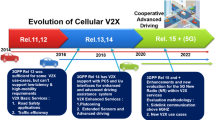
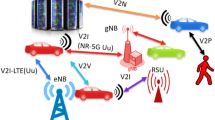
Abstract
In the past couple of decade, mobile communication experiences fast development. Recently, 5G mobile communication has been deployed worldwide, and 5G can reach superior capability and performance. 5G ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (uRLLC) scenario can meet the service high requirements in latency and reliability. Therefore, 5G uRLLC is suitable for Vehicle to Everything (V2X) services. This chapter briefly introduces 5G, and then this chapter analyzes 5G uRLLC scenario, characteristics, challenges, as well as 5G uRLLC integration with V2X. Furthermore, this chapter discusses 5G applications for V2X, including V2X security applications, transportation efficiency applications, V2X entertainment applications, Metaverse applications, etc. Then, this chapter introduces the standardization and industrialization of Cellular Vehicle to Everything (C-V2X).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 5GAA:
-
5G Automotive Association
- ADAS:
-
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems
- AGV:
-
Automated Guided Vehicle
- AR:
-
Augmented Reality
- BS:
-
Base Station
- C-V2X:
-
Cellular Vehicle to Everything
- CAN:
-
Controller Area Network
- CVIS:
-
Cooperative Vehicle Infrastructure System
- DSRC:
-
Dedicated Short-Range Communications
- eMBB:
-
Enhanced Mobile Broadband
- FCC:
-
Federal Communications Commission
- FCW:
-
Forwarding Collision Warning
- GPS:
-
Global Position System
- GSA:
-
Global mobile Suppliers Association
- HMI:
-
Human Machine Interface
- IMT:
-
International Mobile Telecommunications
- IoV:
-
Internet of Vehicles
- ITS:
-
Intelligent Transportation System
- MEC:
-
Mobile Edge Computing
- MIIT:
-
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology
- mMTC:
-
Massive Machine Type Communication
- NFV:
-
Network Functions Virtualization
- OBU:
-
On-Board Units
- OEMs:
-
Original Equipment Manufacturers
- RSU:
-
Road Side Unit
- SDN:
-
Software Defined Network
- uRLLC:
-
ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication
- UPF:
-
User Plane Function
- V2C:
-
Vehicle to Cloud
- V2I:
-
Vehicle to Infrastructure
- V2N:
-
Vehicle to Network
- V2P:
-
Vehicle to Pedestrian
- V2V:
-
Vehicle to Vehicle
- V2X:
-
Vehicle to Everything
- VR:
-
Virtual Reality
References
IMT2020(5G) Advancing Group, 5G Vision and Requirements (2014)
H. Chen, R. Abbas et al., Ultra-reliable low latency cellular networks: use cases, challenges and approaches. IEEE Commun. Mag. 56(12), 119–125 (2018)
M. Fallgren, M. Dillinger, T. Mahmoodi, T. Svensson, Cellular V2X for Connected Automated Driving (Wiley, 2021)
G. Cao, J. Li, Y. Li, F. Li, Research advances of 5G network architecture standards. Mob. Commun. 41(2), 32–37 (2017)
A.K. Bairagi, M.S. Munir, M. Alsenwi et al., Coexistence mechanism between eMBB and uRLLC in 5G wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 69(3), 1736–1749 (2021)
X. Liu, F. N, P. Li, C. Liu, Introduction of 5G Standardization and analysis of network architecture, Telecom Eng. Tech. Stand. 30(8), 44–49 (2017)
3GPP TR 38.824 (v2.0.1), Study on Physical Layer Enhancements for NR Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Case (uRLLC) (2019)
C. Pan, Z. Wang, Z. Zhou, X. Ren, Deep reinforcement learning-based URLLC-aware task offloading in collaborative vehicular networks. China Commun. 18(7), 134–146 (2021)
D. Segura, E.J. Khatib, R. Barco, Dynamic packet duplication for industrial URLLC. Sensors 22(2), 587–587 (2022)
H. Bagheri, M. Noor-A-Rahim, Z. Liu et al., 5G NR-V2X: toward connected and cooperative autonomous driving. IEEE Commun. Stand. Mag. 5(1), 48–54 (2021)
S. Chen, S. Kang, A tutorial on 5G and the progress in China. Front. Inf. Technol. & Electron. Eng. (2018)
Y. Yoon, H. Seon, H. Kim, A defensive scheduling scheme to accommodate random selection devices in 5G NR V2X. IEEE Commun. Lett. 25(6), 2068–2072 (2021)
J. Hu, X. Ren, R. Zhao, L. Zhao, S. Zheng, Y. Shi, Design and Evaluation of Synchronization Signals for NR-V2X Sidelink, in 2020 IEEE 91st Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2020-Spring) (2020), pp. 1–6
P. Wang, “Vehicle to Everything,” China Machine Press, 2020, 536–538.
J. Shi, X. Wang, M. Huang, K. Li, S.l K. Das, Social-based routing scheme for fixed-line VANET. Comput. Netw. (2017)
M. Bonola, L. Bracciale, P. Loreti, R. Amici, Opportunistic communication in smart city: experimental insight with small-scale taxi fleets as data carriers. Ad Hoc Netw. 43, 43–55 (2016)
T. Huynh-The, Q. V. Pham, X. Q. Pham, T. T. Nguyen, Z. Han, D. S. Kin, Artificial Intelligence for the Metaverse: A Survey (Cornell University, 2022), pp.1–24
Y. Wang, Z. Su, N. Zhang, D. Liu, R. **ng, T. H. Luan, X. Shen, “A Survey on Metaverse: Fundamentals, Security, and Privacy,” ar**v e-prints, pp.1–23, 2022.
S. Chen, J. Hu, Y. Shi, L. Zhao, W. Li, A vision of C-V2X: technologies, field testing, and challenges with Chinese development. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(5), 3872–3881 (2020)
Global mobile Suppliers Association (GSA), Global C-V2X Ecosystem: Status Update Executive Summary (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Shi, J. et al. (2023). 5G Meets V2X: Integration, Application, Standard and Industrialization. In: Zhu, Y., Cao, Y., Hua, W., Xu, L. (eds) Communication, Computation and Perception Technologies for Internet of Vehicles. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-5439-1_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-5439-1_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-5438-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-5439-1
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)