Abstract
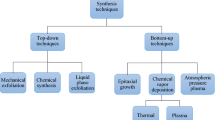
This chapter describes various state-of-the-art fabrication routes for high-quality graphene included: chemical vapour deposition (CVD), mechanical exfoliation, chemical exfoliation, electrochemical exfoliation, arc discharge, epitaxial growth, and pyrolysis. CVD is a widely used technique for growing high-quality graphene films on metal catalyst substrates, and copper foil has shown promising results. Mechanical exfoliation involves peeling graphite flakes from highly oriented pyrolytic carbon (HOPG) platelets using Scotch tape, resulting in single-layer graphene. Chemical exfoliation has two methods: solution-assisted and low-temperature chemical exfoliation. Electrochemical exfoliation involves the intercalation and exfoliation of graphite into graphene nanosheets through electrolyte solutions. Arc discharge is a plasma deposition technique for synthesizing high-quality graphene sheets using alternating current arc-discharge processes. Epitaxial growth involves growing single-layer or multilayer graphene on a SiC substrate using high-temperature sublimation growth. Pyrolysis is a 6-step process of poly(methyl methacrylate) composite that results in carbon derivatives that dissolve in the Ni catalyst surface, resulting in the epitaxial growth of graphene. Each method has its unique features, advantages, and disadvantages, making them suitable for different applications. For example, mechanical exfoliation remains one of the most reliable ways of producing high-quality graphene and has led to the discovery of graphene's extraordinary physical properties. Chemical exfoliation can produce graphene on a large scale, and electrochemical exfoliation is effective in creating biocompatible and fluorescent carbon nanomaterials for biological labelling and imaging. CVD as well as epitaxial growth can produce high-quality graphene films, and pyrolysis produces graphene with a high degree of graphitization. The choice of the appropriate technique is crucial for specific applications.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alanyalioǧlu, M., Segura, J.J., Oró-Sol, J., Casañ-Pastor, N.: The synthesis of graphene sheets with controlled thickness and order using surfactant-assisted electrochemical processes. Carbon 50(1), 142–152 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2011.07.064
Bae, S., Kim, H., Lee, Y., Xu, X., Park, J.S., Zheng, Y., Balakrishnan, J., Lei, T., Ri Kim, H., Song, Y.I., Kim, Y.J., Kim, K.S., Özyilmaz, B., Ahn, J.H., Hong, B.H., Iijima, S.: Roll-to-roll production of 30-inch graphene films for transparent electrodes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 5(8), 574–578 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2010.132
Berlouis, L.E.A., Schiffrin, D.J.: The electrochemical formation of graphitebisulphate intercalation compounds. J. Appl. Electrochem. 13(2), 147–155 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00612475
Blake, P., Hill, E.W., Castro Neto, A.H., Novoselov, K.S., Jiang, D., Yang, R., Booth, T.J., Geim, A.K.: Making graphene visible. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91(6), (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2768624
Casallas Caicedo, F.M., Vera López, E., Agarwal, A., Drozd, V., Durygin, A., Franco Hernandez, A., Wang, C.: Synthesis of graphene oxide from graphite by ball milling. Diam. Relat. Mater. 109(September), 108064 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2020.108064
Chen, C., Zhai, W., Lu, D., Zhang, H., Zheng, W.: A facile method to prepare stable noncovalent functionalized graphene solution by using thionine. Mater. Res. Bull. 46(4), 583–587 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2010.12.024
Chen, J., Cui, M., Wu, G., Wang, T., Mbengue, J.M., Li, Y., Li, M.: Fast growth of large single-crystalline graphene assisted by sequential double oxygen passivation. Carbon 116, 133–138 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.01.108
Chen, J.H., Jang, C., **ao, S., Ishigami, M., Fuhrer, M.S.: Intrinsic and extrinsic performance limits of graphene devices on SiO2. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3(4), 206–209 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.58
Chen, L., Tang, Y., Wang, K., Liu, C., Luo, S.: Direct electrodeposition of reduced graphene oxide on glassy carbon electrode and its electrochemical application. Electrochem. Commun. 13(2), 133–137 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2010.11.033
Chen, Z., Ren, W., Liu, B., Gao, L., Pei, S., Wu, Z.S., Zhao, J., Cheng, H.M.: Bulk growth of mono- to few-layer graphene on nickel particles by chemical vapor deposition from methane. Carbon 48(12), 3543–3550 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2010.05.052
Choy, K.L.: Chemical vapour deposition of coatings. Prog. Mater Sci. 48(2), 57–170 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6425(01)00009-3
De Heer, W.A., Berger, C., Ruan, M., Sprinkle, M., Li, X., Hu, Y., Zhang, B., Hankinson, J., Conrad, E.: Large area and structured epitaxial graphene produced by confinement controlled sublimation of silicon carbide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108(41), 16900–16905 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1105113108
Di, C.A., Wei, D., Yu, G., Liu, Y., Guo, Y., Zhu, D.: Patterned graphene as source/drain electrodes for bottom-contact organic field-effect transistors. Adv. Mater. 20(17), 3289–3293 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200800150
Dimovski, S., Nikitin, A., Ye, H., Gogotsi, Y.: Synthesis of graphite by chlorination of iron carbide at moderate temperatures. J. Mater. Chem. 14(2), 238–243 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1039/b311938f
Economopoulos, S.P., Rotas, G., Miyata, Y., Shinohara, H., Tagmatarchis, N.: Exfoliation and chemical modification using microwave irradiation affording highly functionalized graphene. ACS Nano 4(12), 7499–7507 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn101735e
Feng, L., Chen, Y., Chen, L.: Easy-to-operate and low-temperature synthesis of gram-scale nitrogen-doped graphene and its application as cathode catalyst in microbial fuel cells. ACS Nano 5(12), 9611–9618 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn202906f
Ferrari, A.C., Robertson, J.: Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Schweiz. Z. Für Hydrol. 31(2), 632–645 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02543692
Ferrari, A.C., Meyer, J.C., Scardaci, V., Casiraghi, C., Lazzeri, M., Mauri, F., Piscanec, S., Jiang, D., Novoselov, K.S., Roth, S., Geim, A.K.: Raman spectrum of graphene and graphene layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97(18), 1–4 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.187401
Film, C., Ago, H., Ito, Y., Mizuta, N., Yoshida, K., Hu, B., Orofeo, C.M.: Epitaxial chemical vapor deposition growth of single-layer graphene over. Acsnano 4(12), 7407–7414 (2010)
Guerrero-Fajardo, C.A., Giraldo, L., Moreno-Piraján, J.C.: Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide for Pb(II) and Zn(II) ions adsorption from aqueous solution: experimental, thermodynamic and kinetic study. Nanomaterials 10(6), (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061022
Hata, K., Futaba, D.N., Mizuno, K., Namai, T., Yumura, M., Iijima, S.: Water-assisted highly efficient synthesis of impurity-free single-walled carbon nanotubes. Science 306(5700), 1362–1364 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1104962
Hathcock, K.W., Brumfield, J.C., Goss, C.A., Irene, E.A., Murray, R.W.: Incipient electrochemical oxidation of highly oriented pyrolytic graphite: correlation between surface blistering and electrolyte anion intercalation. Anal. Chem. 67(13), 2201–2206 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00109a045
Hong, N., Yang, W., Bao, C., Jiang, S., Song, L., Hu, Y.: Facile synthesis of graphene by pyrolysis of poly(methyl methacrylate) on nickel particles in the confined microzones. Mater. Res. Bull. 47(12), 4082–4088 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.08.049
Hu, B., Ago, H., Ito, Y., Kawahara, K., Tsuji, M., Magome, E., Sumitani, K., Mizuta, N., Ikeda, K.I., Mizuno, S.: Epitaxial growth of large-area single-layer graphene over Cu(1 1 1)/sapphire by atmospheric pressure CVD. Carbon 50(1), 57–65 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2011.08.002
Huang, H., Chen, W., Chen, S., Thye, A., Wee, S.: Bottom-up growth of epitaxial. ACS Nano 2(12), 2513–2518 (2008)
Huang, L., Cui, X., Dukovic, G., O’Brien, S.P.: Self-organizing high-density single-walled carbon nanotube arrays from surfactant suspensions. Nanotechnology 15(11), 1450–1454 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/15/11/012
Huang, P.Y., Ruiz-Vargas, C.S., Van Der Zande, A.M., Whitney, W.S., Levendorf, M.P., Kevek, J.W., Garg, S., Alden, J.S., Hustedt, C.J., Zhu, Y., Park, J., McEuen, P.L., Muller, D.A.: Grains and grain boundaries in single-layer graphene atomic patchwork quilts. Nature 469(7330), 389–392 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09718
Hummers W.S., Offeman, R.E.: Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 208(1937), 1937 (1957). https://pubs.acs.org/sharingguidelines
Hwang, J., Kim, M., Campbell, D., Alsalman, H.A., Kwak, J.Y., Shivaraman, S., Woll, A.R., Singh, A.K., Hennig, R.G., Gorantla, S., Rümmeli, M.H., Spencer, M.G.: Van der waals epitaxial growth of graphene on sapphire by chemical vapor deposition without a metal catalyst. ACS Nano 7(1), 385–395 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn305486x
Jayasena, B., Subbiah, S.: A novel mechanical cleavage method for synthesizing few-layer graphenes. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6(1), 1–7 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-6-95
Jeong, H.K., Yun, P.L., Lahaye, R.J.W.E., Park, M.H., Kay, H.A., Ick, J.K., Yang, C.W., Chong, Y.P., Ruoff, R.S., Young, H.L.: Evidence of graphitic AB stacking order of graphite oxides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130(4), 1362–1366 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja076473o
Karmakar, S., Nawale, A.B., Lalla, N.P., Sathe, V.G., Kolekar, S.K., Mathe, V.L., Das, A.K., Bhoraskar, S.V.: Gas phase condensation of few-layer graphene with rotational stacking faults in an electric-arc. Carbon 55, 209–220 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2012.12.029
Kim, J., Ishihara, M., Koga, Y., Tsugawa, K., Hasegawa, M., Iijima, S.: Low-temperature synthesis of large-area graphene-based transparent conductive films using surface wave plasma chemical vapor deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98(9), 2011–2014 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3561747
Kim, K., Artyukhov, V.I., Regan, W., Liu, Y., Crommie, M.F., Yakobson, B.I., Zettl, A.: Rip** graphene: preferred directions. Nano Lett. 12(1), 293–297 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl203547z
Kim, K.S., Zhao, Y., Jang, H., Lee, S.Y., Kim, J.M., Kim, K.S., Ahn, J.H., Kim, P., Choi, J.Y., Hong, B.H.: Large-scale pattern growth of graphene films for stretchable transparent electrodes. Nature 457(7230), 706–710 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07719
Kim, N.S., Lee, Y.T., Park, J., Han, J.B., Choi, Y.S., Choi, S.Y., Choo, J., Lee, G.H.: Vertically aligned carbon nanotubes grown by pyrolysis of iron, cobalt, and nickel phthalocyanines. J. Phys. Chem. B 107(35), 9249–9255 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp034895o
Lambert, T.N., Luhrs, C.C., Chavez, C.A., Wakeland, S., Brumbach, M.T., Alam, T.M.: Graphite oxide as a precursor for the synthesis of disordered graphenes using the aerosol-through-plasma method. Carbon 48(14), 4081–4089 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2010.07.015
Li, D., Kaner, R.B.: Materials science: graphene-based materials. Science 320(5880), 1170–1171 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1158180
Li, N., Zhen, Z., Zhang, R., Xu, Z., Zheng, Z., He, L.: Nucleation and growth dynamics of graphene grown by radio frequency plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 1–10 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-85537-3
Li, N., Wang, Z., Zhao, K., Shi, Z., Gu, Z., Xu, S.: Large scale synthesis of N-doped multi-layered graphene sheets by simple arc-discharge method. Carbon 48(1), 255–259 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2009.09.013
Li, X., Cai, W., An, J., Kim, S., Nah, J., Piner, R., Velamakanni, A., Jung, I., Tutuc, E., Banerjee, S.K.: Large-area synthesis of high-quality and uniform graphene films on copper foils. Science 324(5932), 1312–1314 (2016)
Lotya, M., Hernandez, Y., King, P.J., Smith, R.J., Nicolosi, V., Karlsson, L.S., Blighe, F.M., De, S., Zhiming, W., McGovern, I.T., Duesberg, G.S., Coleman, J.N.: Liquid phase production of graphene by exfoliation of graphite in surfactant/water solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131(10), 3611–3620 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja807449u
Low, C.T.J., Walsh, F.C., Chakrabarti, M.H., Hashim, M.A., Hussain, M.A.: Electrochemical approaches to the production of graphene flakes and their potential applications. Carbon 54, 1–21 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2012.11.030
Lu, J., Yang, J., Wang, J., Lim, A., Wang, S., Loh, K.P.: One-pot synthesis of fluorescent carbon graphene by the exfoliation of graphite in ionic liquids. ACS Nano 3(8), 2367–2375 (2009)
Luo, B., Liu, H., Jiang, L., Jiang, L., Geng, D., Wu, B., Hu, W., Liu, Y., Yu, G.: Synthesis and morphology transformation of single-crystal graphene domains based on activated carbon dioxide by chemical vapor deposition. J. Mater. Chem. C 1(17), 2990–2995 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tc30124a
Lv, H., Pan, Q., Song, Y., Liu, X.X., Liu, T.: A review on nano-/microstructured materials constructed by electrochemical technologies for supercapacitors. Nano-Micro Lett. 12(1), (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-020-00451-z. (Springer Singapore)
Lv, W., Tang, D.M., He, Y.B., You, C.H., Shi, Z.Q., Chen, X.C., Chen, C.M., Hou, P.X., Liu, C., Yang, Q.H.: Low-temperature exfoliated graphenes: vacuum-promoted exfoliation and electrochemical energy storage. ACS Nano 3(11), 3730–3736 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn900933u
Mattevi, C., Kim, H., Chhowalla, M.: A review of chemical vapour deposition of graphene on copper. J. Mater. Chem. 21(10), 3324–3334 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/c0jm02126a
Merlen, A., Buijnsters, J.G., Pardanaud, C.: A guide to and review of the use of multiwavelength Raman spectroscopy for characterizing defective aromatic carbon solids: from graphene to amorphous carbons. Coatings 7(10), (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings7100153
Meyer, J.C., Geim, A.K., Katsnelson, M.I., Novoselov, K.S., Booth, T.J., Roth, S.: The structure of suspended graphene sheets. Nature 446(7131), 60–63 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05545
Meyer, J.C., Kisielowski, C., Erni, R., Rossell, M.D., Crommie, M.F., Zettl, A.: Direct imaging of lattice atoms and topological defects in graphene membranes. Nano Lett. 8(11), 3582–3586 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl801386m
Miller, J.R., Outlaw, R.A., Holloway, B.C.: Graphene double-layer capacitor with ac line-filtering performance. Science 329(5999), 1637–1639 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1194372
Ni, Z.H., Chen, W., Fan, X.F., Kuo, J.L., Yu, T., Wee, A.T.S., Shen, Z.X.: Raman spectroscopy of epitaxial graphene on a SiC substrate. Phys. Rev. B-Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 77(11), 1–6 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.77.115416
Ni, Z., Wang, Y., Yu, T., Shen, Z.: Raman spectroscopy and imaging of graphene. Nano Res. 1(4), 273–291 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-008-8036-1
Ortiz Balbuena, J., Tutor De Ureta, P., Rivera Ruiz, E., Mellor Pita, S.: Enfermedad de Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada. Med. Clin. 146(2), 93–94 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medcli.2015.04.005
Othman, M., Ritikos, R., Muhammad Hafiz, S., Khanis, N.H., Abdul Rashid, N.M., Abdul Rahman, S.: Low-temperature plasma-enhanced chemical vapour deposition of transfer-free graphene thin films. Mater. Lett. 158, 436–438 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.06.039
Panchakarla, L.S., Govindaraj, A., Rao, C.N.R.: Boron- and nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes and graphene. Inorg. Chim. Acta 363(15), 4163–4174 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2010.07.057
Qian, W., Liu, T., Wang, Z., Yu, H., Li, Z., Wei, F., Luo, G.: Effect of adding nickel to iron-alumina catalysts on the morphology of as-grown carbon nanotubes. Carbon 41(13), 2487–2493 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(03)00324-5
Qin, B., Zhang, T., Chen, H., Ma, Y.: The growth mechanism of few-layer graphene in the arc discharge process. Carbon 102, 494–498 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.02.074
Rasool, H.I., Song, E.B., Mecklenburg, M., Regan, B.C., Wang, K.L., Weiller, B.H., Gimzewski, J.K.: Atomic-scale characterization of graphene grown on copper (100) single crystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133(32), 12536–12543 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja200245p
Reina, A., Jia, X., Ho, J., Nezich, D., Son, H., Bulovic, V., Dresselhaus, M.S., Kong, J.: Large Area, Few-Layer Graphene Films on Arbitrary Substrates by Chemical Vapor Deposition, pp. 1–6 (2008)
Soldano, C., Mahmood, A., Dujardin, E.: Production, properties and potential of graphene. Carbon 48(8), 2127–2150 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2010.01.058
Stankovich, S., Dikin, D.A., Piner, R.D., Kohlhaas, K.A., Kleinhammes, A., Jia, Y., Wu, Y., Nguyen, S.B.T., Ruoff, R.S.: Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 45(7), 1558–1565 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2007.02.034
Su, Y., Zhang, Y.: Carbon nanomaterials synthesized by arc discharge hot plasma. Carbon 83(November), 90–99 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2014.11.023
Subrahmanyam, K.S., Panchakarla, L.S., Govindaraj, A., Rao, C.N.R.: Simple method of preparing graphene flakes by an arc-discharge method. J. Phys. Chem. C 113(11), 4257–4259 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp900791y
Tan, H., Wang, D., Guo, Y.: A strategy to synthesize multilayer graphene in arc-discharge plasma in a semi-opened environment. Materials 12(14), (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12142279
Tang, T., Chen, X., Meng, X., Chen, H., Ding, Y.: Synthesis of multiwalled carbon nanotubes by catalytic combustion of polypropylene. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 44(10), 1517–1520 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200461506
Teng, C., **e, D., Wang, J., Yang, Z., Ren, G., Zhu, Y.: Ultrahigh conductive graphene paper based on ball-milling exfoliated graphene. Adv. Funct. Mater. 27(20), (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201700240
Tontegode, A.Y.: Carbon on transition metal surfaces. Prog. Surf. Sci. 38(3–4), 201–429 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1016/0079-6816(91)90002-L
Tu, Z., Liu, Z., Li, Y., Yang, F., Zhang, L., Zhao, Z., Xu, C., Wu, S., Liu, H., Yang, H., Richard, P.: Controllable growth of 1–7 layers of graphene by chemical vapour deposition. Carbon 73, 252–258 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2014.02.061
Tung, V.C., Allen, M.J., Yang, Y., Kaner, R.B.: High-throughput solution processing of large-scale graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 4(1), 25–29 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.329
Viera Skakalova, A.B.K.: Graphene Properties, Preparation, Characterisation and Devices (2014)
Wang, G., Wang, B., Park, J., Wang, Y., Sun, B., Yao, J.: Highly efficient and large-scale synthesis of graphene by electrolytic exfoliation. Carbon 47(14), 3242–3246 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2009.07.040
Wang, J.J., Zhu, M.Y., Outlaw, R.A., Zhao, X., Manos, D.M., Holloway, B.C., Mammana, V.P.: Free-standing subnanometer qraphite sheets. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85(7), 1265–1267 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1782253
Wang, J., Manga, K.K., Bao, Q., Loh, K.P.: High-yield synthesis of few-layer graphene flakes through electrolyte. J. Am. Chem. Soc 133, 8888–8891 (2011)
Wang, Z., Li, N., Shi, Z., Gu, Z.: Low-cost and large-scale synthesis of graphene nanosheets by arc discharge in air. Nanotechnology 21(17), (2010). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/21/17/175602
Wintterlin, J., Bocquet, M.L.: Graphene on metal surfaces. Surf. Sci. 603(10–12), 1841–1852 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susc.2008.08.037
Wu, T., Ding, G., Shen, H., Wang, H., Sun, L., Jiang, D., **e, X., Jiang, M.: Triggering the continuous growth of graphene toward millimeter-sized grains. Adv. Func. Mater. 23(2), 198–203 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201201577
Wu, X., Liu, Y., Yang, H., Shi, Z.: Large-scale synthesis of high-quality graphene sheets by an improved alternating current arc-discharge method. RSC Adv. 6(95), 93119–93124 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra22273k
Wu, Y., Wang, B., Ma, Y., Huang, Y., Li, N., Zhang, F., Chen, Y.: Efficient and large-scale synthesis of few-layered graphene using an arc-discharge method and conductivity studies of the resulting films. Nano Res. 3(9), 661–669 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-010-0027-3
Xu, X., Zhang, Z., Qiu, L., Zhuang, J., Zhang, L., Wang, H., Liao, C., Song, H., Qiao, R., Gao, P., Hu, Z., Liao, L., Liao, Z., Yu, D., Wang, E., Ding, F., Peng, H., Liu, K.: Ultrafast growth of single-crystal graphene assisted by a continuous oxygen supply. Nat. Nanotechnol. 11(11), 930–935 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2016.132
Xu, Z., Li, H., Li, W., Cao, G., Zhang, Q., Li, K., Fu, Q., Wang, J.: Large-scale production of graphene by microwave synthesis and rapid cooling. Chem. Commun. 47(4), 1166–1168 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cc03520c
Yazdi, G.R., Vasiliauskas, R., Iakimov, T., Zakharov, A., Syväjärvi, M., Yakimova, R.: Growth of large area monolayer graphene on 3C-SiC and a comparison with other SiC polytypes. Carbon 57, 477–484 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.02.022
Yousef, S., Khattab, A., Osman, T.A., Zaki, M.: Effects of increasing electrodes on CNTs yield synthesized by using arc-discharge technique. J. Nanomater. 2013, (2013). https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/392126
Yu, Q., Jauregui, L.A., Wu, W., Colby, R., Tian, J., Su, Z., Cao, H., Liu, Z., Pandey, D., Wei, D., Chung, T.F., Peng, P., Guisinger, N.P., Stach, E.A., Bao, J., Pei, S.S., Chen, Y.P.: Control and characterization of individual grains and grain boundaries in graphene grown by chemical vapour deposition. Nat. Mater. 10(6), 443–449 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3010
Yuan, C., Hsin, Y., Jong, L.: Growth of large‑sized graphene thin‑films by liquid precursor‑based chemical vapor deposition under atmospheric pressure (2011)
Zhang, W., Cui, J., Tao, C., Wu, Y., Li, Z., Ma, L., Wen, Y., Li, G.: A strategy for producing pure single-layer graphene sheets based on a confined self-assembly approach. Angew. Chem. 121(32), 5978–5982 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.200902365
Zhu, M., Wang, J., Holloway, B.C., Outlaw, R.A., Zhao, X., Hou, K., Shutthanandan, V., Manos, D.M.: A mechanism for carbon nanosheet formation. Carbon 45(11), 2229–2234 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2007.06.017
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Yip, T.M., Tong, G.B. (2023). Fabrication Routes of Graphene. In: Subramaniam, R.T., Kasi, R., Bashir, S., Kumar, S.S.A. (eds) Graphene. Engineering Materials. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1206-3_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1206-3_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-1205-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-1206-3
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)