugioka K, Midorikawa K (2010) UV waveguides light fabricated in fluoropolymer CYTOP by femtosecond laser direct writing. Optics Express 18(2):446. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.18.000446
Kawata S, Sun H-B, Tanaka T, Takada K (2001) Finer features for functional microdevices. Nature 412(6848):697–698. https://doi.org/10.1038/35089130
Rudd J, Korn G, Kane S, Squier J, Mourou GA, Bado P (1993) Chirped-pulse amplification of 55-fs pulses at a 1-kHz repetition rate in a Ti: Al2O3 regenerative amplifier. Opt Lett 18(23):2044–2046. https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.18.002044
Arai A, Bovatsek J, Yoshino F, Liu Z, Cho G, Shah L, Fermann M, Uehara Y (2006) Fiber chirped pulse amplification system for micromachining. Photonics North 2006. International Society for Optics and Photonics 63430S
Kleinbauer J, Eckert D, Weiler S, Sutter D (2008) 80 W ultrafast CPA-free disk laser, Solid State Lasers XVII: Technology and Devices. International Society for Optics and Photonics 68711B
Orazi L, Romoli L, Schmidt M, Li L (2021) Ultrafast laser manufacturing: from physics to industrial applications, CIRP Annals (prepublish). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CIRP.2021.05.007
Rethfeld B, Kaiser A, Vicanek M, Simon G (1999) Femtosecond laser-induced heating of electron gas in aluminium. Appl Phys A 69(1)S109-S112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003399900228
Nedialkov N, Imamova S, Atanasov P (2004) Ablation of metals by ultrashort laser pulses. J Phys D Appl Phys 37(4):638. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/37/4/016
Ahmmed K, Colin G, Anne-Marie K (2014) Fabrication of Micro/Nano Structures on Metals by Femtosecond Laser Micromachining. Micromachines 5(4):1219–1253
Von der Linde D, Sokolowski-Tinten K, Bialkowski J (1997) Laser–solid interaction in the femtosecond time regime. Appl Surf Sci 109:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-4332(96)00611-3
Rethfeld B, Sokolowski-Tinten K, Von Der Linde D, Anisimov S (2004) Timescales in the response of materials to femtosecond laser excitation. Appl Phys A 79(4–6):767–769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-004-2805-9
**g J, Meng C, Bai Z, Chao Y, Gang L (2013) Influence of polarization on the hole formation with picosecond laser. Opt Rev 20(6):496–499. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10043-013-0084-4
Jandeleit J, Horn A, Weichenhain R, Kreutz EW, Poprawe R (1998) Fundamental investigations of micromachining by nano- and picosecond laser radiation. Appl Surf Sci 127–129:885–891. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-4332(97)00762-9
Oehl CF, Breitling D, Jasper K, Radtke J, Dausinger F (2002) Precision drilling of metals and ceramics with short- and ultrashort-pulsed solid state lasers. Proc SPIE-Int Soc Opt Eng. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.456897
Ostendorf A, Siegel F (2004) Micro-machining using high energy picosecond laser pulses a cause-effect consideration. https://doi.org/10.2351/1.5060348
Hu W, Shin YC, King GB (2010) Micromachining of Metals, Alloys, and Ceramics by Picosecond Laser Ablation. J Manuf Sci Eng 132(1):165–174. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4000836
Liu X, Du D, Mourou G (1997) Laser ablation and micromachining with ultrashort laser pulses. IEEE J Quantum Electron 33(10):1706–1716. https://doi.org/10.1109/3.631270
Ashcom JB (2003) The role of* focusing in the interaction of femtosecond laser pulses with transparent materials. Harvard University
Mannion P, Magee J, Coyne E, O’connor G, Glynn T (2004) The effect of damage accumulation behaviour on ablation thresholds and damage morphology in ultrafast laser micro-machining of common metals in air. Appl Surf Sci 233(1–4):275–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2004.03.229
Martynyuk M (1976) Mechanism for metal damage by intense electromagnetic radiation. Soviet Physics-Technical Physics 21(4):430–433
Lee C, Koumvakalis N, Bass M (1982) Spot‐size dependence of laser‐induced damage to diamond‐turned Cu mirrors. Appl Phys Lett 41(7):625–627. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.93629
Anisimov S, Kapeliovich B, Perelman T (1974) Electron emission from metal surfaces exposed to ultrashort laser pulses. Zh Eksp Teor Fiz 66(2):375–377
Jiang D, Long J, Han J, Cai M, Lin Y, Fan P, Zhang H, Zhong M (2017) Comprehensive enhancement of the mechanical and thermo-mechanical properties of W/Cu joints via femtosecond laser fabricated micro/nano interface structures. Mater Sci Eng A 696:429–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.04.063
Wang L (2016) Method and Theoretical study of Metal Micromachining Based on Femtosecond Laser. Shandong University of Technology
Payne MC, Teter MP, Allan DC, Arias T, Joannopoulos AJ (1992) Iterative minimization techniques for ab initio total-energy calculations: molecular dynamics and conjugate gradients. Rev Mod Phys 64(4):1045. https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.64.1045
Richert R, Angell C (1998) Dynamics of glass-forming liquids. V. On the link between molecular dynamics and configurational entropy. J Chem Phys 108(21):9016–9026. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.476348
Wu H, Zhang N, He M, Shih C-Y, Zhu X (2016) Ar/Al atom interaction potential calculation and its application in molecular dynamics simulation of femtosecond laser ablation. Chin J Lasers 43(8):110–116. https://doi.org/10.3788/CJL201643.0802004
Gan Y (2020) Coupling of material point method and molecular dynamics for modeling ultrafast laser interaction with metals. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements 110:104–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enganabound.2019.10.012
Li G (2018) Bionic Functional Structures by Femtosecond Laser Micro/nanofabrication Technologies. Springer
Wang Z, Wang C, Wang M, Zhao Q (2016) Manipulation of tribological properties of stainless steel by picosecond laser texturing and quenching. Tribology international 99:14–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2016.03.002
Lu Y (2016) The study of femtosecond laser ablation and electrochemical deposition on metal surface through mask effect. Bei**g Institute of Technology
Zhang W, Cheng G, Feng Q (2012) Unclassical ripple patterns in single-crystal silicon produced by femtosecond laser irradiation. Appl Surf Sci 263:436–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.09.075
Qin X, Huang T, **ao R (2019) Periodic microstructure on Ti surface induced by high power green femtosecond laser. Chin J Lasers 46(10):138–146. https://doi.org/10.3788/CJL201946.1002006
Liu B, Wang W, Jiang G, Mei X, Wang Z, Wang K, Cui J (2016) Study on hierarchical structured PDMS for surface super-hydrophobicity using imprinting with ultrafast laser structured models. Appl Surf Sci 364:528–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.12.190
Jiang G, Pan R, Chen C, Hu X, Zhang H, Zhong M (2020) Ultrafast Laser Fabrication of Drag Reduction Micro-nano Structures and Their Corrosion Resistance. Chin J Lasers (8):73–81. https://doi.org/10.3788/CJL202047.0802005
Yang Q, Deng B, Wang Y, **ao C, Wang X, Chen L, Zheng Z, Lou D, Tao Q, Zhai Z (2017) Superhydrophobic surface of Aluminium Induced by Femtosecond Laser, Laser & Optoelectronics Progress (10):314–320. https://doi.org/10.3788/LOP54.101408
Nayak BK, Gupta MC (2010) Self-organized micro/nano structures in metal surfaces by ultrafast laser irradiation. Opt Lasers Eng 48(10):940–949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2010.04.010
Ahmmed KMT, Ling EJY, Servio P, Kietzig AM (2015) Introducing a new optimization tool for femtosecond laser-induced surface texturing on titanium, stainless steel, aluminum and copper. Opt Lasers Eng 66:258–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2014.09.017
Richerzhagen B, Kutsuna M, Okada H, Ikeda T (2003) Water jet-guided laser processing. Proc SPIE-Int Soc Opt Eng 4830. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.486514
Shi Y, Jiang Z, Cao J, Ehmann KF (2020) Texturing of metallic surfaces for superhydrophobicity by water jet guided laser micro-machining. Appl Surf Sci 500:144286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144286
Fan P, Zhong M, Li L, Huang T, Zhang H (2013) Rapid fabrication of surface micro/nano structures with enhanced broadband absorption on Cu by picosecond laser. Opt Express 21(10):11628–11637. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.21.011628
Tang G, Hourd AC, Abdolvand A (2012) Nanosecond pulsed laser blackening of copper. Appl Phys Lett 101(23):231902. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4769215
Vorobyev A, Guo C (2008) Femtosecond laser blackening of platinum. J Appl Phys 104(5):053516. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2975989
Vorobyev AY, Guo C (2008) Colorizing metals with femtosecond laser pulses. Appl Phys Lett 92(4):041914. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2834902
Vorobyev A, Topkov A, Gurin O, Svich V, Guo C (2009) Enhanced absorption of metals over ultrabroad electromagnetic spectrum. Appl Phys Lett 95(12):121106. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3227668
Vorobyev AY, Guo C (2010) Metallic light absorbers produced by femtosecond laser pulses. Adv Mech Eng 2:452749. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/452749
Yang Y, Yang J, Liang C, Wang H (2008) Ultra-broadband enhanced absorption of metal surfaces structured by femtosecond laser pulses. Opt express 16(15):11259–11265. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.16.011259
Huang M, Zhao F, Cheng Y, Xu N, Xu Z (2010) The morphological and optical characteristics of femtosecond laser-induced large-area micro/nanostructures on GaAs, Si, and brass. Opt Express 18(104):A600-A619. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.18.00A600
Vorobyev A, Guo C (2006) Femtosecond laser nanostructuring of metals. Opt Express 14(6):2164–2169. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.14.002164
Koch J, Korte F, Bauer T, Fallnich C, Ostendorf A, Chichkov BN (2005) Nanotexturing of gold films by femtosecond laser-induced melt dynamics. Appl Phys A 81(2)325–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-005-3212-6
Birnbaum M (1965) Semiconductor Surface Damage Produced by Ruby Lasers. J Appl Phys 36(11):3688–3689. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1703071
Vorobyev AY, Guo C (2013) Direct femtosecond laser surface nano/microstructuring and its applications. Laser Photonics Rev 7(3):385–407. https://doi.org/10.1002/lpor.201200017
Bonse J, Krueger J, Rosenfeld A (2009) On the role of surface plasmon polaritons in the formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures upon irradiation of silicon by femtosecond-laser pulses. J Appl Phys 106(10):3688. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3261734
Lazzini G, Romoli L, Tantussi F, Fuso F (2018) Nanostructure patterns on stainless-steel upon ultrafast laser ablation with circular polarization. Opt Laser Technol 107:435–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.06.023
Bonse J, KrueGer J, HoeHm S, Rosenfeld A (2012) Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures. J Laser Appl 24(4):042006. https://doi.org/10.2351/1.4712658
Zhang Y, Zou G, Liu L, Zhao Y, Liang Q, Wu A, Zhou YN (2016) Time-dependent wettability of nano-patterned surfaces fabricated by femtosecond laser with high efficiency. Appl Surf Sci 389:554–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.07.089
Bizi-bandoki P, Valette S, Audouard E, Benayoun S (2013) Time dependency of the hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity of metallic alloys subjected to femtosecond laser irradiations. Appl Surf Sci 273:399–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.02.054
Kietzig AM, Hatzikiriakos SG, Englezos P (2009) Patterned superhydrophobic metallic surfaces, Langmuir the Acs. Journal of Surfaces & Colloids 25(8):4821–7. https://doi.org/10.1021/la8037582
Li G (2018) Micropore-Arrayed Ultrathin Aluminum Foil for Oil/Water Separation and Particle Filtration, Bionic Functional Structures by Femtosecond Laser Micro/nanofabrication Technologies. Springer Theses (Recognizing Outstanding Ph.D. Research). Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-0359-3_8
Liu Z, Yang J, Li Y, Li W, Chen J, Shen L, Zhang P, Yu Z (2020) Wetting and spreading behaviors of Al-Si alloy on surface textured stainless steel by ultrafast laser. Appl Surf Sci 46316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146316
Pan H, Wang Z, Fan W, Wang C, LI H, Bai F, Qian J, Zhao Q (2016) Superhydrophobic Titanium Surface Micro/nanostructures Induced by Femtosecond Laser. Chin J Lasers 43(008):95–101. https://doi.org/10.3788/CJL201643.0802002
Xu C (2009) Design and Preparation of Nanoporous Metals and their Catalytic Performance. Journal of Shandong University
Li Y, Zhou X, Qi W, **e H, Yin K, Tong Y, He J, Gong S, Li Z (2020) Ultrafast fabrication of Cu oxide micro/nano-structures via laser ablation to promote oxygen evolution reaction. Chem Eng J 383:123086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123086
Wang X, Xu B, Chen Y, Ma C, Huang Y (2019) Fabrication of micro/nano-hierarchical structures for droplet manipulation via velocity-controlled picosecond laser surface texturing. Opt Lasers Eng 122:319–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2019.06.021
Cunha A, Serro AP, Oliveira V, Almeida A, Vilar R, Durrieu M-C (2013) Wetting behaviour of femtosecond laser textured Ti–6Al–4V surfaces. Appl Surf Sci 265:688–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.11.085
Chen Z, Chang T, Liu C, Hsiao W, Huang C (2020) Picosecond laser surface modification of aluminum oxide with fish-scale structures for cell culture. Ceram Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.04.067
Pan R, Zhang H, Zhong M (2020) Triple-scale superhydrophobic surface with excellent anti-icing and icephobic performance via ultrafast laser hybrid fabrication. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13(1):1743–1753. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c16259
Yang J, Oliveira JP, Li Y, Tan C, Gao CK, Zhao YX, Yu ZS (2022) Dissimilar laser techniques for joining of aluminum alloys to steels: A critical review. J Mater Process Technol 301:117443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117443
Zuhlke CA, Anderson TP, Alexander DR (2013) Formation of multiscale surface structures on nickel via above surface growth and below surface growth mechanisms using femtosecond laser pulses. Opt Express 21(7):8460–8473. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.21.008460
Czyz K, Marczak J, Major R, Mzyk A, Rycyk A, Sarzynski A, Strzelec M (2016) Selected laser methods for surface structuring of biocompatible diamond-like carbon layers. Diamond Relat Mater 67:26–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2016.01.013
Ahmmed KMT, Grambow C, Kietzig AM (2014) Fabrication of Micro/Nano Structures on Metals by Femtosecond Laser Micromachining. Micromachines 5(4):1219–1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi5041219
McDaniel C, Gladkovskaya O, Flanagan A, Rochev Y, O'Connor GM (2015) In vitro study on the response of RAW264.7 and MS-5 fibroblast cells on laser-induced periodic surface structures for stainless steel alloys. Rsc Advances 5(53):42548–42558. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra04342e
Rusen L, Cazan M, Mustaciosu C, Filipescu M, Simion S, Zamfirescu M, Dinca V, Dinescu M (2014) Tailored topography control of biopolymer surfaces by ultrafast lasers for cell-substrate studies. Appl Surf Sci 302:256–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.10.023
Erdogan M, Oktem B, Kalaycioglu H, Yavas S, Mukhopadhyay PK, Eken K, Ozgoren K, Aykac Y, Tazebay UH, Ilday OH (2011) Texturing of titanium (Ti6Al4V) medical implant surfaces with MHz-repetition-rate femtosecond and picosecond Yb-doped fiber lasers. Opt Express 19(11):10986–10996. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.19.010986
Dumas V, Guignandon A, Vico L, Mauclair C, Zapata X, Linossier MT, Bouleftour W, Granier J, Peyroche S, Dumas J-C, Zahouani H, Rattner A (2015) Femtosecond laser nano/micro patterning of titanium influences mesenchymal stem cell adhesion and commitment. Biomed Mater 10(5). https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-6041/10/5/055002
Cunha A, Zouani OF, Plawinski L, Botelho do Rego AM, Almeida A, Vilar R, Durrieu M-C (2015) Human mesenchymal stem cell behavior on femtosecond laser-textured Ti-6Al-4V surfaces. Nanomedicine 10(5):725–739. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm.15.19
Oberringer M, Akman E, Lee J, Metzger W, Akkan CK, Kacar E, Demir A, Abdul-Khaliq H, Puetz N, Wennemuth G, Pohlemann T, Veith M, Aktas C (2013) Reduced myofibroblast differentiation on femtosecond laser treated 316LS stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng C 33(2):901–908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2012.11.018
Cheng CW, Chen JK (2016) Femtosecond laser sintering of copper nanoparticles. Appl Phys A 122(4pt.1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-9814-3
Wang C (2016) First-principles calculations and their validations for ultrafast micro/nanofabrication based on electron dynamics control. J Mech Eng 000(002):76–76. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-1641.2016.02.030
Funding
Financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51805315) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
** Yang: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing-review & editing. Zongjie Chen: Writing-original draft, Data curation, Investigation. Hongbing Liu: Visualization, Software. Yixuan Zhao: Validation. Rui Pan: Writing-review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Yang, J., Liu, H. et al. A short review on functionalized metallic surfaces by ultrafast laser micromachining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 119, 6919–6948 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-08560-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-08560-8