Abstract
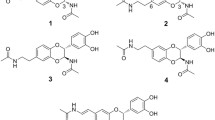
FXIa has emerged as a promising therapeutic target for treating thrombotic diseases. With the aim to replace the aniline motif of asundexian with novel P2’ fragments, bicyclic isoquinoline and naphthalene rings were designed. The target compounds with isoquinoline ring were synthesized via 13 steps of chemical reactions. Substituents within the rings were investigated to elucidate the structural determinants governing selective or dual inhibition of FXIa and Plasma Kallikrein (PKa). In vitro testing showed that some of the designed compounds exhibited comparable potency against both FXIa and PKa, while others achieved up to 94-fold selectivity. Analysis of structure-activity relationships (SARs) uncovered the pivotal role of the carboxylic acid moiety in retaining inhibition of FXIa and PKa, and the steric hindrance and hydrogen-bond receptor functional groups were identified as key factors influencing the selectivity of FXIa inhibition over PKa. The docking study additionally unveiled different binding modes that play a significant role in the observed activity and selectivity. Furthermore, the selected compounds significantly extended the plasma coagulation time in a dose-dependent manner. Altogether, the bicyclic compounds may be promising lead compounds for the development of highly effective FXIa inhibitors.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mortality GBD. Causes of Death C Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388:1459–544.
Roth GA, Mensah GA, Johnson CO, Addolorato G, Ammirati E, Baddour LM, et al. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76:2982–3021.
Mackman N, Bergmeier W, Stouffer GA, Weitz JI. Therapeutic strategies for thrombosis: New targets and approaches. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020;19:333–52.
Handin RI. The history of antithrombotic therapy: the discovery of Heparin, the Vitamin K antagonists, and the utility of Aspirin. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2016;30:987–93.
Chan N, Sobieraj-Teague M, Eikelboom JW. Direct oral anticoagulants: Evidence and unresolved issues. Lancet. 2020;396:1767–76.
Piran S, Schulman S. Treatment of bleeding complications in patients on anticoagulant therapy. Blood. 2019;133:425–35.
Fredenburgh JC, Weitz JI. New anticoagulants: Moving beyond the direct oral anticoagulants. J Thromb Haemost. 2021;19:20–29.
Zhang H, Lowenberg EC, Crosby JR, MacLeod AR, Zhao C, Gao D, et al. Inhibition of the intrinsic coagulation pathway factor XI by antisense oligonucleotides: A novel antithrombotic strategy with lowered bleeding risk. Blood. 2010;116:4684–92.
Preis M, Hirsch J, Kotler A, Zoabi A, Stein N, Rennert G, et al. Factor XI deficiency is associated with lower risk for cardiovascular and venous thromboembolism events. Blood. 2017;129:1210–15.
Weitz JI, Eikelboom JW. What is the future of Factor XI inhibitors? Circulation. 2022;146:1899–902.
Seligsohn U. Factor XI deficiency in humans. J Thromb Haemost. 2009;7:84–7.
Meijers JC, Tekelenburg WL, Bouma BN, Bertina RM, Rosendaal FR. High levels of coagulation factor XI as a risk factor for venous thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:696–701.
Salomon O, Steinberg DM, Koren-Morag N, Tanne D, Seligsohn U. Reduced incidence of ischemic stroke in patients with severe factor XI deficiency. Blood. 2008;111:4113–7.
Tucker EI, Marzec UM, White TC, Hurst S, Rugonyi S, McCarty OJ, et al. Prevention of vascular graft occlusion and thrombus-associated thrombin generation by inhibition of factor XI. Blood. 2009;113:936–44.
**e Z, Meng Z, Yang X, Duan Y, Wang Q, Liao C. Factor XIa inhibitors in anticoagulation therapy: recent advances and perspectives. J Med Chem. 2023;66:5332–63.
Dilger AK, Pabbisetty KB, Corte JR, De Lucca I, Fang T, Yang W, et al. Discovery of Milvexian, a high-affinity, orally Bioavailable inhibitor of Factor XIa in clinical studies for antithrombotic therapy. J Med Chem. 2022;65:1770–85.
Roehrig S, Ackerstaff J, Jimenez Nunez E, Teller H, Ellerbrock P, Meier K, et al. Design and Preclinical Characterization Program toward Asundexian (BAY 2433334), an Oral Factor XIa inhibitor for the prevention and treatment of thromboembolic disorders. J Med Chem. 2023;66:12203–24.
Weitz JI, Strony J, Ageno W, Gailani D, Hylek EM, Lassen MR, et al. Milvexian for the prevention of venous Thromboembolism. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2161–72.
Piccini JP, Caso V, Connolly SJ, Fox KAA, Oldgren J, Jones WS, et al. Safety of the oral factor XIa inhibitor asundexian compared with apixaban in patients with atrial fibrillation (PACIFIC-AF): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, dose-finding phase 2 study. Lancet. 2022;399:1383–90.
Wong PC, Crain EJ, Bozarth JM, Wu Y, Dilger AK, Wexler RR, et al. Milvexian, an orally bioavailable, small-molecule, reversible, direct inhibitor of factor XIa: In vitro studies and in vivo evaluation in experimental thrombosis in rabbits. J Thromb Haemost. 2022;20:399–408.
Schmaier AH. The contact activation and kallikrein/kinin systems: pathophysiologic and physiologic activities. J Thromb Haemost. 2016;14:28–39.
Ponczek MB, Shamanaev A, LaPlace A, Dickeson SK, Srivastava P, Sun MF, et al. The evolution of factor XI and the kallikrein-kinin system. Blood Adv. 2020;4:6135–47.
Kotian PL, Wu M, Vadlakonda S, Chintareddy V, Lu P, Juarez L, et al. Berotralstat (BCX7353): Structure-guided design of a potent, selective, and oral plasma Kallikrein inhibitor to prevent attacks of Hereditary Angioedema (HAE). J Med Chem. 2021;64:12453–68.
Kearney KJ, Butler J, Posada OM, Wilson C, Heal S, Ali M. et al. Kallikrein directly interacts with and activates Factor IX, resulting in thrombin generation and fibrin formation independent of Factor XI. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2021;118:e2014810118.
Visser M, van Oerle R, Ten Cate H, Laux V, Mackman N, Heitmeier S, et al. Plasma Kallikrein contributes to coagulation in the absence of Factor XI by activating Factor IX. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020;40:103–11.
Visser M, Heitmeier S, Ten Cate H, Spronk HMH. Role of Factor XIa and Plasma Kallikrein in arterial and venous thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 2020;120:883–993.
Girolami A, Scarparo P, Candeo N, Lombardi AM. Congenital prekallikrein deficiency. Expert Rev Hematol. 2010;3:685–95.
**e Z, Li Z, Shao Y, Liao C. Discovery and development of plasma kallikrein inhibitors for multiple diseases. Eur J Med Chem. 2020;190:112137.
Partridge JR, Choy RM, Silva-Garcia A, Yu C, Li Z, Sham H, et al. Structures of full-length plasma kallikrein bound to highly specific inhibitors describe a new mode of targeted inhibition. J Struct Biol. 2019;206:170–82.
Heitmeier S, Visser M, Tersteegen A, Dietze-Torres J, Glunz J, Gerdes C, et al. Pharmacological profile of asundexian, a novel, orally bioavailable inhibitor of factor XIa. J Thromb Haemost. 2022;20:1400–11.
Lorthiois E, Roache J, Barnes-Seeman D, Altmann E, Hassiepen U, Turner G, et al. Structure-based design and preclinical characterization of selective and orally bioavailable factor xia inhibitors: demonstrating the power of an integrated S1 Protease family approach. J Med Chem. 2020;63:8088–113.
Yao N, Jia Z, Tian Y, Hou S, Yang X, Han J, et al. Targeting the S2 subsite enables the structure-based discovery of novel highly selective factor XIa inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2022;65:4318–34.
Sun D, Gao W, Hu H, Zhou S. Why 90% of clinical drug development fails and how to improve it? Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022;12:3049–62.
Piel I, Engelen A, Lang D, Schulz SI, Gerisch M, Brase C, et al. Metabolism and disposition of the novel oral factor XIa inhibitor Asundexian in rats and in humans. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2023;48:411–25.
Stepan AF, Walker DP, Bauman J, Price DA, Baillie TA, Kalgutkar AS, et al. Structural alert/reactive metabolite concept as applied in medicinal chemistry to mitigate the risk of idiosyncratic drug toxicity: a perspective based on the critical examination of trends in the top 200 drugs marketed in the United States. Chem Res Toxicol. 2011;24:1345–410.
Rao SV, Kirsch B, Bhatt DL, Budaj A, Coppolecchia R, Eikelboom J, et al. A multicenter, Phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group, dose-finding trial of the oral factor XIa Inhibitor Asundexian to prevent adverse cardiovascular outcomes after acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2022;146:1196–206.
Shoamanesh A, Mundl H, Smith EE, Masjuan J, Milanov I, Hirano T, et al. Factor XIa inhibition with asundexian after acute non-cardioembolic ischaemic stroke (PACIFIC-Stroke): an international, randomised, double-blind, placebo- controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet. 2022;400:997–1007.
Zhan P, Itoh Y, Suzuki T, Liu X. Strategies for the discovery of target-specific or Isoform-selective modulators. J Med Chem. 2015;58:7611–33.
Al-Horani RA, Afosah DK. Recent advances in the discovery and development of factor XI/XIa inhibitors. Med Res Rev. 2018;38:1974–2023.
Sodano TM, Combee LA, Stephenson CRJ. Recent advances and outlook for the isosteric replacement of Anilines. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020;11:1785–88.
Pinto DJP, Orwat MJ, Koch S, Rossi KA, Alexander RS, Smallwood A, et al. Discovery of 1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-(4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro- 1H-pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxamide (Apixaban, BMS-562247), a highly potent, selective, efficacious, and orally bioavailable inhibitor of blood coagulation Factor Xa. J Med Chem. 2007;50:5339–56.
Roesch KR, Larock RC. Synthesis of Isoquinolines and Pyridines by the Palladium/Copper-catalyzed coupling and cyclization of terminal Acetylenes and unsaturated Imines: The total synthesis of Decumbenine B. J Org Chem. 2002;67:86–94.
Schaefer M, Buchmueller A, Dittmer F, Strassburger J, Wilmen A. Allosteric inhibition as a new mode of action for BAY 1213790, a neutralizing antibody targeting the activated form of coagulation factor XI. J Mol Biol. 2019;431:4817–33.
Smith LM 2nd, Orwat MJ, Hu Z, Han W, Wang C, Rossi KA, et al. Novel phenylalanine derived diamides as Factor XIa inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016;26:472–78.
Friesner RA, Banks JL, Murphy RB, Halgren TA, Klicic JJ, Mainz DT, et al. Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J Med Chem. 2004;47:1739–49.
Case DA, Aktulga HM, Belfon K, Cerutti DS, Cisneros GA, Cruzeiro VWD, et al. AmberTools. J Chem Inf Model. 2023;63:6183–91.
Davie RL, Edwards HJ, Evans DM, Hodgson ST, Stocks MJ, Smith AJ, et al. Sebetralstat (KVD900): A potent and selective small molecule plasma Kallikrein inhibitor featuring a novel P1 group as a potential oral on-demand treatment for hereditary angioedema. J Med Chem. 2022;65:13629–44.
Xu Y, Li Q, Meng L, Zhang Y, Deng X, Qi W, et al., Preparation of heterocyclic amide derivatives as FXIa inhibitor and/or plasma bradykinin kinase PKA inhibitor, in: L. Chengdu Taihe Weiye Biotechnology Co. (Ed.), CN116283750, 2022
Tian C, Kasavajhala K, Belfon KAA, Raguette L, Huang H, Migues AN, et al. ff19SB: Amino-acid-specific protein backbone parameters trained against quantum mechanics energy surfaces in solution. J Chem Theory Comput. 2020;16:528–52.
Vassetti D, Pagliai M, Procacci P. Assessment of GAFF2 and OPLS-AA general force fields in combination with the water models TIP3P, SPCE, and OPC3 for the solvation free energy of druglike organic molecules. J Chem Theory Comput. 2019;15:1983–95.
Gotz AW, Williamson MJ, Xu D, Poole D, Le Grand S, Walker RC. Routine microsecond molecular dynamics simulations with AMBER on GPUs. 1. Generalized born. J Chem Theory Comput. 2012;8:1542–55.
Korff M, Imberg L, Will JM, Buckreiss N, Kalinina SA, Wenzel BM, et al. Acylated 1H-1,2,4-Triazol-5-amines targeting human coagulation Factor XIIa and Thrombin: conventional and microscale synthesis, anticoagulant properties, and mechanism of action. J Med Chem. 2020;63:13159–86.
Acknowledgements
We thank the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22107082), the Natural Science Foundation of SiChuan (2024NSFSC0290), the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2021YFG0111), and Sichuan Province’s Central Government-led Local Science and Technology Development Project (2021ZYD0058).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Yi Zhang, Linjun Dai
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Dai, L., Tan, Y. et al. Design and synthesis of novel factor XIa Inhibitors with bicyclic isoquinoline and naphthalene fragments. Med Chem Res 33, 1003–1023 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-024-03245-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-024-03245-9