Abstract
Purpose
In tendon research, using ultrasound (US), studies often refer to tendon thickness, structural abnormalities and neovascularisation. The reliability concerning these measurements and evaluations is seldom reported. The aim of this study was to assess the intra- and inter-observer reliability for quantitative measures (thickness) and qualitative evaluations (structure and neovascularisation) of symptomatic and asymptomatic Achilles and patellar tendons with US and colour Doppler using a modified Öhberg score.
Methods
Twenty-eight consecutive patients with symptomatic and asymptomatic Achilles (n = 27) and patellar tendons (n = 26) were included. Tendon anteroposterior thickness was measured. Tendon structure and neovascularisation were evaluated using a modified Öhberg score. US-images were evaluated twice by four independent observers.
Results
Mean thickness for Achilles and patellar tendons was 8.4 mm (±2.0) and 5.5 mm (±1.7), respectively. The reliability for measures of distance was high all over (ICC = 0.963–0.999). A moderate-strong correlation was found between observers concerning evaluation of neovascularisation (r = 0.767–0.992) and poor-moderate correlation concerning evaluation of structural changes (r = 0.379–0.837). Intra-observer reliability was moderate strong for evaluations of both tendon structure (k = 0.537–0.873) and neovascularisation (k = 0.639–0.864).
Conclusions
With a strict method for how to measure tendon thickness and set criteria for evaluating structural changes and amount and distribution of neovascularisation, US and colour Doppler is a reliable method for evaluating Achilles and patellar tendons. The modified, 4-graded, Öhberg score was found to be a reproducible instrument for assessment of tendon structure and neovascularisation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfredson H, Ohberg L (2005) Neovascularisation in chronic painful patellar tendinosis–promising results after sclerosing neovessels outside the tendon challenge the need for surgery. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 13(2):74–80
Alfredson H, Ohberg L (2006) Increased intratendinous vascularity in the early period after sclerosing injection treatment in Achilles tendinosis : a healing response? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 14(4):399–401
Astrom M, Gentz CF, Nilsson P, Rausing A, Sjoberg S, Westlin N (1996) Imaging in chronic achilles tendinopathy: a comparison of ultrasonography, magnetic resonance imaging and surgical findings in 27 histologically verified cases. Skeletal Radiol 25(7):615–620
Black J, Cook J, Kiss ZS, Smith M (2004) Intertester reliability of sonography in patellar tendinopathy. J Ultrasound Med 23(5):671–675
Blazina ME, Kerlan RK, Jobe FW, Carter VS, Carlson GJ (1973) Jumper’s knee. Orthop Clin North Am 4(3):665–678
Bleakney RR, White LM (2005) Imaging of the Achilles tendon. Foot Ankle Clin 10(2):239–254
Boesen AP, Boesen MI, Torp-Pedersen S, Christensen R, Boesen L, Holmich P, Nielsen MB, Koenig MJ, Hartkopp A, Ellegaard K, Bliddal H, Langberg H (2012) Associations between abnormal ultrasound color Doppler measures and tendon pain symptoms in badminton players during a season: a prospective cohort study. Am J Sport Med 40(3):548–555
Cassel M, Muller S, Carlsohn A, Baur H, Jerusel N, Mayer F (2012) Intra- and interrater variability of sonographic investigations of patella and achilles tendons. Sportverletz Sportschaden 26(1):21–26
Cook JL, Khan KM, Harcourt PR, Kiss ZS, Fehrmann MW, Griffiths L, Wark JD (1998) Patellar tendon ultrasonography in asymptomatic active athletes reveals hypoechoic regions: a study of 320 tendons. Victorian institute of sport tendon study group. Clin J Sport Med 8(2):73–77
Cook JL, Khan KM, Kiss ZS, Coleman BD, Griffiths L (2001) Asymptomatic hypoechoic regions on patellar tendon ultrasound: a 4-year clinical and ultrasound followup of 46 tendons. Scand J Med Sci Sports 11(6):321–327
Cook JL, Malliaras P, De Luca J, Ptasznik R, Morris ME, Goldie P (2004) Neovascularization and pain in abnormal patellar tendons of active jum** athletes. Clin J Sport Med 14(5):296–299
Cook JL, Ptazsnik R, Kiss ZS, Malliaras P, Morris ME, De Luca J (2005) High reproducibility of patellar tendon vascularity assessed by colour Doppler ultrasonography: a reliable measurement tool for quantifying tendon pathology. Br J Sports Med 39(10):700–703
Enwemeka CS (1989) Inflammation, cellularity, and fibrillogenesis in regenerating tendon: implications for tendon rehabilitation. Phys Ther 69(10):816–825
Ferretti A (1986) Epidemiology of jumper’s knee. Sports Med 3(4):289–295
Fessell DP, Vanderschueren GM, Jacobson JA, Ceulemans RY, Prasad A, Craig JG, Bouffard JA, Shirazi KK, van Holsbeeck MT (1998) US of the ankle: technique, anatomy, and diagnosis of pathologic conditions. Radiographics 18(2):325–340
Fornage BD (1986) Achilles tendon: US examination. Radiology 159(3):759–764
Gellhorn AC, Morgenroth DC, Goldstein B (2012) A novel sonographic method of measuring patellar tendon length. Ultrasound Med Biol 38(5):719–726
Genc H, Cakit BD, Tuncbilek I, Erdem HR (2005) Ultrasonographic evaluation of tendons and enthesal sites in rheumatoid arthritis: comparison with ankylosing spondylitis and healthy subjects. Clin Rheumatol 24(3):272–277
Giombini A, Dragoni S, Di Cesare A, Di Cesare M, Del Buono A, Maffulli N (2013) Asymptomatic Achilles, patellar, and quadriceps tendinopathy: a longitudinal clinical and ultrasonographic study in elite fencers. Scand J Med Sci Sports 23(3):311–316
Hirschmuller A, Frey V, Konstantinidis L, Baur H, Dickhuth HH, Sudkamp NP, Helwig P (2012) Prognostic value of Achilles tendon Doppler sonography in asymptomatic runners. Med Sci Sports Exerc 44(2):199–205
Jacobson JA (2002) Ultrasound in sports medicine. Radiol Clin North Am 40(2):363–386
Kainberger FM, Engel A, Barton P, Huebsch P, Neuhold A, Salomonowitz E (1990) Injury of the Achilles tendon: diagnosis with sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 155(5):1031–1036
Kartus J, Rostgard-Christensen L, Movin T, Lindahl S, Ejerhed L, Karlsson J (2000) Evaluation of harvested and normal patellar tendons: a reliability analyses of magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasonography. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 8(5):275–280
Khan KM, Forster BB, Robinson J, Cheong Y, Louis L, Maclean L, Taunton JE (2003) Are ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging of value in assessment of Achilles tendon disorders? A two year prospective study. Br J Sports Med 37(2):149–153
Koivunen-Niemela T, Parkkola K (1995) Anatomy of the Achilles tendon (tendo calcaneus) with respect to tendon thickness measurements. Surg Radiol Anat 17(3):263–268
Lee KS (2012) Musculoskeletal sonography of the tendon. J Ultrasound Med 31(12):1879–1884
Machin D, Campbell MJ, Walters SJ (2007) Textbook medical statistics: a textbook for the health sciences, 4th edn. Wiley, Chichester
Malliaras P, Purdam C, Maffulli N, Cook J (2010) Temporal sequence of greyscale ultrasound changes and their relationship with neovascularity and pain in the patellar tendon. Br J Sports Med 44(13):944–947
Martinoli C, Derchi LE, Pastorino C, Bertolotto M, Silvestri E (1993) Analysis of echotexture of tendons with US. Radiology 186(3):839–843
Ohberg L, Alfredson H (2002) Ultrasound guided sclerosis of neovessels in painful chronic Achilles tendinosis: pilot study of a new treatment. Br J Sports Med 36 (3):173–175; discussion 176-177
Ohberg L, Alfredson H (2003) Sclerosing therapy in chronic Achilles tendon insertional pain-results of a pilot study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 11(5):339–343
Ohberg L, Alfredson H (2004) Effects on neovascularisation behind the good results with eccentric training in chronic mid-portion Achilles tendinosis? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 12(5):465–470
Peers KH, Brys PP, Lysens RJ (2003) Correlation between power Doppler ultrasonography and clinical severity in Achilles tendinopathy. Int Orthop 27(3):180–183
Robinson P (2009) Sonography of common tendon injuries. AJR Am J Roentgenol 193(3):607–618
Sengkerij PM, de Vos RJ, Weir A, van Weelde BJ, Tol JL (2009) Interobserver reliability of neovascularization score using power Doppler ultrasonography in midportion achilles tendinopathy. Am J Sports Med 37(8):1627–1631
Sunding K, Willberg L, Werner S, Alfredson H, Forssblad M, Fahlstrom M (2014) Sclerosing injections and ultrasound-guided arthroscopic shaving for patellar tendinopathy: good clinical results and decreased tendon thickness after surgery-a medium-term follow-up study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-014-3028-z
Taylor R (1990) Interpretation of the correlation coefficient: a basic review. J Diagn Med Sonogr 1:35–39
Weinberg EP, Adams MJ, Hollenberg GM (1998) Color Doppler sonography of patellar tendinosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 171(3):743–744
Viera AJ, Garrett JM (2005) Understanding interobserver agreement: the kappa statistic. Fam Med 37(5):360–363
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Swedish National Centre for Research in Sports, and all clinical resources were provided by Capio Artro Clinic AB, Sophiahemmet, Stockholm, Sweden. Our great appreciation to Per Larsson, biomedical technician, and Urban Niklasson, MD PhD, for their valuable contribution in collecting data and also to Dr Lars Öhberg, MD PhD, for invaluable advice and guidance in ultrasound imaging and evaluations of tendon pathology.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
167_2014_3270_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Achilles tendons in longitudinal and transversal views. US-images showing examples of how the structure was evaluated with the use of Öhberg score (0-3) according to consensus between observers. Scores are shown in the middle, between images. (TIFF 582 kb)
167_2014_3270_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Patellar tendons in longitudinal and transversal views. US-images showing examples of how the structure was evaluated with the use of Öhberg score (0-3) according to consensus between observers. Scores are shown in the middle, between images. (TIFF 593 kb)
167_2014_3270_MOESM3_ESM.tif
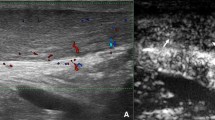
US-images showing examples of how neovascularisation was evaluated with the use of Öhberg score (0-3) according to consensus between observers. Scores are shown in the middle, between images. To the left Achilles tendons and to the right Patellar tendons. (TIFF 792 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sunding, K., Fahlström, M., Werner, S. et al. Evaluation of Achilles and patellar tendinopathy with greyscale ultrasound and colour Doppler: using a four-grade scale. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24, 1988–1996 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-3270-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-3270-4