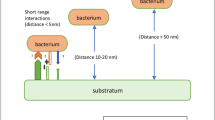
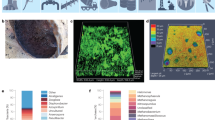
Abstract
This article reports a review of microbiological corrosion. It addresses the general perspectives of the various bacteria involved in the biocorrosion, and these include sulphate-reducing bacteria, slime-forming bacteria, iron-oxidizing bacteria and sulphur bacteria. The review also reported on biofilms and effects, various sulphate-reducing bacteria mechanisms, the biodeterioration control methods, environment, fouling and the impact of microbiological corrosion. Microbial corrosion, as it affects stainless steel, mildsteel, aluminium alloy, the AL6XN (N083677) super austenitic stainless steel, and manufacturing and transportation, were reviewed
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion (MIC) WebCorr Cons. Serv, http://www.corrosionclinic.com/types_of_corrosion/microbiologically_influenced_biological_microbial_corrosion.htm. Retrieved: 28 12. 2016
Microbial Corrosion https://en.wiki2.org/wiki/Microbial_corrosion. Retrieved: 15–01-2017
Iwona B, Alain B, Alfonso M, Hans-Curt F, Vittoria S, Wolfgang S (2000), Microbially influenced corrosion of industrial materials—biocorrosion network (Brite-Euram III Thematic Network N° ERB BRRT-CT98–5084
Iwona BB, Sunner J (2004) Biocorrosion: towards understanding interactions between biofilms and metals. Curr Opini Biotech 15:181–186
Hamilton W (1985) Sulphate-reducing bacteria and anaerobic corrosion. Annual Rev Microbiolo 39(1):195–217
Lee W et al (1995) Role of sulfate-reducing bacteria in corrosion of mild steel: a review. Biofouling 8(3):165–194
King RA, Miller JDA (1971) Corrosion by sulphate-reducing bacteria. Nature 233:491–492
King RA, Miller JDA, Smith JS (1973) Corrosion of mild steel by iron sulphides. Brit Corrosion J 8:137–142
Videla HA, Edyvean G, Herrera LK (2005). An updated overview of SRB induced corrosion and protection of carbon steel. Corrosion, 2005
TPC-3 (1990) Microbiologically influenced corrosion and biofouling in oilfield equipment. NACE, Houston
Postgate JR (1984) The sulphate-reducing bacteria, 2nd ed. Cambridge Press, London
Whonchee L, Zbigniew L, Nielsen PH, Hamilton WA (1995) Role of sulphate-reducing bacteria in corrosion of mild steel: a review. Biofouling- The Journal of Bioadhesion and Biofilm Research 8(3):165–194. doi:10.1080/0892 70195 09 3 78271
Muyzer G, Stams AJM (2008) The ecology and biotechnology of sulphate-reducing bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:441–454
Frobisher M (1965) Fundamentals of microbiology. W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, p 512
Respiration, bacteria and industrial systems. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Biofilm&oldid=756393899”– 23-12-2016
Little B, Wagner P, Mansfeld F (1991) Microbiologically influenced corrosion of metals and alloys. Int Matls Reviews 36(1):253–272
Materials Centre, Sandvik Materials Technology, Microbiologically influenced corrosion of stainless steels—http://smt.sandvik.com/ en/materials-center/corrosion/wet-corrosion/microbiologically-influenced-corrosion-mic/ - Retrieved: 14–01-2017
Yang SS, Lin JY, Lin YT (1998) Microbiologically induced corrosion of aluminum alloys in fuel-oil/aqueous system. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 31(3):151–164
H&C Heat transfer solutions: http://www.hcheattransfer.com/fouling_factors.html Retrieved: 02–02-2017
Lee W, Characklis WG (1993) Corrosion of mild steel under anaerobic biofilm. Corrosion 49(3):186–199. doi:10.5006/1.3316040
Vert M, Doi Y, Hellwich K-H, Hess M, Hodge P, Kubisa P, Rinaudo M, Schué F (2012) “Terminology for biorelated polymers and applications (IUPAC Recommendations)” (PDF). P Appl Chem 84(2):377–410. doi:10.1351/PAC-REC-10-12-04
Microbial corrosion - https://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Microbial_corrosion. Retrieved: 27–12-2016
Hall-Stoodley L, Costerton JW, Stoodley P (2004) Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat Rev Microbiol 2(2):95–108. doi:10.1038/nrmicro821
Lear G, Lewis GD (eds) (2012) Microbial biofilms: Curr Res and Applica. Caister Academic Press, UK
Flemming H-C, Wingender J (2010) The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:623–633. doi:10.1038/nrmicro2415
Characklis WG, Little BJ, Stoodley P, Mccaughey MS (1991) Microbial fouling and corrosion in nuclear power plant service water systems, Corrosion 91
Tiller AK (1983) “Is Stainless Steel Susceptibility to Microbial Corrosion?” National Corrosion Service, March 8–10
Lee AK, Newman DK (2003) Microbal iron respiration: impacts on corrosion processes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 62:134. doi:10.1007/s00253-003-1314-7
Little B, Ray R (2002) A perspective on corrosion inhibition by biofilms. Corrosion 58(5):424–428. doi:10.5006/1.3277632
Gadd G (2010) Metals, minerals and microbes: geomicrobiology and bioremediation. Microbiology. doi:10.1099/mic.0.037143-0
Beech I, Sunner J, Hiraoka K (2005) “Microbe–surface interactions in biofouling and biocorrosion processes.” Int Microbiol
Lovely D, Coates J, Blunt-Harris E, Phillips E, Woodward J (1996) Humic substances as electron acceptors for microbial respiration. Nature. doi:10.1038/382445a0
Briandet R, Herry JM, Bellon-Fontaine MN (2001) Determination of the van der Waals, electron donor and electron acceptor surface tension components of static gram-positive microbial biofilms. Collo Surf B: Biointerf 21(4):299–310
Takahashi H, Suda T, Tanaka Y, Kimura B (2010) Cellular hydrophobicity of Listeria monocytogenes involves initial attachment and biofilm formation on the surface of polyvinyl chloride. Appl Microbio 50(6):618–625
Donlan RM (2002) Biofilms: microbial life on surfaces. Emerg Infect Dis 8(9):881–890
Stewart PS, Costerton JW (2001) Antibiotic resistance of bacteria in biofilms. Lancet 358(9276):135–138. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(01)05321-1.
Molin S, Tolker-Nielsen T (2003) Gene transfer occurs with enhanced efficiency in biofilms and induces enhanced stabilisation of the biofilm structure. Curr Opini Biotech 14(3):255–261. doi:10.1016/S0958-1669(03)00036-3
Jakubovics NS, Shields RC, Rajarajan N, Burgess JG (2013) Lett Appl Microbiol 57(6):467–475. doi:10.1111/lam.12134.
Biofilm- “https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Biofilm&oldid=756393899”. Retrieved: 10–01- 2017
Liang S, Squier T, Zachara J, Fredrickson J (2007) Respiration of metal (hydr)oxides by Shewanella and Geobacter: a key role for multihaem C-type cytochromes. Mol Microbiol. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05783.x
Willey J, Sherwood L, Woolverton C (2011) Prescott’s microbiology, 8th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 534–535
CTL - Corrosion of Iron Pi** in a Fire Sprinkler System. Corrosion Testing Laboratories (2007). www.corrosionlab.com/Failure.../30010.corrosion-bad-fitting.iron-sprinkler.htm
Iverson W (1987) Microbial corrosion of metals. Adv in Appl Microbiol. doi:10.1016/S0065-2164(08)70077-7
Nuhoglu Y (2004) “The biodeteriorative of microorganisms and the effects on stone monuments under air pollution and continental-cold climatic condition in Erzurum, Turkey.” Fresenius Environ Bull
Kakooei S, Ismail MC, Ariwahjoedi B (2012) Mechanism of microbiologically influenced corrosion—a review. World Appl Sci J 17(4):524–531
Kuhr VW, der Vlugt V (1934) De grafteering van geitizer als electrobiochemisch process in anaerobe groden. Water, Den Haag 18(16):147–165
Castaneda H, Benetton XD (2008) SRB-biofilm influence in active corrosion sites formed at the steel-electrolyte interface when exposed to artificial seawater conditions. Corros Sci 50(4):1169–1183
Costello JA (1974) Cathodic depolarization by sulphate reducing bacteria. South Afric J Sci 70(7):202–204
Obuekwe C, Westlake D, Plambeck J (1981) Corrosion of mild steel in cultures of ferric iron reducing bacterium isolated from crude oil. II.—mechanism of anodic depolarization. Corrosion 37(11):632–637
Crolet J (1992) Biocorrosion: pH regulation by sulphate-reduction bacteria. Mater Tech (Paris) 80(9–10):71–77
Araujo-Jorge TC, CML C, LEV A (1992) Sulphate-reducing bacteria associated with biocorrosion: a review. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 87(3):329–337
Ford T, Mitchell R (1990) The ecology and microbial corrosion. Adv Microb Ecol 11:231–262
Coetser S, Cloete T (2005) Biofouling and biocorrosion in industrial water systems. Crit Rev in Microbiol 31(4):213–232
Miller JDA (1970) Microbial aspects of metallurgy. Elsevier Publishing Co. Inc, New York
Inverson WP (2001) Research on the mechanisms of anaerobic corrosion. Int Biodeter & Biodegrad 47(2):63–70. doi:10.1016/S0964-8305(00)00111-6
Wolfram JH, Mizia RE, Jex R, Nelson L, Garcia KM (1996) The impact of microbially influenced corrosion on spent nuclear fuel and storage life, INEL-96;0335--- Idaho National Engineering Laboratory. Lockheed Martin Idaho Technologies Company, USA
Pope DH, Duquette DJ, Johannes AH, Wayner PC (1984), “Microbiologically influenced corrosion of industrial alloys∼‘MatL Perform
Microbiological corrosion - http://www2.mtec.or.th/th/research/famd/corro/mic.htm Retrieved: 28–12-2016
Gua J-D (2003) Microbiological deterioration and degradation of synthetic polymeric materials: recent research advances. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation 52:69–91
Loto CA, Ives MB (1994) Corrosion resistance of super austenitic stainless steels in sea water. Nigerian Society of Engineers Technical Trans Vol 29(1):1–9
Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion in Industrial Systems https://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Microbiologically_Influenced_Corrosion_in_Industrial_Systems Retrirved: 15–01-2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loto, C.A. Microbiological corrosion: mechanism, control and impact—a review. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92, 4241–4252 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0494-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0494-8