Abstract
Background
Myocardial inflammation and apoptosis are key processes in coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3)-induced acute viral myocarditis (AVMC). Accumulating evidence reveals the essential roles of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in the pathogenesis of AVMC. Here, we aimed to evaluate the biological functions of a novel lncRNA guanylate-binding protein 9 (lncGBP9) in AVMC progression and further explore its underlying mechanisms.
Methods
Initially, mouse models of AVMC were constructed by CVB3 infection. The expression and localization of lncGBP9 in heart tissues were analyzed using RT-qPCR and FISH. Adeno-associated virus serotype 9 (AAV9)-mediated lncGBP9 knockdown was then employed to clarify its roles in survival, cardiac function, and myocardial inflammation and apoptosis. Moreover, the mRNA and protein levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β) were detected by RT-qPCR and ELISA, and the regulation of lncGBP9 knockdown on the NF-κB signaling pathway was investigated by Western blotting. Using an in vitro model of HL-1 cardiomyocytes exposed to CVB3 infection, the effects of lncGBP9 knockdown on cell viability, inflammation, and apoptosis were further evaluated in vitro.
Results
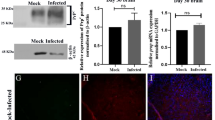
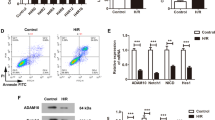
Increased lncGBP9 expression was detected in the heart tissues of AVMC mice and CVB3-infected HL-1 cells, and was mainly located in the cytoplasm. Knockdown of lncGBP9 remarkably alleviated the severity of AVMC in CVB3-infected mice, as verified by improved cardiac function, and reduced myocardial inflammation and apoptosis. Additionally, lncGBP9 knockdown suppressed the NF-κB signaling pathway and consequently reduced productions of pro-inflammatory cytokines in vivo. In vitro functional assays further confirmed that lncGBP9 knockdown promoted cell viability, inhibited cell apoptosis, and reduced pro-inflammatory cytokines release in CVB3-infected HL-1 cells through suppressing NF-κB activation.
Conclusions
Collectively, lncGBP9 knockdown exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects in CVB3-induced AVMC, which may be mediated in part via NF-κB signaling pathway. These findings highlight lncGBP9 as an attractive target for therapeutic interventions.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this manuscript and its supplementary files.
Abbreviations
- AVMC:
-
Acute viral myocarditis
- CVB3:
-
Coxsackievirus B3
- LncRNAs:
-
Long noncoding RNAs
- LncGBP9:
-
LncRNA guanylate-binding protein 9
- AAV9:
-
Adeno-associated virus serotype 9
- FISH:
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridization
- RT-qPCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
References
Sagar S, Liu PP, Cooper LT Jr. Myocarditis. Lancet. 2012;379(9817):738–47.
Kearney MT, Cotton JM, Richardson PJ, Shah AM. Viral myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy: mechanisms, manifestations, and management. Postgrad Med J. 2001;77(903):4–10.
Swirski FK, Nahrendorf M. Cardioimmunology: the immune system in cardiac homeostasis and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018;18(12):733–44.
Whitton JL, Cornell CT, Feuer R. Host and virus determinants of picornavirus pathogenesis and tropism. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005;3(10):765–76.
Pankuweit S, Klingel K. Viral myocarditis: from experimental models to molecular diagnosis in patients. Heart Fail Rev. 2013;18(6):683–702.
Kytö V, Saraste A, Saukko P, Henn V, Pulkki K, Vuorinen T, Voipio-Pulkki LM. Apoptotic cardiomyocyte death in fatal myocarditis. Am J Cardiol. 2004;94(6):746–50.
Pasparakis M, Vandenabeele P. Necroptosis and its role in inflammation. Nature. 2015;517(7534):311–20.
Kuffner M, Pawlak A, Przybylski M. Viral infection of the heart: pathogenesis and diagnosis. Pol J Microbiol. 2017;65(4):391–8.
Tsai MC, Manor O, Wan Y, Mosammaparast N, Wang JK, Lan F, Shi Y, Segal E, Chang HY. Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science. 2010;329(5992):689–93.
Ma Y, Ma W, Huang L, Feng D, Cai B. Long non-coding RNAs, a new important regulator of cardiovascular physiology and pathology. Int J Cardiol. 2015;188:105–10.
Clark MB, Mattick JS. Long noncoding RNAs in cell biology. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011;22(4):366–76.
Xu J, Cao X. Long noncoding RNAs in the metabolic control of inflammation and immune disorders. Cell Mol Immunol. 2019;16(1):1–5.
Nie X, Li H, Wang J, Cai Y, Fan J, Dai B, Chen C, Wang DW. Expression profiles and potential functions of long non-coding RNAs in the heart of mice with Coxsackie B3 virus-induced myocarditis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11: 704919.
Zhang C, **ong Y, Zeng L, Peng Z, Liu Z, Zhan H, Yang Z. The role of non-coding RNAs in viral myocarditis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:312.
Xue YL, Zhang SX, Zheng CF, Li YF, Zhang LH, Su QY, Hao YF, Wang S, Li XW. Long non-coding RNA MEG3 inhibits M2 macrophage polarization by activating TRAF6 via microRNA-223 down-regulation in viral myocarditis. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(21):12341–54.
Cao H, Yang B, Zhao Y, Deng X, Shen X. The pro-apoptosis and pro-inflammation role of LncRNA HIF1A-AS1 in Coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis via targeting miR-138. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2020;10(5):1245–55.
Zhang Y, Li X, Wang C, Zhang M, Yang H, Lv K. lncRNA AK085865 promotes macrophage M2 polarization in CVB3-induced VM by regulating ILF2-ILF3 complex-mediated miRNA-192 biogenesis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;21:441–51.
Zeng M, Yi S, **ao Y, Chen Z. LncRNA ROR promotes NLRP3-mediated cardiomyocyte pyroptosis by upregulating FOXP1 via interactions with PTBP1. Cytokine. 2022;152: 155812.
Zhou J, Li Z, Wu T, Zhao Q, Zhao Q, Cao Y. LncGBP9/miR-34a axis drives macrophages toward a phenotype conducive for spinal cord injury repair via STAT1/STAT6 and SOCS3. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):134.
Luo H, Yanagawa B, Zhang J, Luo Z, Zhang M, Esfandiarei M, Carthy C, Wilson JE, Yang D, McManus BM. Coxsackievirus B3 replication is reduced by inhibition of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway. J Virol. 2002;76(7):3365–73.
Inagaki K, Fuess S, Storm TA, Gibson GA, Mctiernan CF, Kay MA, Nakai H. Robust systemic transduction with AAV9 vectors in mice: efficient global cardiac gene transfer superior to that of AAV8. Mol Ther. 2006;14(1):45–53.
Carai P, Ruozi G, Paye A, Debing Y, Bortolotti F, Lecomte J, Zentilin L, Jones EAV, Giacca M, Heymans S. AAV9-mediated functional screening for cardioprotective cytokines in Coxsackievirus-B3-induced myocarditis. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):7304.
Blackwood EA, Azizi K, Thuerauf DJ, Paxman RJ, Plate L, Kelly JW, Wiseman RL, Glembotski CC. Pharmacologic ATF6 activation confers global protection in widespread disease models by reprograming cellular proteostasis. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):187.
Li Y, Garson CD, Xu Y, Beyers RJ, Epstein FH, French BA, Hossack JA. Quantification and MRI validation of regional contractile dysfunction in mice post myocardial infarction using high resolution ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2007;33(6):894–904.
Grabie N, Delfs MW, Westrich JR, Love VA, Stavrakis G, Ahmad F, Seidman CE, Seidman JG, Lichtman AH. IL-12 is required for differentiation of pathogenic CD8+ T cell effectors that cause myocarditis. J Clin Invest. 2003;111(5):671–80.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–8.
Claycomb WC, Lanson NA Jr, Stallworth BS, Egeland DB, Delcarpio JB, Bahinski A, Izzo NJ Jr. HL-1 cells: a cardiac muscle cell line that contracts and retains phenotypic characteristics of the adult cardiomyocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(6):2979–84.
Mingozzi F, High KA. Therapeutic in vivo gene transfer for genetic disease using AAV: progress and challenges. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12(5):341–55.
Zhou L, He X, Gao B, **ong S. Inhibition of histone deacetylase activity aggravates coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis by promoting viral replication and myocardial apoptosis. J Virol. 2015;89(20):10512–23.
Shi H, Yu Y, Wang Y, Liu X, Yu Y, Li M, Zou Y, Chen R, Ge J. Inhibition of calpain alleviates apoptosis in coxsackievirus B3-induced acute virus myocarditis through suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress. Int Heart J. 2021;62(4):900–9.
Valaperti A. Drugs Targeting the canonical NF-κB pathway to treat viral and autoimmune myocarditis. Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22(4):440–9.
White SM, Constantin PE, Claycomb WC. Cardiac physiology at the cellular level: use of cultured HL-1 cardiomyocytes for studies of cardiac muscle cell structure and function. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004;286(3):H823–9.
Miteva K, Pappritz K, Sosnowski M, El-Shafeey M, Müller I, Dong F, Savvatis K, Ringe J, Tschöpe C, Van Linthout S. Mesenchymal stromal cells inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome activation in a model of Coxsackievirus B3-induced inflammatory cardiomyopathy. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):2820.
Sallam T, Sandhu J, Tontonoz P. Long noncoding RNA discovery in cardiovascular disease: decoding form to function. Circ Res. 2018;122(1):155–66.
Liu Q, Kong Y, Han B, Jiang D, Jia H, Zhang L. Long non-coding RNA expression profile and functional analysis in children with acute fulminant myocarditis. Front Pediatr. 2019;7:283.
Yao RW, Wang Y, Chen LL. Cellular functions of long noncoding RNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(5):542–51.
Lai F, Orom UA, Cesaroni M, Beringer M, Taatjes DJ, Blobel GA, Shiekhattar R. Activating RNAs associate with Mediator to enhance chromatin architecture and transcription. Nature. 2013;494(7438):497–501.
Krause HM. New and Prospective Roles for lncRNAs in Organelle Formation and Function. Trends Genet. 2018;34(10):736–45.
Murray PJ, Allen JE, Biswas SK, Fisher EA, Gilroy DW, Goerdt S, Gordon S, Hamilton JA, Ivashkiv LB, Lawrence T, Locati M, Mantovani A, Martinez FO, Mege JL, Mosser DM, Natoli G, Saeij JP, Schultze JL, Shirey KA, Sica A, Suttles J, Udalova I, van Ginderachter JA, Vogel SN, Wynn TA. Macrophage activation and polarization: nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity. 2014;41(1):14–20.
Zhang Y, Cai S, Ding X, Lu C, Wu R, Wu H, Shang Y, Pang M. MicroRNA-30a-5p silencing polarizes macrophages toward M2 phenotype to alleviate cardiac injury following viral myocarditis by targeting SOCS1. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021;320(4):H1348–60.
Kiraz Y, Adan A, Kartal Yandim M, Baran Y. Major apoptotic mechanisms and genes involved in apoptosis. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(7):8471–86.
Banjara S, Mao J, Ryan TM, Caria S, Kvansakul M. Grouper iridovirus GIV66 is a Bcl-2 protein that inhibits apoptosis by exclusively sequestering Bim. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(15):5464–77.
Shalini S, Dorstyn L, Dawar S, Kumar S. Old, new and emerging functions of caspases. Cell Death Differ. 2015;22(4):526–39.
Boyd JH, Mathur S, Wang Y, Bateman RM, Walley KR. Toll-like receptor stimulation in cardiomyocytes decreases contractility and initiates an NF-kappaB dependent inflammatory response. Cardiovasc Res. 2006;72(3):384–93.
Liang Y, Zhou Y, Shen P. NF-kappaB and its regulation on the immune system. Cell Mol Immunol. 2004;1(5):343–50.
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D, Sun SC. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2017;2:17023.
Daniluk J, Liu Y, Deng D, Chu J, Huang H, Gaiser S, Cruz-Monserrate Z, Wang H, Ji B, Logsdon CD. An NF-κB pathway-mediated positive feedback loop amplifies Ras activity to pathological levels in mice. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(4):1519–28.
Cao YY, Chen ZW, Gao YH, Wang XX, Ma JY, Chang SF, Qian JY, Ge JB. Exenatide reduces tumor necrosis factor-α-induced apoptosis in cardiomyocytes by alleviating mitochondrial dysfunction. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128(23):3211–8.
Okada M, Yamawaki H. Levosimendan inhibits interleukin-1β-induced apoptosis through activation of Akt and inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase in rat cardiac fibroblasts. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;769:86–92.
Li Z, Wang C, Mao Y, Cui J, Wang X, Dang J, Wang S. The expression of STAT3 inhibited the NF-ΚB signaling pathway and reduced inflammatory responses in mice with viral myocarditis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;95: 107534.
Liu T, Zhang M, Niu H, Liu J, Ruilian M, Wang Y, **ao Y, **ao Z, Sun J, Dong Y, Liu X. Astragalus polysaccharide from Astragalus Melittin ameliorates inflammation via suppressing the activation of TLR-4/NF-κB p65 signal pathway and protects mice from CVB3-induced virus myocarditis. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;126:179–86.
Jiang P, Liu R, Zheng Y, Liu X, Chang L, **ong S, Chu Y. MiR-34a inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response through targeting Notch1 in murine macrophages. Exp Cell Res. 2012;318(10):1175–84.
Ge Y, Huang M, Ma YF. The effects of microRNA-34a regulating Notch-1/NF-κB signaling pathway on lipopolysaccharide-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells. World J Emerg Med. 2017;8(4):292–6.
Li X, Ma G, Zhang C, Chen M, Huang X, Gu C. miR-34a overexpression protects against hippocampal neuron damage caused by ketamine-induced anesthesia in immature rats through the Notch-1/NF-κB signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(12):13452–61.
Acknowledgements
We appreciate all participants who provided technical supports for our research.
Funding
This study was supported by Fujian Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2022J01402, 2020J011058), the Startup Fund for Scientific Research of Fujian Medical University (2020QH1191), and High-Level Hospital Foster Grants from Fujian Provincial Hospital of Fujian Province (2020HSJJ04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YX and FC conceived and designed the study. YX, JZ, JK, LZ, KC, XH, and FC carried out the experimental studies and data collection. YX and JZ performed data analysis and drafted the manuscript. FC coordinated the study and reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures associated with the study were approved by the Animal Experimentation Ethics Committee of Shengli Clinical Medical College of Fujian Medical University.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Di Battista.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, Y., Zhang, J., Ke, J. et al. LncGBP9 knockdown alleviates myocardial inflammation and apoptosis in mice with acute viral myocarditis via suppressing NF-κB signaling pathway. Inflamm. Res. 71, 1559–1576 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-022-01644-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-022-01644-5