Abstract
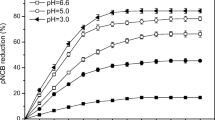
Para-chloronitrobenzene (p-CNB) in soil has posed significant health risks because of its persistence and high toxicity. The efficacy of catalyzed Zero-Valent Iron (ZVI), activated persulfate, and ZVI-persulfate processes for the degradation of p-CNB in soil was investigated. The p-CNB removal rate significantly increased from 10.8 to 90.1% with increased ZVI dosage from 0.1 mmol g−1 to 1.0 mmol g−1. The p-CNB removal increased with the decrease of initial pH and a removal efficiency of 85.3% was obtained at an initial pH value of 6.8 in combined system. The p-CNB removal rate in the single persulfate system and ZVI system was 36.5% and 60.2%, while the ZVI-persulfate system showed more sufficient p-CNB removal capacity and the removal rate of p-CNB was 88.7%. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) was adopted in order to explore the degradation mechanism by ZVI-Persulfate system in soil.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anipsitakis GP, Dionysiou DD (2004) Radical generation by the interaction of transition metals with common oxidants. Environ Sci Technol 38(13):3705
Bergendahl JA, Thies TP (2004) Fenton’s oxidation of MTBE with zero-valent iron. Water Res 38(2):327
Fang GD, Dionysiou DD, Wang Y, Al-Abed SR, Zhou DM (2012a) Sulfate radical-based degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls: effects of chloride ion and reaction kinetics. J Hazard Mater 227–228(43):394
Fang GD, Dionysiou DD, Wang Y, Al-Abed SR, Zhou DM (2012b) Sulfate radical-based degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls: effects of chloride ion and reaction kinetics. J Hazard Mater 227–228:394–401
Freitag D, Scheunert I, Klein W, Korte F (1984) Long-term fate of 4-chloroaniline-14C in soil and plants under outdoor conditions. A contribution to terrestrial ecotoxicology of chemicals. J Agric Food Chem 32(2):203–207
Furman OS (2010) Mechanism of base activation of persulfate. Environ Sci Technol 44(16):6423–6428
Ghauch A, Ayoub G, Naim S (2013) Degradation of sulfamethoxazole by persulfate assisted micrometric Fe0 in aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 228:1168–1181
Gogate PR, Pandit AB (2004) A review of imperative technologies for wastewater treatment I: oxidation technologies at ambient conditions. Adv Environ Res 8(3):501–551
Gu X, Wang Y, Miao Z, Lu S, Qiu Z, Sui Q, Guo X (2017) Degradation of trichloroethylene in aqueous solution by persulfate activated with Fe(III)–EDDS complex. Res Chem Intermed 43(1):1–13
Huang KC, Couttenye RA, Hoag GE (2002) Kinetics of heat-assisted persulfate oxidation of methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE). J Soil Contam 11(3):447–448
Hussain I, Zhang Y, Huang S, Du X (2012) Degradation of p-chloroaniline by persulfate activated with zero-valent iron. Chem Eng J 203(5):269–276
Keum YS, Li QX (2004) Reduction of nitroaromatic pesticides with zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 54(3):255–263
Le C, Liang J, Wu J, Li P, Wang X, Zhu N, Yang B (2011) Effective degradation of para-chloronitrobenzene through a sequential treatment using zero-valent iron reduction and Fenton oxidation. Water Sci Technol 64(10):2126–2131
Li H, Wan J, Ma Y, Huang M, Wang Y, Chen Y (2014a) New insights into the role of zero-valent iron surface oxidation layers in persulfate oxidation of dibutyl phthalate solutions. Chem Eng J 250:137–147
Li H, Zhang Z, Xu X, Liang J, **a S (2014b) Bioreduction of para-chloronitrobenzene in a hydrogen-based hollow-fiber membrane biofilm reactor: effects of nitrate and sulfate. Biodegradation 25(2):205–215
Liang C, Bruell CJ, Marley MC, Sperry KL (2004) Persulfate oxidation for in situ remediation of TCE. I. Activated by ferrous ion with and without a persulfate-thiosulfate redox couple. Chemosphere 55(9):1213–1223
Liang C, Wang ZS, Bruell CJ (2007) Influence of pH on persulfate oxidation of TCE at ambient temperatures. Chemosphere 66(1):106–113
LINCH AL (1974) Biological monitoring for industrial exposure to cyanogenic aromatic nitro and amino compounds. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 35(7):426–432
Liu Z, Guo W, Han X, Li X, Ke Z, Qiao Z (2016) In situ remediation of ortho -nitrochlorobenzene in soil by dual oxidants (hydrogen peroxide/persulfate). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(19):1–6
Matzek LW, Carter KE (2016) Activated persulfate for organic chemical degradation: a review. Chemosphere 151:178–188
Nefso EK, Burns SE, McGrath CJ (2005) Degradation kinetics of TNT in the presence of six mineral surfaces and ferrous iron. J Hazard Mater 123(1–3):79–88
Nie M, Yan C, Li M, Wang X, Bi W, Dong W (2015) Degradation of chloramphenicol by persulfate activated by Fe2+ and zerovalent iron. Chem Eng J 279:507–515
Oh S, Kang SG, Chiu PC (2010) Degradation of 2,4-dinitrotoluene by persulfate activated with zero-valent iron. Sci Total Environ 408(16):3464–3468
Schultz CA, Grundl TJ (2000) pH Dependence on reduction rate of 4-Cl-nitrobenzene by Fe(II)/montmorillonite systems. Environ Sci Technol 34(17):3641–3648
USEPA (1988) National pollutant discharge elimination system, code of federal regulations. Agency EP, US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC
Waldemer RH, Tratnyek PG (2006) Kinetics of contaminant degradation by permanganate. Environ Sci Technol 40(3):1055–1061
Wei X, Gao N, Li C, Deng Y, Zhou S, Li L (2016) Zero-valent iron (ZVI) activation of persulfate (PS) for oxidation of bentazon in water. Chem Eng J 285:660–670
Wu Y, Gan L, Zhang S, Jiang B, Song H, Li W, Li A (2017) Enhanced electrocatalytic dechlorination of para-chloronitrobenzene based on Ni/Pd foam electrode. Chem Eng J 316:146–153
Xu X, Zhou H, Zhou M (2006) Catalytic amination and dechlorination of para-nitrochlorobenzene (p-NCB) in water over palladium-iron bimetallic catalyst. Chemosphere 62(5):847–852
Zhao J, Zhang Y, **e Q, Chen S (2010) Enhanced oxidation of 4-chlorophenol using sulfate radicals generated from zero-valent iron and peroxydisulfate at ambient temperature. Sep Purif Technol 71(3):302–307
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Support Plan Program of Jiangsu Province (No. BY2016077-03) and the Science and Technology Program of Jiangsu (No. BE2018679).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, J., Wu, W., Liu, W. et al. Zero-valent iron (ZVI) Activation of Persulfate (PS) for Degradation of Para-Chloronitrobenzene in Soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 103, 140–146 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2511-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2511-5