Abstract
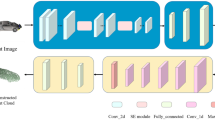
For the processing of point clouds, an accurate assessment of the quality is essential. However, point cloud quality assessment has proven to be a difficult issue, especially when the pristine point clouds are unavailable. Most existing no-reference point cloud quality assessment methods adopt projection-based routes, which inevitably suffer from occlusion and misalignment, resulting in loss of information. Alternatively, this paper proposes a novel no-reference point cloud quality assessment method via a contextual point-wise deep learning network (CPW-Net). Compared with projection-based methods, it reduces information loss by learning features directly from point coordinates and attributes. In particular, CPW-Net utilizes an Offset Attention Feature Encoder (OAFE) module to extract local and contextual features. Experiment results demonstrate that the proposed method overwhelms most publicly available no-reference metrics on SJTU dataset and gains compatible performance in comparison with most full-reference methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thomas, P.C., David, W.M.: Augmented reality: an application of heads-up display technology to manual manufacturing processes. In: Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences. ACM SIGCHI Bulletin, vol. 2 (1992)
Yuen, S.C.Y., Yaoyuneyong, G., Johnson, E.: Augmented reality: An overview and five directions for AR in education. J. Educ. Technol. Dev. Exch. (JETDE) 4(1), 11 (2011)
Radianti, J., Majchrzak, T.A., Fromm, J., et al.: A systematic review of immersive virtual reality applications for higher education: design elements, lessons learned, and research agenda. Comput. Educ. 147, 103778 (2020)
Slavova, Y., Mu, M.: A comparative study of the learning outcomes and experience of VR in education. In: 2018 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (VR), pp. 685–686. IEEE (2018)
Mohammadi, P., Ebrahimi-Moghadam, A., Shirani, S.: Subjective and objective quality assessment of image: A survey. ar**v preprint ar**v:1406.7799 (2014)
Wang, X., Liang, X., Yang, B., et al.: No-reference synthetic image quality assessment with convolutional neural network and local image saliency. Comput. Vis. Media 5, 193–208 (2019)
Liu, Q., Yuan, H., Su, H., et al.: PQA-Net: deep no reference point cloud quality assessment via multi-view projection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 31(12), 4645–4660 (2021)
Bourbia, S., Karine, A., Chetouani, A., et al.: No-reference point clouds quality assessment using transformer and visual saliency. In: Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Quality of Experience in Visual Multimedia Applications, pp. 57–62 (2022)
Fan, Y., Zhang, Z., Sun, W., et al.: A no-reference quality assessment metric for point cloud based on captured video sequences. In: 2022 IEEE 24th International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP), pp. 1–5. IEEE (2022)
De Silva, V., Fernando, A., Worrall, S., et al.: Sensitivity analysis of the human visual system for depth cues in stereoscopic 3-D displays. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 13(3), 498–506 (2011)
Liu, Y., Wang, W., Hu, Y., et al.: Multi-agent game abstraction via graph attention neural network. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 34(05), 7211–7218 (2020)
Zhu, X., Cheng, D., Zhang, Z., et al.: An empirical study of spatial attention mechanisms in deep networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 6688–6697 (2019)
Mekuria, R., Li, Z., Tulvan, C., et al.: Evaluation criteria for point cloud compression. ISO/IEC MPEG 16332 (2016)
Tian, D., Ochimizu, H., Feng, C., et al.: Geometric distortion metrics for point cloud compression. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 3460–3464. IEEE (2017)
Yang, Q., Ma, Z., Xu, Y., et al.: Inferring point cloud quality via graph similarity. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(6), 3015–3029 (2020)
Alexiou, E., Ebrahimi, T.: Towards a point cloud structural similarity metric. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), pp. 1–6 IEEE (2020)
De Queiroz, R.L., Chou, P.A.: Motion-compensated compression of dynamic voxelized point clouds. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(8), 3886–3895 (2017)
Meynet, G., Nehmé, Y., Digne, J., et al.: PCQM: a full-reference quality metric for colored 3D point clouds. In: 2020 Twelfth International Conference on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2020)
Viola, I., Cesar, P.: A reduced reference metric for visual quality evaluation of point cloud contents. IEEE Sig. Process. Lett. 27, 1660–1664 (2020)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 60(6), 84–90 (2017)
Zhang, Z., Sun, W., Min, X., et al.: No-reference quality assessment for 3D colored point cloud and mesh models. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 32(11), 7618–7631 (2022)
Yang, Q., Liu, Y., Chen, S., et al.: No-Reference Point Cloud Quality Assessment via Domain Adaptation. ar**v preprint ar**v:2112.02851 (2021)
Liu, Y., Yang, Q., Xu, Y., et al.: Point Cloud Quality Assessment: Dataset Construction and Learning-based No-Reference Approach. ar**v preprint ar**v:2012.11895 (2020)
Zhang, Z., Sun, W., Min, X., et al.: Treating Point Cloud as Moving Camera Videos: A No-Reference Quality Assessment Metric. ar**v preprint ar**v:2208.14085 (2022)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. ar**v preprint ar**v:1412.6980 (2014)
Yang, Q., Chen, H., Ma, Z., et al.: Predicting the perceptual quality of point cloud: a 3D-to-2D projection-based exploration. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 23, 3877–3891 (2020)
Chetouani, A., Quach, M., Valenzise, G., et al.: Deep learning-based quality assessment of 3D point clouds without reference. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), pp. 1–6 IEEE (2021)
Liu, Q., Su, H., Duanmu, Z., et al.: Perceptual quality assessment of colored 3D point clouds. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 29(8), 3642–3655 (2022)
Torlig, E.M., Alexiou, E., Fonseca, T.A., et al.: A novel methodology for quality assessment of voxelized point clouds. In: Applications of Digital Image Processing XLI. SPIE, vol. 10752, pp. 174–190 (2018)
Mittal, A., Moorthy, A.K., Bovik, A.C.: No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(12), 4695–4708 (2012)
Mittal, A., Soundararajan, R., Bovik, A.C.: Making a “completely blind” image quality analyzer. IEEE Sig. Process. Lett. 20(3), 209–212 (2012)
Acknowledgment
This work was sponsored by the Bei**g Natural Science Foundation (No. 4232020), Scientific and Technological Innovation 2030 - “New Generation Artificial Intelligence” Major Project (No. 2022ZD0119502), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62201017, No.62201018, No.62076012). The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers who put in efforts to help improve this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, X., Liu, R., Wang, X. (2024). No-Reference Point Cloud Quality Assessment via Contextual Point-Wise Deep Learning Network. In: Sun, F., Meng, Q., Fu, Z., Fang, B. (eds) Cognitive Systems and Information Processing. ICCSIP 2023. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1919. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8021-5_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8021-5_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-8020-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-8021-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)