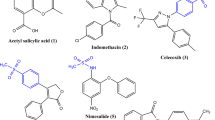
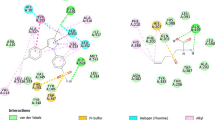
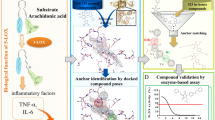
Abstract
Inflammation is the body’s defense mechanism against external stressors. However, diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, diabetes, allergies, and infections have all been linked to excessive physiopathological damage. Anti-inflammatory drugs are used to treat inflammation symptoms, which mostly include pain, an increase in body temperature, flushing, and edema. It has been determined in this case to focus on prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) inhibition while develo** novel anti-inflammatory medications. The treatment of inflammatory illnesses with the least amount of adverse effects possible could be achieved by selectively inhibiting both cyclooxygenase (COX) and lipoxygenase (LOX). Recently, approaches for computer-aided drug design (CADD) have been employed with effectiveness in the procedures of develo** medications. This article presents a thorough analysis of structure-based drug design proposals for the creation of novel LOX inhibitors and COX inhibitors.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelall EKA, Kamel GM (2016) Synthesis of new thiazolo-celecoxib analogues as dual cyclooxygenase-2/15-lipoxygenase inhibitors: determination of regio-specific different pyrazole cyclization by 2D NMR. Eur J Med Chem 118:250–258
Ahmed AU (2011) An overview of inflammation: mechanism and consequences. Front Biol (Bei**g) 6:274–281
Ajith V, Nair A (2017) Computer aided drug discovery – an overview
Al-Ostoot FH, Geetha D, Mohammed YHE et al (2020) Design-based synthesis, molecular docking analysis of an anti-inflammatory drug, and geometrical optimization and interaction energy studies of an indole acetamide derivative. J Mol Struct 1202:127244
Angajala KK, Vianala S, Macha R et al (2016) Synthesis, anti-inflammatory, bactericidal activities and docking studies of novel 1, 2, 3-triazoles derived from ibuprofen using click chemistry. Springerplus 5:1–15
Ansar W, Ghosh S (2016) Inflammation and inflammatory diseases, markers, and mediators: role of CRP in some inflammatory diseases. In: Biology of C reactive protein in health and disease. Springer, pp 67–107
Aparoy P, Kumar Reddy K, Reddanna P (2012) Structure and ligand based drug design strategies in the development of novel 5-LOX inhibitors. Curr Med Chem 19:3763–3778
Balaban AT, Basak SC, Colburn T, Grunwald GD (1994) Correlation between structure and normal boiling points of haloalkanes C1-C4 using neural networks. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 34:1118–1121
Bensman A (2020) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) systemic use: the risk of renal failure. Front Pediatr 7:517
Bernard D, Coop A, MacKerell AD Jr (2005) Computer-aided drug design: structure-activity relationships of delta opioid ligands. Drug Des Rev Online (Discontinued) 2:277–291
Blobaum AL, Marnett LJ (2007) Structural and functional basis of cyclooxygenase inhibition. J Med Chem 50:1425–1441
Dagvadorj J, Naiki Y, Tumurkhuu G et al (2008) Interleukin-10 inhibits tumor necrosis factor-α production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells through reduced MyD88 expression. Innate Immun 14:109–115
Davidson FF, Dennis EA, Powell M, Glenney JR Jr (1987) Inhibition of phospholipase A2 by “lipocortins” and calpactins. An effect of binding to substrate phospholipids. J Biol Chem 262:1698–1705
el Sayed MT, El-Sharief MAMS, Zarie ES et al (2018) Design, synthesis, anti-inflammatory activity and molecular docking of potential novel antipyrine and pyrazolone analogs as cyclooxygenase enzyme (COX) inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 28:952–957
El-Nagar MKS, Abdu-Allah HHM, Salem OIA et al (2018) Novel N-substituted 5-aminosalicylamides as dual inhibitors of cyclooxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase enzymes: synthesis, biological evaluation and docking study. Bioorg Chem 78:80–93
Flower RJ (1974) Drugs which inhibit prostaglandin biosynthesis. Pharmacol Rev 26:33–67
Flower RJ (1986) Background and discovery of lipocortins. Agents Actions 17:255–262
Ford-Hutchinson AW, Brunet G, Savard P, Charleson S (1984) Leukotriene B4, polymorphonuclear leukocytes and inflammatory exudates in the rat. Prostaglandins 28:13–27
Geronikaki AA, Lagunin AA, Hadjipavlou-Litina DI et al (2008) Computer-aided discovery of anti-inflammatory thiazolidinones with dual cyclooxygenase/lipoxygenase inhibition. J Med Chem 51:1601–1609
Halliday RG, Walker SR, Lumley CE (1992) R & D philosophy and management in the world’s leading pharmaceutical companies. J Pharmaceut Med 2:139–154
Higgs GA, Vane JR, Hart FD, Wojtulewski JA (1974) Effects of anti-inflammatory drugs on prostaglandins in rheumatoid arthritis. Prostaglandin Synthetase Inhibitors 165–173
Irwin J, Lorber DM, McGovern SL et al (2002) Docking and drug discovery. Comput Nanosci Nanotechnol 2:50–51
Kore PP, Mutha MM, Antre R et al (2012) Computer-aided drug design: an innovative tool for modeling
Kubinyi H (1993) 3D QSAR in drug design: volume 1: theory methods and applications. Springer Science & Business Media
Mahdavi M, Saeedi M, Nadri H et al (2017) Synthesis of thiazolone derivatives as novel soybean 15-LOX inhibitors. Lett Org Chem 14:186–191
Martin YC (1998) Perspective in drug discovery and design, vol 12. Springer, New York, pp 3–23
Mohammed KO, Nissan YM (2014) Synthesis, molecular docking, and biological evaluation of some novel hydrazones and pyrazole derivatives as anti-inflammatory agents. Chem Biol Drug Des 84:473–488
Moncada S, Ferreira SH, Vane JR (1973) Prostaglandins, aspirin-like drugs and the oedema of inflammation. Nature 246:217–219
Moos WH, Green GD, Pavia MR (1993) Recent advances in the generation of molecular diversity. Annu Rep Med Chem 28:315–324
Müller K (1994) 5-lipoxygenase and 12-lipoxygenase: attractive targets for the development of novel antipsoriatic drugs. 5-lipoxygenase und 12-lipoxygenase: Attraktive target-enzyme für die Entwicklung neuer Antipsoriatika. Arch Pharm (Weinheim) 327:1–19
Muzamil A, Tahir HM, Ali S et al (2021) Inflammatory process and role of cytokines in inflammation: an overview. Punjab Univ J Zool 36:237–252
Nair V, Das KP, Banerjee S, Bagchi S (2017) Achieving oral health the natural way: pomegranate. J Med Health Res 2:110–118
Oldenburg KR (1998) Annual report in medicinal chemistry, vol 33. Academic Press, London, pp 301–307
Omar YM, Abdu-Allah HHM, Abdel-Moty SG (2018) Synthesis, biological evaluation and docking study of 1, 3, 4-thiadiazole-thiazolidinone hybrids as anti-inflammatory agents with dual inhibition of COX-2 and 15-LOX. Bioorg Chem 80:461–471
Ooma F (2000) Molecular modeling and computer aided drug design. Examples of their application in medicinal chemistry. Curr Med Chem 7:141–158
Reigner BG, Blesch K (2002) Estimating the starting dose for entry into humans: principles and practice. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 57:835–845
Scherer D, Dubois P, Sherwood B (2000) VPython: 3D interactive scientific graphics for students. Comput Sci Eng 2:56–62
Sibbald B (2004) Rofecoxib (Vioxx) voluntarily withdrawn from market. CMAJ 171:1027–1028
Simmons PM, Salmon JA, Moncada S (1983) The release of leukotriene B4 during experimental inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol 32:1353–1359
Taft CA (2008) Silva VB da, Silva CHT de P da. Current topics in computer-aided drug design. J Pharm Sci 97:1089–1098
Tomlinson R, Ringold HJ, Qureshi MC, Forchielli E (1972) Relationship between inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis and drug efficacy: support for the current theory on mode of action of aspirin-like drugs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 46:552–559
Ugwu DI, Okoro UC, Ukoha PO et al (2018) Novel anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents: synthesis, molecular docking and in vivo studies. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 33:405–415
Wallner BP, Mattaliano RJ, Hession C et al (1986) Cloning and expression of human lipocortin, a phospholipase A2 inhibitor with potential anti-inflammatory activity. Nature 320:77–81
Whittle BJR, Higgs GA, Eakins KE et al (1980) Selective inhibition of prostaglandin production in inflammatory exudates and gastric mucosa. Nature 284:271–273
Williams FMK, Spector TD (2009) A new 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor seems to be safe and effective for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 5:132–133
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Maiti, N.J., Singh, N.K. (2023). CADD Approaches in Anti-inflammatory Drug Discovery. In: Rudrapal, M., Khan, J. (eds) CADD and Informatics in Drug Discovery. Interdisciplinary Biotechnological Advances. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1316-9_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1316-9_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-1315-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-1316-9
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)