Abstract
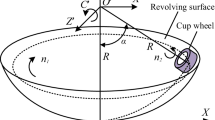
This paper deals with the optimal structural design of a Biglide parallel grinder for drill grinding. A pair of spatial modules is adopted to replace the conventional parallelogram to enhance the out-of-plane stiffness of the latter. A multi-objective design optimization problem is formulated, of which the stiffness, motion/force transmission, and work space are taken into consideration. The Pareto front of the optimization problem is obtained to provide the optimum design of the Biglide machine, and a scatter matrix is visualized to reveal the influence of the link dimensions to the performance. The selected design from the Pareto front guarantees the requirement on the elastostatic performance in the grinding process with increased dexterous workspace size.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yan L, Jiang F (2013) A practical optimization design of helical geometry drill point and its grinding process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 64(9–12):1387–1394
Zou P (2003) Kinematic analysis of a Biglide parallel grinder. J Mater Process Technol 138(1–3):461–463
Li B, Hu Y, Wang H (2007) Analysis and simulation for a parallel drill point grinder, part 2: grinding kinematic modeling and simulation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 31(9–10):915–925
Zou P, Yang XL, Ai MZ (2010) Study on helical drill point grinding with a Biglide parallel grinder. Adv Mater Res 97:2119–2122
Wu G, Zou P (2016) Stiffness analysis and comparison of a Biglide parallel grinder with alternative spatial modular parallelograms. Robotica FirstView:1–17
Wenger P, Chablat D (2000) Kinematic analysis of a new parallel machine tool: the Orthoglide. In: Advances in robot kinematics. Springer, pp 305–314
Stamper RE, Tsai L-W, Walsh GC (1997) Optimization of a three DOF translational platform for well-conditioned workspace. In: IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, vol 4. IEEE, pp 3250–3255
Merlet J-P (2006) Jacobian, manipulability, condition number, and accuracy of parallel robots. J Mech Des 128(1):199–206
Huang T, Zhao X, Whitehouse DJ (2002) Stiffness estimation of a tripod-based parallel kinematic machine. IEEE Trans Robot Autom 18(1):50–58
Hay AM, Snyman JA (2004) Methodologies for the optimal design of parallel manipulators. Int J Numer Methods Eng 59(1):131– 152
Chablat D, Caro S, Ur-Rehman R, Wenger P (2010) Comparison of planar parallel manipulator architectures based on a multi-objective design optimization approach. In: ASME 2010 international design engineering technical conferences and computers and information in engineering conference. Montreal , pp 861–870
Stock M, Miller K (2003) Optimal kinematic design of spatial parallel manipulators: application to linear Delta robot. J Mech Des 125(2):292–301
Hao F, Merlet J-P (2005) Multi-criteria optimal design of parallel manipulators based on interval analysis. Mech Mach Theory 40(2):157–171
Krefft M, Hesselbach J (2005) Elastodynamic optimization of parallel kinematics. In: IEEE international conference on automation science and engineering, pp 357–362
Altuzarra O, Hernandez A, Salgado O, Angeles J (2009) Multiobjective optimum design of a symmetric parallel Schönflies-motion generator. J Mech Des 131(3):031002
Ur-Rehman R, Caro S, Chablat D, Wenger P (2010) Multi-objective path placement optimization of parallel kinematics machines based on energy consumption, shaking forces and maximum actuator torques: application to the orthoglide. Mech Mach Theory 45(8):1125–1141
Wu G, Caro S, Bai S, Kepler J (2014) Dynamic modeling and design optimization of a 3-DOF spherical parallel manipulator. Robot Auton Syst 62(10):1377–1386
Huo D, Cheng K, Wardle F (2010) Design of a five-axis ultra-precision micro-milling machine–UltraMill. part 1: holistic design approach, design considerations and specifications. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 47(9):867–877
Huo D, Cheng K, Wardle F (2010) Design of a five-axis ultra-precision micro-milling machine—UltraMill. Part 2: integrated dynamic modelling, design optimisation and analysis. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 47(9):879–890
Germain C, Caro S, Briot S, Wenger P (2013) Singularity-free design of the translational parallel manipulator IRSBot-2. Mech Mach Theory 64:262–285
Gosselin C (1990) Stiffness map** for parallel manipulators. IEEE Trans Robot Autom 6(3):377–382
Chen S-F, Kao I (2000) Conservative congruence transformation for joint and cartesian stiffness matrices of robotic hands and fingers. Int J Robot Res 19:835–847
Alici G, Shirinzadeh B (2005) Enhanced stiffness modeling, identification and characterization for robot manipulators. IEEE Trans Robot 21(4):554–564
Majou F, Gosselin C, Wenger P, Chablat D (2007) Parametric stiffness analysis of the Orthoglide. Mech Mach Theory 42 (3):296–311
Pashkevich A, Chablat D, Wenger P (2009) Stiffness analysis of overconstrained parallel manipulators. Mech Mach Theory 44(5):966–982
Nagai K, Liu Z (2008) A systematic approach to stiffness analysis of parallel mechanisms. In: IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, pp 1543–1548
Klimchik A, Furet B, Caro S, Pashkevich A (2015) Identification of the manipulator stiffness model parameters in industrial environment. Mech Mach Theory 90:1–22
Wu G, Bai S, Kepler J (2014) Mobile platform center shift in spherical parallel manipulators with flexible limbs. Mech Mach Theory 75:12–26
Wang D, Fan R, Chen W (2013) Stiffness analysis of a hexaglide parallel loading mechanism. Mech Mach Theory 70:454– 473
Shigley JE, Mischke CR, Brown TH (2004) Standard handbook of machine design. McGraw-Hill
Angeles J (2010) On the nature of the Cartesian stiffness matrix. Ingeniería Mecánica 3(5):163–170
Roberts RG (2002) On the normal form of a spatial stiffness matrix. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, vol 1, pp 556–561
Angeles J (2007) Fundamentals of robotic mechanical systems: theory, methods, and algorithms. Springer, New York
Strang G (2005) Linear algebra and its applications, 4th edn. Cengage Learning
Tao DC (1964) Applied linkage synthesis. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T (2002) A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 6(2):182–197
Paul A, Kapoor SG, DeVor RE (2005) Chisel edge and cutting lip shape optimization for improved twist drill point design. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 45(4):421–431
Acknowledgments
The work is partially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities. The support from Aalborg University is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, G. Optimal structural design of a Biglide parallel drill grinder. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 90, 2979–2990 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9625-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9625-x