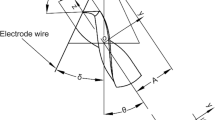
Abstract
A modeling method is presented for grinding of the designated geometrical parameters of twist drill in a Biglide parallel machine, which has the more effective and economic potentialities for grinding of drill point. The grinding kinematics trajectory and condition are analyzed based on the structure of the Biglide parallel machine. Moreover, the mathematical model of twist drill flank are derived and used to develop the parametric models of twist drill based on the grinding parameters of the Biglide parallel machine. The optimal grinding parameters are obtained for the custom-oriented twist drill using genetic algorithm. The grinding experiment results using the optimal grinding parameters agree well with the designated geometrical parameters of twist drill and show a marked improvement in grinding precision of the drill point in the Biglide parallel machine, depending on the customers’ demands.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yan L, Jiang F (2013) A practical optimization design of helical geometry drill point and its grinding process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 64(9-12):1387–1394. doi:10.1007/s00170-012-4109-0
Rao RV, Kalyankar VD (2014) Optimization of modern machining processes using advanced optimization techniques: a review. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 73(5):1159–1188. doi:10.1007/s00170-014-5894-4
Wang X, Huang C, Zou B, Liu H, Wang J (2013) Effects of geometric structure of twist drill bits and cutting condition on tool life in drilling 42CrMo ultrahigh-strength steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 64:41–47. doi:10.1007/s00170-012-4026-2
Galloway DF (1957) Some experiments on the influence of various factors on drill performance. Trans ASME 79:191–231
Hsieh JF (2008) NC data generation for 6-axis machine tools to produce a helical drill. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 36:535–546. doi:10.1007/s00170-006-0858-y
25. Abele E, Fujara M (2010) Simulation-based twist drill design and geometry optimization. CIRP Ann-Manuf Technol 59: 145-150. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2010.03.063 DOI:10.1016/j.cirp.2010.03.063#doilink
Tang F, Bai J, Wang X (2014) Practical and reliable carbide drill grinding methods based on a five-axis CNC grinder. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 73:659–667. doi:10.1007/s00170-014-5781-z
Ehmann KF (1990) Grinding wheel profile definition for the manufacture of drill flutes. CIRP Ann-Manuf Technol 39(1): 153-156. doi:10.1016/S0007-8506(07)61024-5 DOI:10.1016/S0007-8506(07)61024-5#doilink
Ren K, Ni J (1999) Analysis of drill flute and cutting angles. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 15(8):546–553
Hsieh JF, Lin PD (2005) Drill point geometry of multi-flute drills. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 26:466–476. doi:10.1007/s00170-003-2027-x
Zhang W, Wang X, He F, **ong D (2005) A practical method of modelling and simulation for drill fluting. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 46(6): 667-672. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.07.007 DOI:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2005.07.007#doilink
Koehler W (2008) Analysis of the high performance drilling process: influence of shape and profile of the cutting edge of twist drills. J Manuf Sci Eng 130(5):051001–51007. doi:10.1115/1.2951932
Sun Y, Wang J, Guo D, Zhang Q (2008) Modeling and numerical simulation for the machining of helical surface profiles on cutting tools. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 36:525–534. doi:10.1007/s00170-006-0860-4
Tandon P, Gupta P, Dhand SG (2008) Modeling of twist drills in terms of 3D angles. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 38(5-6):543–550. doi:10.1007/s00170-007-1150-5
Hsieh JF (2009) Mathematical modeling of complex helical dill point. J Manuf Sci Eng 131(6): 061006-1-061006-11. doi: 10.1115/1.4000438
Anna P, Lluı́s PV, Dani T (2003) 3D Simulation of tool machining. Comput Graph 27(1):99–106
Ma W, But WC, He P (2004) NURBS-based adaptive slicing for efficient rapid prototy**. Computer-Aided Design 36(13): 1309-1325. doi:10.1016/j.cad.2004.02.001 DOI:10.1016/j.cad.2004.02.001#doilink
Dani T, Anna P, Lluı́s PV (2004) Boolean operations for 3D simulation of CNC machining of drilling tools. Comp-Aided Design 36(4):315–323. doi:10.1016/S0010-4485(03)00104-0
Paul A, Kapoor SG. and DeVor RE (2004) Chisel edge and cutting lip shape optimization for improved twist drill point design. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 45: 421-431. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools..09.010 DOI:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2004.09.010#doilink
Hsieh JF (2005) Mathematical model for helical drill point. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 45(7-8):967–977. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2004.10.001
Hsieh JM (2008) Manufacturing models for design and NC grinding of truncated-cone ball-end cutters. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 35:1124–1135. doi:10.1007/s00170-006-0794-x
Wu YR, Fong ZH, Zhang ZX (2010) Simulation of a cylindrical form grinding process by the radial-ray shooting (RRS) method. Mech Mach Theor 45(2): 261-272. doi:10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2009.09.005 DOI:10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2009.09.005#doilink
Zhang W, Li Z, **ong D, He F, Hu J (2013) Machining movement based analytical modeling of twist drill and its application. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 6: 13-21. doi:10.1016/j.cirpj.2012.07.001 DOI:10.1016/j.cirpj.2012.07.001#doilink
Rehsteiner F, Neugebauer R, Spiewak S and Wieland F (1999) Putting parallel kinematics machines(PKM) to productive work. CIRP Ann-Manuf Technol 48(1): 345-350. doi:10.1016/S0007-8506(07)63199-0 DOI:10.1016/S0007-8506(07)63199-0#doilink
Tlusty J, Ziegert J and Ridgrway S (1999) Fundamental comparison of the use of serial and parallel kinematics for machine tools. CIRP Ann-Manuf Technol 48(1): 351-356. doi:10.1016/S0007-8506(07)63200-4 DOI:10.1016/S0007-8506(07)63200-4#doilink
Wang JS and Tang XQ (2003) Analysis and dimensional design of a novel hybrid machine tool. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 43(7): 647-655. doi:10.1016/S0890-6955(03)00040-3 DOI:10.1016/S0890-6955(03)00040-3#doilink
Weck M and Staimer D (2002) Parallel kinematic machine tools-current state and future potentials. CIRP Ann-Manuf Technol 51(2): 671-683. doi:10.1016/S0007-8506(07)61706-5 DOI:10.1016/S0007-8506(07)61706-5#doilink
Olarra A, Allen JM, Axinte DA (2014) Experimental evaluation of a special purpose miniature machine tool with parallel kinematics architecture-Free leg hexapod. Precis Eng 2: 1-16. doi:10.1016/j.precisioneng.2014.02.009 DOI:10.1016/j.precisioneng.2014.02.009#doilink
Chyan HC and Ehmann KF (1998) Development of curved helical micro-drill point technology for micro-hole drilling. Mechatronics 8: 337-358. doi:10.1016/S0957-4158(97)00055-X DOI:10.1016/S0957-4158(97)00055-X#doilink
Li B, Hu X, Wang H (2006) Analysis and simulation for a parallel drill point grinder. Part 2, grinding kinematic modeling and simulation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 30(3-4):221–226. doi:10.1007/s00170-005-0079-9
Zou P (2003) Kinematic analysis of a Biglide parallel grinder. J Mater Process Technol 138(1): 461-463,. doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00118-3 DOI:10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00118-3#doilink
Li B, Hu Y, Wang H (2007) Analysis and simulation for a parallel drill point grinder. Part 1, kinematics, workspace and singularity analysis. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 31(9-10):915–925. doi:10.1007/s00170-005-0265-9
Zou P, Yang X, Ai M (2010) Study on twist drill grinding with a biglide parallel grinder. Adv Mater Res 97–101(3):2119–2122. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.97-101.2119
Li Z, Zhang W, **ong D (2010) A practical method to determine rake angles of twist drill by measuring the cutting edge. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 50(8), 747-751. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2010.04.001 DOI:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2010.04.001#doilink
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, P., Kim, M.I. & Liu, F. Modeling and optimization of grinding parameters for custom-oriented twist drill with a Biglide parallel machine. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 88, 691–699 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8805-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8805-z