Abstract
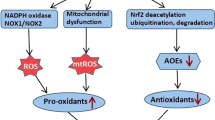
Respiratory viral infections remain the major cause of severe lower respiratory tract disease in both children and adults worldwide. Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family Pneumoviridae, which is responsible for acute lower respiratory tract infections (LRTI) in children and is a major cause of severe respiratory morbidity and mortality in the elderly and immunocompromised. These LRTI in young children are often characterized by wheezing and are defined as “bronchiolitis.” RSV bronchiolitis in infancy is strongly associated with the subsequent development of asthma and other forms of bronchial disease. Currently, there is no effective vaccine or specific therapy available for RSV infection, and natural immunity is inadequate, resulting in reinfections through adulthood. The high risk of recurrence and mortality rates of respiratory viral infections in young children and the elderly explains the importance for continuing efforts to understand the pathogenesis of respiratory virus-induced lung inflammation in order to design better therapeutic strategies. Lung epithelial cells are the major targets of RSV infection and play a central role in orchestrating the response to oxidative stress. Although the pathogenic mechanisms of RSV-induced acute airway disease and associated long-term consequences are still unclear, experimental evidence suggests that early inflammatory and immune events in the lung play a fundamental role in the outcome of the disease. Moreover, oxidative stress plays an important role in the pathogenesis of many inflammatory lung diseases including asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Studies have shown that the oxidative stress response in the airways, which results from an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and lung antioxidant defenses, plays a major role in the pathogenesis of RSV-associated lung inflammatory disease as RSV induces excess oxidant production and inhibits antioxidant enzymes expression. Studies have also demonstrated the role of ROS as important intracellular messengers of RSV-induced cellular signaling leading to the expression of key proinflammatory mediators, such as cytokines and chemokines. This chapter reviews the various mechanisms of RSV-induced oxidative stress and associated pathogenicity. Specifically, we will focus on recent studies demonstrating the role of ROS as important regulators of respiratory virus-induced cellular signaling and inflammatory responses induced as a result of RSV-induced oxidative stress.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 4-HNE:
-
4-hydrynonenal
- AECs:
-
airway epithelial cells
- AMs:
-
alveolar macrophages
- AOE:
-
antioxidant enzymes
- AP-1:
-
activator protein-1
- ARE:
-
antioxidant response element
- BHA:
-
butylated hydroxyanisole
- bZIP:
-
basic-leucine-zipper
- CF:
-
cystic fibrosis
- CNC:
-
cap-n-collar
- COPD:
-
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- DCFDA:
-
2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate
- DCs:
-
dendritic cells
- DHE:
-
dihydroethidium
- DNA:
-
deoxyribonucleic acid
- DUOX:
-
dual oxidase
- eNOS:
-
endothelial type nitric oxide synthase
- ERK 1/2:
-
extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2
- GPx:
-
glutathione peroxidase
- GSH:
-
reduced glutathione
- GSSG:
-
oxidized glutathione
- GST:
-
glutathione S-transferase
- H2O2:
-
hydrogen peroxide
- HIF:
-
hypoxia-inducible factor
- HIV:
-
human immunodeficiency virus
- HPLC:
-
high performance liquid chromatography
- IFN:
-
interferon
- IL:
-
interleukins
- iNOS:
-
inducible type nitric oxide synthase
- IRF:
-
interferon-regulatory factor
- Keap 1:
-
kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1
- LRTI:
-
lower respiratory tract infections
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- MDA-5:
-
melanoma differentiation antigen-5
- Mn:
-
manganese
- MSK1:
-
mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase 1
- MΦs:
-
macrophages
- N2O3:
-
dinitrogen trioxide
- N2O4:
-
dinitrogen tetroxide
- NADPH:
-
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor-kappa B
- nNOS:
-
neuronal type nitric oxide synthase
- NO.:
-
nitric oxide radical
- NO2-:
-
nitrite
- NO2:
-
nitrogen dioxide
- NO3:
-
nitrate
- NOS:
-
nitric oxide synthase
- NOX:
-
NADPH-oxidase
- NQO1:
-
NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase
- Nrfs:
-
nuclear factor (NF)-E2-related transcription factors
- O.2-:
-
superoxide ion radical
- OH.:
-
hydroxyl radical
- ONOO-:
-
peroxynitrite
- P13K:
-
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases
- pDCs:
-
plasmacytoid DCs
- PRR:
-
pattern recognition receptors
- RIG-I:
-
RNA helicases, retinoic acid-inducible gene-I
- RNA:
-
ribonucleic acid
- RNS:
-
reactive nitrogen species
- RO.:
-
alkoxyl radicals
- ROO.:
-
peroxyl
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- RSV:
-
respiratory syncytial virus
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutases
- STAT:
-
signal transducer and activator of transcription
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- TNFα:
-
tumor necrosis factor α
- XO:
-
xanthine oxidase
References
Chauhan AJ, Johnston SL (2003) Air pollution and infection in respiratory illness. Br Med Bull 68:95–112
Grissell TV, Powell H, Shafren DR, Boyle MJ, Hensley MJ, Jones PD, Whitehead BF, Gibson PG (2005) Interleukin-10 gene expression in acute virus-induced asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 172(4):433–439
Bezerra PG, Britto MC, Correia JB, Duarte MC, Fonceca AM, Rose K, Hopkins MJ, Cuevas LE, McNamara PS (2011) Viral and atypical bacterial detection in acute respiratory infection in children under five years. PLoS One 6(4):e18928. PMCID:PMC3078930
Hall CB (2001) Respiratory syncytial virus and parainfluenza virus. N Engl J Med 344(25):1917–1928
Afonso CL, Amarasinghe GK, Banyai K, Bao Y, Basler CF, Bavari S, Bejerman N, Blasdell KR, Briand FX, Briese T et al (2016) Taxonomy of the order Mononegavirales: update 2016. Arch Virol 161(8):2351–2360. PMCID:PMC4947412
Graham BS, Rutigliano JA, Johnson TR (2002) Respiratory syncytial virus immunobiology and pathogenesis. Virology 297(1):1–7
Hacking D, Hull J (2002) Respiratory syncytial virus–viral biology and the host response. J Infect 45(1):18–24
Blount RE Jr, Morris JA, Savage RE (1956) Recovery of cytopathogenic agent from chimpanzees with coryza. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 92(3):544–549
Shay DK, Holman RC, Newman RD, Liu LL, Stout JW, Anderson LJ (1999) Bronchiolitis-associated hospitalizations among US children, 1980–1996. JAMA 282(15):1440–1446
Ogra PL (2004) Respiratory syncytial virus: the virus, the disease and the immune response. Paediatr Respir Rev 5(Suppl A):S119–S126
Mufson MA, Belshe RB, Orvell C, Norrby E (1988) Respiratory syncytial virus epidemics: variable dominance of subgroups A and B strains among children, 1981–1986. J Infect Dis 157(1):143–148
Waris M (1991) Pattern of respiratory syncytial virus epidemics in Finland: two-year cycles with alternating prevalence of groups A and B. J Infect Dis 163(3):464–469
Gilca R, De SG, Tremblay M, Vachon ML, Leblanc E, Bergeron MG, Dery P, Boivin G (2006) Distribution and clinical impact of human respiratory syncytial virus genotypes in hospitalized children over 2 winter seasons. J Infect Dis 193(1):54–58
Falsey AR, Hennessey PA, Formica MA, Cox C, Walsh EE (2005) Respiratory syncytial virus infection in elderly and high-risk adults. N Engl J Med 352(17):1749–1759
Henrickson KJ, Hoover S, Kehl KS, Hua W (2004) National disease burden of respiratory viruses detected in children by polymerase chain reaction. Pediatr Infect Dis J 23(1 Suppl):S11–S18
Wohl ME, Chernick V (1978) State of the art: bronchiolitis. Am Rev Respir Dis 118(4):759–781
Sigurs N, Bjarnason R, Sigurbergsson F, Kjellman B (2000) Respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis in infancy is an important risk factor for asthma and allergy at age 7. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 161(5):1501–1507
Sigurs N, Bjarnason R, Sigurbergsson F, Kjellman B, Bjorksten B (1995) Asthma and immunoglobulin E antibodies after respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis: a prospective cohort study with matched controls. Pediatrics 95(4):500–505
Gardner PS, McQuillin J, Court SD (1970) Speculation on pathogenesis in death from respiratory syncytial virus infection. Br Med J 1(5692):327–330. PMCID:PMC1699011
Zheng S, De BP, Choudhary S, Comhair SA, Goggans T, Slee R, Williams BR, Pilewski J, Haque SJ, Erzurum SC (2003) Impaired innate host defense causes susceptibility to respiratory virus infections in cystic fibrosis. Immunity 18(5):619–630
Navas L, Wang E, de Carvalho V, Robinson J (1992) Improved outcome of respiratory syncytial virus infection in a high-risk hospitalized population of Canadian children. Pediatric investigators collaborative network on infections in Canada. J Pediatr 121(3):348–354
MacDonald NE, Hall CB, Suffin SC, Alexson C, Harris PJ, Manning JA (1982) Respiratory syncytial viral infection in infants with congenital heart disease. N Engl J Med 307(7):397–400
Buckingham SC, Quasney MW, Bush AJ, DeVincenzo JP (2001) Respiratory syncytial virus infections in the pediatric intensive care unit: clinical characteristics and risk factors for adverse outcomes. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2(4):318–323
Feltes TF, Cabalka AK, Meissner HC, Piazza FM, Carlin DA, Top FH Jr, Connor EM, Sondheimer HM (2003) Palivizumab prophylaxis reduces hospitalization due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children with hemodynamically significant congenital heart disease. J Pediatr 143(4):532–540
Bogomolov BP (1990) Respiratory infections as a risk factor for patients with ischemic heart disease. Klin Med (Mosk) 68(7):35–39
Falsey AR, Walsh EE (2000) Respiratory syncytial virus infection in adults. Clin Microbiol Rev 13(3):371–384. PMCID:PMC88938
Welliver RC (2010) Pharmacotherapy of respiratory syncytial virus infection. Curr Opin Pharmacol 10(3):289–293
Crotty S, Andino R (2002) Implications of high RNA virus mutation rates: lethal mutagenesis and the antiviral drug ribavirin. Microbes Infect 4(13):1301–1307
Zhu Q, Patel NK, McAuliffe JM, Zhu W, Wachter L, McCarthy MP, Suzich JA (2012) Natural polymorphisms and resistance-associated mutations in the fusion protein of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV): effects on RSV susceptibility to palivizumab. J Infect Dis 205(4):635–638
Feltes TF, Sondheimer HM, Tulloh RM, Harris BS, Jensen KM, Losonsky GA, Griffin MP (2011) A randomized controlled trial of motavizumab versus palivizumab for the prophylaxis of serious respiratory syncytial virus disease in children with hemodynamically significant congenital heart disease. Pediatr Res 70(2):186–191
Prince GA (2001) An update on respiratory syncytial virus antiviral agents. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 10(2):297–308
Peebles RS Jr, Moore ML (2007) A mechanistic advance in understanding RSV pathogenesis, but still a long way from therapy. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 37(4):375–377
Blanco JC, Boukhvalova MS, Hemming P, Ottolini MG, Prince GA (2005) Prospects of antiviral and anti-inflammatory therapy for respiratory syncytial virus infection. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 3(6):945–955
Kim HW, Canchola JG, Brandt CD, Pyles G, Chanock RM, Jensen K, Parrott RH (1969) Respiratory syncytial virus disease in infants despite prior administration of antigenic inactivated vaccine. Am J Epidemiol 89(4):422–434
Garofalo RP, Haeberle H (2000) Epithelial regulation of innate immunity to respiratory syncytial virus. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 23(5):581–585
Kato H, Takeuchi O, Sato S, Yoneyama M, Yamamoto M, Matsui K, Uematsu S, Jung A, Kawai T, Ishii KJ et al (2006) Differential roles of MDA5 and RIG-I helicases in the recognition of RNA viruses. Nature 441(7089):101–105
Pichlmair A, Schulz O, Tan CP, Naslund TI, Liljestrom P, Weber F (2006) Reis e Sousa. RIG-I-mediated antiviral responses to single-stranded RNA bearing 5’-phosphates. Science 314(5801):997–1001
Bacon KB, Schall TJ (1996) Chemokines as mediators of allergic inflammation. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 109(2):97–109
Graham BS, Johnson TR, Peebles RS (2000) Immune-mediated disease pathogenesis in respiratory syncytial virus infection. Immunopharmacology 48(3):237–247
Zhang Y, Luxon BA, Casola A, Garofalo RP, Jamaluddin M, Brasier AR (2001) Expression of respiratory syncytial virus-induced chemokine gene networks in lower airway epithelial cells revealed by cDNA microarrays. J Virol 75(19):9044–9058. PMCID:PMC114473
Haeberle HA, Kuziel WA, Dieterich HJ, Casola A, Gatalica Z, Garofalo RP (2001) Inducible expression of inflammatory chemokines in respiratory syncytial virus-infected mice: role of MIP-1alpha in lung pathology. J Virol 75(2):878–890. PMCID:PMC113984
Garofalo RP, Goldman AS (1999) Expression of functional immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory factors in human milk. Clin Perinatol 26(2):361–377
Garofalo R, Kimpen JL, Welliver RC, Ogra PL (1992) Eosinophil degranulation in the respiratory tract during naturally acquired respiratory syncytial virus infection. J Pediatr 120(1):28–32
Casola A, Burger N, Liu T, Jamaluddin M, Brasier AR, Garofalo RP (2001) Oxidant tone regulates RANTES gene expression in airway epithelial cells infected with respiratory syncytial virus. Role in viral-induced interferon regulatory factor activation. J Biol Chem 276(23):19715–19722
Liu T, Castro S, Brasier AR, Jamaluddin M, Garofalo RP, Casola A (2004) Reactive oxygen species mediate virus-induced STAT activation: role of tyrosine phosphatases. J Biol Chem 279(4):2461–2469
Hosakote YM, Komaravelli N, Mautemps N, Liu T, Garofalo RP, Casola A (2012) Antioxidant mimetics modulate oxidative stress and cellular signaling in airway epithelial cells infected with respiratory syncytial virus. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 303(11):L991–L1000. PMCID:PMC3532525
Hosakote YM, Liu T, Castro SM, Garofalo RP, Casola A (2009) Respiratory syncytial virus induces oxidative stress by modulating antioxidant enzymes. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 41(3):348–357. PMCID:PMC2742754
Hosakote YM, Jantzi PD, Esham DL, Spratt H, Kurosky A, Casola A, Garofalo RP (2011) Viral-mediated inhibition of antioxidant enzymes contributes to the pathogenesis of severe respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 183(11):1550–1560. PMCID:PMC3137144
Harrison AM, Bonville CA, Rosenberg HF, Domachowske JB (1999) Respiratory syncytical virus-induced chemokine expression in the lower airways: eosinophil recruitment and degranulation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 159(6):1918–1924
Garofalo RP, Patti J, Hintz KA, Hill V, Ogra PL, Welliver RC (2001) Macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha (not T helper type 2 cytokines) is associated with severe forms of respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. J Infect Dis 184(4):393–399
Sakai A, Han J, Cato AC, Akira S, Li JD (2004) Glucocorticoids synergize with IL-1beta to induce TLR2 expression via MAP Kinase Phosphatase-1-dependent dual Inhibition of MAPK JNK and p38 in epithelial cells. BMC Mol Biol 5:2. PMCID:PMC419700
Homma T, Kato A, Hashimoto N, Batchelor J, Yoshikawa M, Imai S, Wakiguchi H, Saito H, Matsumoto K (2004) Corticosteroid and cytokines synergistically enhance toll-like receptor 2 expression in respiratory epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 31(4):463–469
Shuto T, Imasato A, Jono H, Sakai A, Xu H, Watanabe T, Rixter DD, Kai H, Andalibi A, Linthicum F et al (2002) Glucocorticoids synergistically enhance nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae-induced Toll-like receptor 2 expression via a negative cross-talk with p38 MAP kinase. J Biol Chem 277(19):17263–17270
Olszewska-Pazdrak B, Casola A, Saito T, Alam R, Crowe SE, Mei F, Ogra PL, Garofalo RP (1998) Cell-specific expression of RANTES, MCP-1, and MIP-1alpha by lower airway epithelial cells and eosinophils infected with respiratory syncytial virus. J Virol 72(6):4756–4764. PMCID:PMC110009
Kimpen JL (2001) Respiratory syncytial virus and asthma. The role of monocytes. Am. J Respir Crit Care Med 163(3 Pt 2):S7–S9
Zaslona Z, Wilhelm J, Cakarova L, Marsh LM, Seeger W, Lohmeyer J, von Wulffen W (2009) Transcriptome profiling of primary murine monocytes, lung macrophages and lung dendritic cells reveals a distinct expression of genes involved in cell trafficking. Respir Res 10:2. PMCID:PMC2639356
Rodero MP, Poupel L, Loyher PL, Hamon P, Licata F, Pessel C, Hume DA, Combadiere C, Boissonnas A (2015) Immune surveillance of the lung by migrating tissue monocytes. Elife 4:e07847. PMCID:PMC4521583
Gordon SB, Read RC (2002) Macrophage defences against respiratory tract infections. Br Med Bull 61:45–61
Becker S, Quay J, Soukup J (1991) Cytokine (tumor necrosis factor, IL-6, and IL-8) production by respiratory syncytial virus-infected human alveolar macrophages. J Immunol 147(12):4307
Stockwin LH, McGonagle D, Martin IG, Blair GE (2000) Dendritic cells: immunological sentinels with a central role in health and disease. Immunol Cell Biol 78(2):91–102
Weng K, Zhang J, Mei X, Wu A, Zhang B, Cai M, Zheng Y, Ke Z (2014) Lower number of plasmacytoid dendritic cells in peripheral blood of children with bronchiolitis following respiratory syncytial virus infection. Influenza Other Respir Virus 8(4):469–473. PMCID:PMC4181807
Qureshi MH, Durre K, Yang W (2007) Skewed polarization of pulmonary dendritic cells in RSV-infection and susceptibility to asthma (39.2). J Immunol 178 (1 Supplement):S25
Guerrero-Plata A, Baron S, Poast JS, Adegboyega PA, Casola A, Garofalo RP (2005) Activity and regulation of alpha interferon in respiratory syncytial virus and human metapneumovirus experimental infections. J Virol 79(16):10190–10199. PMCID:PMC1182647
Chung HL, Kim SG (2002) RANTES may be predictive of later recurrent wheezing after respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis in infants. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 88(5):463–467
Smyth RL, Fletcher JN, Thomas HM, Hart CA (1997) Immunological responses to respiratory syncytial virus infection in infancy. Arch Dis Child 76(3):210–214. PMCID:PMC1717100
Bermejo-Martin JF, Garcia-Arevalo MC, Alonso A, De Lejarazu RO, Pino M, Resino S, Tenorio A, Bernardo D, Leon AJ, Garrote JA et al (2007) Persistence of proinflammatory response after severe respiratory syncytial virus disease in children. J Allergy Clin Immunol 119(6):1547–1550
Phipps S, Lam CE, Mahalingam S, Newhouse M, Ramirez R, Rosenberg HF, Foster PS, Matthaei KI (2007) Eosinophils contribute to innate antiviral immunity and promote clearance of respiratory syncytial virus. Blood 110(5):1578–1586
Smith PK, Wang SZ, Dowling KD, Forsyth KD (2001) Leucocyte populations in respiratory syncytial virus-induced bronchiolitis. J Paediatr Child Health 37(2):146–151
O’Donnell DR, Carrington D (2002) Peripheral blood lymphopenia and neutrophilia in children with severe respiratory syncytial virus disease. Pediatr Pulmonol 34(2):128–130
Welliver TP, Garofalo RP, Hosakote Y, Hintz KH, Avendano L, Sanchez K, Velozo L, Jafri H, Chavez-Bueno S, Ogra PL et al (2007) Severe human lower respiratory tract illness caused by respiratory syncytial virus and influenza virus is characterized by the absence of pulmonary cytotoxic lymphocyte responses. J Infect Dis 195(8):1126–1136
Heidema J, Lukens MV, van Maren WW, van Dijk ME, Otten HG, van Vught AJ, van der Werff DB, van Gestel SJ, Semple MG, Smyth RL et al (2007) CD8+ T cell responses in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of infants with severe primary respiratory syncytial virus infections. J Immunol 179(12):8410–8417
Emboriadou M, Hatzistilianou M, Magnisali C, Sakelaropoulou A, Exintari M, Conti P, Aivazis V (2007) Human neutrophil elastase in RSV bronchiolitis. Ann Clin Lab Sci 37(1):79–84
Abu-Harb M, Bell F, Finn A, Rao WH, Nixon L, Shale D, Everard ML (1999) IL-8 and neutrophil elastase levels in the respiratory tract of infants with RSV bronchiolitis. Eur Respir J 14(1):139–143
Lukens MV, van de Pol AC, Coenjaerts FE, Jansen NJ, Kamp VM, Kimpen JL, Rossen JW, Ulfman LH, Tacke CE, Viveen MC, et al (2010) A systemic neutrophil response precedes robust CD8(+) T-cell activation during natural respiratory syncytial virus infection in infants. J Virol 84(5):2374–2383. PMCID:PMC2820924
De WW, Twilhaar WN, Kimpen JL (1998) T cell subset analysis in peripheral blood of children with RSV bronchiolitis. Scand J Infect Dis 30(1):77–80
Roman M, Calhoun WJ, Hinton KL, Avendano LF, Simon V, Escobar AM, Gaggero A, Diaz PV (1997) Respiratory syncytial virus infection in infants is associated with predominant Th-2-like response. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156(1):190–195
Aberle JH, Aberle SW, Dworzak MN, Mandl CW, Rebhandl W, Vollnhofer G, Kundi M, Popow-Kraupp T (1999) Reduced interferon-gamma expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of infants with severe respiratory syncytial virus disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 160(4):1263–1268
Pinto RA, Arredondo SM, Bono MR, Gaggero AA, Diaz PV (2006) T helper 1/T helper 2 cytokine imbalance in respiratory syncytial virus infection is associated with increased endogenous plasma cortisol. Pediatrics 117(5):e878–e886
de Waal L, Koopman LP, van Benten IJ, Brandenburg AH, Mulder PG, de Swart RL, Fokkens WJ, Neijens HJ, Osterhaus AD (2003) Moderate local and systemic respiratory syncytial virus-specific T-cell responses upon mild or subclinical RSV infection. J Med Virol 70(2):309–318
Reed JL, Welliver TP, Sims GP, McKinney L, Velozo L, Avendano L, Hintz K, Luma J, Coyle AJ, Welliver RC Sr (2009) Innate immune signals modulate antiviral and polyreactive antibody responses during severe respiratory syncytial virus infection. J Infect Dis 199(8):1128–1138
Raes M, Peeters V, Alliet P, Gillis P, Kortleven J, Magerman K, Rummens JL (1997) Peripheral blood T and B lymphocyte subpopulations in infants with acute respiratory syncytial virus brochiolitis. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 8(2):97–102
Larranaga CL, Ampuero SL, Luchsinger VF, Carrion FA, Aguilar NV, Morales PR, Palomino MA, Tapia LF, Avendano LF (2009) Impaired immune response in severe human lower tract respiratory infection by respiratory syncytial virus. Pediatr Infect Dis J 28(10):867–873
Noyola DE, Juarez-Vega G, Monjaras-Avila C, Escalante-Padron F, Rangel-Ramirez V, Cadena-Mota S, Monsivais-Urenda A, Garcia-Sepulveda CA, Gonzalez-Amaro R (2015) NK cell immunophenotypic and genotypic analysis of infants with severe respiratory syncytial virus infection. Microbiol Immunol 59(7):389–397
Persson BD, Jaffe AB, Fearns R, Danahay H (2014) Respiratory syncytial virus can infect basal cells and alter human airway epithelial differentiation. PLoS One 9(7):e102368. PMCID:PMC4102526
Aruoma OI, Halliwell B, Hoey BM, Butler J (1989) The antioxidant action of N-acetylcysteine: its reaction with hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical, superoxide, and hypochlorous acid. Free Radic Biol Med 6(6):593–597
Gutteridge JM, Halliwell B (1992) Comments on review of free radicals in biology and medicine, second edition, by Barry Halliwell and John M. C Gutteridge. Free Radic Biol Med 12(1):93–95
Haddad JJ (2002) Antioxidant and prooxidant mechanisms in the regulation of redox(y)-sensitive transcription factors. Cell Signal 14(11):879–897
Rahman I (2002) Oxidative stress, transcription factors and chromatin remodelling in lung inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol 64(5-6):935–942
Kohen R, Nyska A (2002) Oxidation of biological systems: oxidative stress phenomena, antioxidants, redox reactions, and methods for their quantification. Toxicol Pathol 30(6):620–650
Droge W (2002) Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiol Rev 82(1):47–95
Inoue M, Sato EF, Nishikawa M, Park AM, Kira Y, Imada I, Utsumi K (2003) Mitochondrial generation of reactive oxygen species and its role in aerobic life. Curr Med Chem 10(23):2495–2505
Akaike T, Ando M, Oda T, Doi T, Ijiri S, Araki S, Maeda H (1990) Dependence on O2- generation by xanthine oxidase of pathogenesis of influenza virus infection in mice. J Clin Invest 85(3):739–745. PMCID:PMC296490
Akaike T, Noguchi Y, Ijiri S, Setoguchi K, Suga M, Zheng YM, Dietzschold B, Maeda H (1996) Pathogenesis of influenza virus-induced pneumonia: involvement of both nitric oxide and oxygen radicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(6):2448–2453. PMCID:PMC39817
Knobil K, Choi AM, Weigand GW, Jacoby DB (1998) Role of oxidants in influenza virus-induced gene expression. Am J Physiol 274(1 Pt 1):L134–L142
Biagioli MC, Kaul P, Singh I, Turner RB (1999) The role of oxidative stress in rhinovirus induced elaboration of IL-8 by respiratory epithelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med 26(3–4):454–462
Schwarz KB (1996) Oxidative stress during viral infection: a review. Free Radic Biol Med 21(5):641–649
Hayes JD, McMahon M (2001) Molecular basis for the contribution of the antioxidant responsive element to cancer chemoprevention. Cancer Lett 174(2):103–113
Allen RG, Tresini M (2000) Oxidative stress and gene regulation. Free Radic Biol Med 28(3):463–499
Gabbita SP, Robinson KA, Stewart CA, Floyd RA, Hensley K (2000) Redox regulatory mechanisms of cellular signal transduction. Arch Biochem Biophys 376(1):1–13
Cash TP, Pan Y, Simon MC (2007) Reactive oxygen species and cellular oxygen sensing. Free Radic Biol Med 43(9):1219–1225. PMCID:PMC2696222
Grandvaux N, Mariani M, Fink K (2015) Lung epithelial NOX/DUOX and respiratory virus infections. Clin Sci (Lond) 128(6):337–347
Hou YC, Janczuk A, Wang PG (1999) Current trends in the development of nitric oxide donors. Curr Pharm Des 5(6):417–441
Cantley LC (2002) The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 296(5573):1655–1657
Park HS, Huh SH, Kim MS, Kim DY, Gwag BJ, Cho SG, Choi EJ (2006) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) modulates the JNK1 activity through redox mechanism: a cGMP independent pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 346(2):408–414
West AP, Shadel GS, Ghosh S (2011) Mitochondria in innate immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol 11(6):389–402. PMCID:PMC4281487
Kaminski MM, Roth D, Krammer PH, Gulow K (2013) Mitochondria as oxidative signaling organelles in T-cell activation: physiological role and pathological implications. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 61(5):367–384
Mittal M, Siddiqui MR, Tran K, Reddy SP, Malik AB (2014) Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxid Redox Signal 20(7):1126–1167. PMCID:PMC3929010
Laniewski NG, Grayson JM (2004) Antioxidant treatment reduces expansion and contraction of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells during primary but not secondary viral infection. J Virol 78(20):11246–11257. PMCID:PMC521823
Sena LA, Li S, Jairaman A, Prakriya M, Ezponda T, Hildeman DA, Wang CR, Schumacker PT, Licht JD, Perlman H, et al (2013) Mitochondria are required for antigen-specific T cell activation through reactive oxygen species signaling. Immunity 38(2):225–236. PMCID:PMC3582741
Kaminski MM, Sauer SW, Klemke CD, Suss D, Okun JG, Krammer PH, Gulow K (2010) Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species control T cell activation by regulating IL-2 and IL-4 expression: mechanism of ciprofloxacin-mediated immunosuppression. J Immunol 184(9):4827–4841
Yang CS, Kim JJ, Lee SJ, Hwang JH, Lee CH, Lee MS, Jo EK (2013) TLR3-triggered reactive oxygen species contribute to inflammatory responses by activating signal transducer and activator of transcription-1. J Immunol 190(12):6368–6377
Asehnoune K, Strassheim D, Mitra S, Kim JY, Abraham E (2004) Involvement of reactive oxygen species in Toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of NF-kappa B. J Immunol 172(4):2522–2529
Jamaluddin M, Wang S, Boldogh I, Tian B, Brasier AR (2007) TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB/RelA Ser(276) phosphorylation and enhanceosome formation is mediated by an ROS-dependent PKAc pathway. Cell Signal 19(7):1419–1433
Brasier AR, Tian B, Jamaluddin M, Kalita MK, Garofalo RP, Lu M (2011) RelA Ser276 phosphorylation-coupled Lys310 acetylation controls transcriptional elongation of inflammatory cytokines in respiratory syncytial virus infection. J Virol 85(22):11752–1169. PMCID:PMC3209292
Jamaluddin M, Tian B, Boldogh I, Garofalo RP, Brasier AR (2009) Respiratory syncytial virus infection induces a reactive oxygen species-MSK1-phospho-Ser-276 RelA pathway required for cytokine expression. J Virol 83(20):10605–10615. PMCID:PMC2753134
Kong X, Thimmulappa R, Craciun F, Harvey C, Singh A, Kombairaju P, Reddy SP, Remick D, Biswal S (2011) Enhancing Nrf2 pathway by disruption of Keap1 in myeloid leukocytes protects against sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 184(8):928–938. PMCID:PMC3208662
Mastronarde JG, Monick MM, Hunninghake GW (1995) Oxidant tone regulates IL-8 production in epithelium infected with respiratory syncytial virus. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 13(2):237–244
Mastronarde JG, Monick MM, Mukaida N, Matsushima K, Hunninghake GW (1998) Activator protein-1 is the preferred transcription factor for cooperative interaction with nuclear factor-kappaB in respiratory syncytial virus-induced interleukin-8 gene expression in airway epithelium. J Infect Dis 177(5):1275–1281
Kabe Y, Ando K, Hirao S, Yoshida M, Handa H (2005) Redox regulation of NF-kappaB activation: distinct redox regulation between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Antioxid Redox Signal 7(3-4):395–403
Trachootham D, Alexandre J, Huang P (2009) Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: a radical therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov 8(7):579–591
Paravicini TM, Touyz RM (2006) Redox signaling in hypertension. Cardiovasc Res 71(2):247–258
Haigis MC, Yankner BA (2010) The aging stress response. Mol Cell 40(2):333–344. PMCID:PMC2987618
Macnee W (2001) Oxidative stress and lung inflammation in airways disease. Eur J Pharmacol 429(1–3):195–207
van Eeden SF, Sin DD (2013) Oxidative stress in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a lung and systemic process. Can Respir J 20(1):27–29. PMCID:PMC3628643
Droge W (2002) Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiol Rev 82(1):47–95
Sahiner UM, Birben E, Erzurum S, Sackesen C, Kalayci O (2011) Oxidative stress in asthma. World Allergy Organ J 4(10):151–158. PMCID:PMC3488912
Rahman I, Morrison D, Donaldson K, Macnee W (1996) Systemic oxidative stress in asthma, COPD, and smokers. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 154(4 Pt 1):1055–1060
Tarpey MM, Wink DA, Grisham MB (2004) Methods for detection of reactive metabolites of oxygen and nitrogen: in vitro and in vivo considerations. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 286(3):R431–R444
Putnam CD, Arvai AS, Bourne Y, Tainer JA (2000) Active and inhibited human catalase structures: ligand and NADPH binding and catalytic mechanism. J Mol Biol 296(1):295–309
Avissar N, Finkelstein JN, Horowitz S, Willey JC, Coy E, Frampton MW, Watkins RH, Khullar P, Xu YL, Cohen HJ (1996) Extracellular glutathione peroxidase in human lung epithelial lining fluid and in lung cells. Am J Physiol 270(2 Pt 1):L173–L182
Finkel T, Holbrook NJ (2000) Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 408(6809):239–247
Babior BM (1999) NADPH oxidase: an update. Blood 93(5):1464–1476
Laurindo FR, Araujo TL, Abrahao TB (2014) Nox NADPH oxidases and the endoplasmic reticulum. Antioxid Redox Signal 20(17):2755–2775. PMCID:PMC4026305
Brandes RP, Weissmann N, Schroder K (2014) Nox family NADPH oxidases: molecular mechanisms of activation. Free Radic Biol Med 76:208–226
Jaiswal AK (2004) Nrf2 signaling in coordinated activation of antioxidant gene expression. Free Radic Biol Med 36(10):1199–1207
Sankaranarayanan K, Jaiswal AK (2004) Nrf3 negatively regulates antioxidant-response element-mediated expression and antioxidant induction of NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase1 gene. J Biol Chem 279(49):50810–50817
Dhakshinamoorthy S, Jain AK, Bloom DA, Jaiswal AK (2005) Bach1 competes with Nrf2 leading to negative regulation of the antioxidant response element (ARE)-mediated NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 gene expression and induction in response to antioxidants. J Biol Chem 280(17):16891–16900
Jones DP (2002) Redox potential of GSH/GSSG couple: assay and biological significance. Methods Enzymol 348:93–112
Camera E, Picardo M (2002) Analytical methods to investigate glutathione and related compounds in biological and pathological processes. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 781(1–2):181–206
Baker MA, Cerniglia GJ, Zaman A (1990) Microtiter plate assay for the measurement of glutathione and glutathione disulfide in large numbers of biological samples. Anal Biochem 190(2):360–365
Briviba K, Fraser G, Sies H, Ketterer B (1993) Distribution of the monochlorobimane-glutathione conjugate between nucleus and cytosol in isolated hepatocytes. Biochem J 294(Pt 3):631–633. PMCID:PMC1134507
Hedley DW (1993) Flow cytometric assays of anticancer drug resistance. Ann NY Acad Sci 677:341–353
Pryor WA, Stanley JP, Blair E (1976) Autoxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids: II. A suggested mechanism for the formation of TBA-reactive materials from prostaglandin-like endoperoxides. Lipids 11(5):370–379
Beretta G, Aldini G, Facino RM, Russell RM, Krinsky NI, Yeum KJ (2006) Total antioxidant performance: a validated fluorescence assay for the measurement of plasma oxidizability. Anal Biochem 354(2):290–298
Pap EH, Drummen GP, Post JA, Rijken PJ, Wirtz KW (2000) Fluorescent fatty acid to monitor reactive oxygen in single cells. Methods Enzymol 319:603–612
Pap EH, Drummen GP, Winter VJ, Kooij TW, Rijken P, Wirtz KW (1999) Op den Kamp JA, Hage WJ, Post JA. Ratio-fluorescence microscopy of lipid oxidation in living cells using C11-BODIPY(581/591). FEBS Lett 453(3):278–282
Morrow JD, Hill KE, Burk RF, Nammour TM, Badr KF, Roberts LJ (1990) A series of prostaglandin F2-like compounds are produced in vivo in humans by a non-cyclooxygenase, free radical-catalyzed mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87(23):9383–9387. PMCID:PMC55169
Drummen GP, Gadella BM, Post JA, Brouwers JF (2004) Mass spectrometric characterization of the oxidation of the fluorescent lipid peroxidation reporter molecule C11-BODIPY(581/591). Free Radic Biol Med 36(12):1635–1644
McCord JM, Fridovich I (1968) The reduction of cytochrome c by milk xanthine oxidase. J Biol Chem 243(21):5753–5760
Tarpey MM, White CR, Suarez E, Richardson G, Radi R, Freeman BA (1999) Chemiluminescent detection of oxidants in vascular tissue. Lucigenin but not coelenterazine enhances superoxide formation. Circ Res 84(10):1203–1211
Tarpey MM, Fridovich I (2001) Methods of detection of vascular reactive species: nitric oxide, superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and peroxynitrite. Circ Res 89(3):224–236
Kundu K, Knight SF, Willett N, Lee S, Taylor WR, Murthy N (2009) Hydrocyanines: a class of fluorescent sensors that can image reactive oxygen species in cell culture, tissue, and in vivo. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 48(2):299–303. PMCID:PMC5935505
Zielonka J, Vasquez-Vivar J, Kalyanaraman B (2008) Detection of 2-hydroxyethidium in cellular systems: a unique marker product of superoxide and hydroethidine. Nat Protoc 3(1):8–21
Pourahmad J, Mortada Y, Eskandari MR, Shahraki J (2011) Involvement of lysosomal labilisation and lysosomal/mitochondrial cross-talk in diclofenac induced hepatotoxicity. Iran J Pharm Res 10(4):877–887. PMCID:PMC3813083
Ruch W, Cooper PH, Baggiolini M (1983) Assay of H2O2 production by macrophages and neutrophils with homovanillic acid and horse-radish peroxidase. J Immunol Methods 63(3):347–357
Hinkle PC, Butow RA, Racker E, Chance B (1967) Partial resolution of the enzymes catalyzing oxidative phosphorylation. XV. Reverse electron transfer in the flavin-cytochrome beta region of the respiratory chain of beef heart submitochondrial particles. J Biol Chem 242(22):5169–5173
Zhou M, Diwu Z, Panchuk-Voloshina N, Haugland RP (1997) A stable nonfluorescent derivative of resorufin for the fluorometric determination of trace hydrogen peroxide: applications in detecting the activity of phagocyte NADPH oxidase and other oxidases. Anal Biochem 253(2):162–168
Reszka KJ, Wagner BA, Burns CP, Britigan BE (2005) Effects of peroxidase substrates on the Amplex red/peroxidase assay: antioxidant properties of anthracyclines. Anal Biochem 342(2):327–337
Uggeri J, Gatti R, Belletti S, Scandroglio R, Corradini R, Rotoli BM, Orlandini G (2004) Calcein-AM is a detector of intracellular oxidative activity. Histochem Cell Biol 122(5):499–505
Nathan C (1992) Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. FASEB J 6(12):3051–3064
Misko TP, Schilling RJ, Salvemini D, Moore WM, Currie MG (1993) A fluorometric assay for the measurement of nitrite in biological samples. Anal Biochem 214(1):11–16
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126(1):131–138
Schwarzlander M, Fricker MD, Muller C, Marty L, Brach T, Novak J, Sweetlove LJ, Hell R, Meyer AJ (2008) Confocal imaging of glutathione redox potential in living plant cells. J Microsc 231(2):299–316
Meyer AJ, Brach T, Marty L, Kreye S, Rouhier N, Jacquot JP, Hell R (2007) Redox-sensitive GFP in Arabidopsis thaliana is a quantitative biosensor for the redox potential of the cellular glutathione redox buffer. Plant J 52(5):973–986
Gutscher M, Pauleau AL, Marty L, Brach T, Wabnitz GH, Samstag Y, Meyer AJ, Dick TP (2008) Real-time imaging of the intracellular glutathione redox potential. Nat Method 5(6):553–559
Hanson GT, Aggeler R, Oglesbee D, Cannon M, Capaldi RA, Tsien RY, Remington SJ (2004) Investigating mitochondrial redox potential with redox-sensitive green fluorescent protein indicators. J Biol Chem 279(13):13044–13053
Bauer M, Grabsch C, Schlink U, Klopp N, Illig T, Kramer U, von BA, Schaaf B, Borte M, Heinrich J et al (2012) Genetic association between obstructive bronchitis and enzymes of oxidative stress. Metabolism 61(12):1771–1779
Griese M, Ramakers J, Krasselt A, Starosta V, Van KS, Fischer R, Ratjen F, Mullinger B, Huber RM, Maier K et al (2004) Improvement of alveolar glutathione and lung function but not oxidative state in cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 169(7):822–828
Chow CW, Herrera Abreu MT, Suzuki T, Downey GP (2003) Oxidative stress and acute lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 29(4):427–431
Azad N, Rojanasakul Y, Vallyathan V. Inflammation and lung cancer: roles of reactive oxygen/nitrogen species. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev 2008;11(1):1-15
Emmendoerffer A, Hecht M, Boeker T, Mueller M, Heinrich U (2000) Role of inflammation in chemical-induced lung cancer. Toxicol Lett 112–113:185–191
Henricks PA, Nijkamp FP (2001) Reactive oxygen species as mediators in asthma. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 14(6):409–420
Morcillo EJ, Estrela J, Cortijo J (1999) Oxidative stress and pulmonary inflammation: pharmacological intervention with antioxidants. Pharmacol Res 40(5):393–404
Dworski R (2000) Oxidant stress in asthma. Thorax 55(Suppl 2):S51–S53. PMCID:PMC1765968
Rahman I, Adcock IM (2006) Oxidative stress and redox regulation of lung inflammation in COPD. Eur Respir J 28(1):219–242
Pinamonti S, Muzzoli M, Chicca MC, Papi A, Ravenna F, Fabbri LM, Ciaccia A (1996) Xanthine oxidase activity in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Free Radic Biol Med 21(2):147–155
Heunks LM, Vina J, van Herwaarden CL, Folgering HT, Gimeno A, Dekhuijzen PN (1999) Xanthine oxidase is involved in exercise-induced oxidative stress in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Physiol 277(6):R1697–R1704
Pinamonti S, Leis M, Barbieri A, Leoni D, Muzzoli M, Sostero S, Chicca MC, Carrieri A, Ravenna F, Fabbri LM et al (1998) Detection of xanthine oxidase activity products by EPR and HPLC in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Free Radic Biol Med 25(7):771–779
Petruzzelli S, Puntoni R, Mimotti P, Pulera N, Baliva F, Fornai E, Giuntini C (1997) Plasma 3-nitrotyrosine in cigarette smokers. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156(6):1902–1907
Calhoun WJ, Reed HE, Moest DR, Stevens CA (1992) Enhanced superoxide production by alveolar macrophages and air-space cells, airway inflammation, and alveolar macrophage density changes after segmental antigen bronchoprovocation in allergic subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis 145(2 Pt 1):317–325
Lim JY, Oh E, Kim Y, Jung WW, Kim HS, Lee J, Sul D (2014) Enhanced oxidative damage to DNA, lipids, and proteins and levels of some antioxidant enzymes, cytokines, and heat shock proteins in patients infected with influenza H1N1 virus. Acta Virol 58(3):253–260
Ng MP, Lee JC, Loke WM, Yeo LL, Quek AM, Lim EC, Halliwell B, Seet RC (2014) Does influenza A infection increase oxidative damage? Antioxid Redox Signal 21(7):1025–1031
Erkekoglu P, Asci A, Ceyhan M, Kizilgun M, Schweizer U, Atas C, Kara A, Kocer GB (2013) Selenium levels, selenoenzyme activities and oxidant/antioxidant parameters in H1N1-infected children. Turk J Pediatr 55(3):271–282
Nin N, Sanchez-Rodriguez C, Ver LS, Cardinal P, Ferruelo A, Soto L, Deicas A, Campos N, Rocha O, Ceraso DH et al (2012) Lung histopathological findings in fatal pandemic influenza A (H1N1). Med Intensiva 36(1):24–31
Hennet T, Peterhans E, Stocker R (1992) Alterations in antioxidant defences in lung and liver of mice infected with influenza A virus. J Gen Virol 73(Pt 1):39–46
Buffinton GD, Christen S, Peterhans E, Stocker R (1992) Oxidative stress in lungs of mice infected with influenza A virus. Free Radic Res Commun 16(2):99–110
Amatore D, Sgarbanti R, Aquilano K, Baldelli S, Limongi D, Civitelli L, Nencioni L, Garaci E, Ciriolo MR, Palamara AT (2015) Influenza virus replication in lung epithelial cells depends on redox-sensitive pathways activated by NOX4-derived ROS. Cell Microbiol 17(1):131–145. PMCID:PMC4311438
Akaike T, Okamoto S, Sawa T, Yoshitake J, Tamura F, Ichimori K, Miyazaki K, Sasamoto K, Maeda H (2003) 8-nitroguanosine formation in viral pneumonia and its implication for pathogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(2):685–690. PMCID:PMC141057
Kaul P, Biagioli MC, Singh I, Turner RB (2000) Rhinovirus-induced oxidative stress and interleukin-8 elaboration involves p47-phox but is independent of attachment to intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and viral replication. J Infect Dis 181(6):1885–1890
Papi A, Contoli M, Gasparini P, Bristot L, Edwards MR, Chicca M, Leis M, Ciaccia A, Caramori G, Johnston SL et al (2008) Role of xanthine oxidase activation and reduced glutathione depletion in rhinovirus induction of inflammation in respiratory epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 283(42):28595–28606. PMCID:PMC2661410
Bao X, Kolli D, Liu T, Shan Y, Garofalo RP, Casola A (2008) Human metapneumovirus small hydrophobic protein inhibits NF-kappaB transcriptional activity. J Virol 82(16):8224–8229. PMCID:PMC2519579
Ye S, Lowther S, Stambas J (1997) Inhibition of reactive oxygen species production ameliorates inflammation induced by influenza A viruses via upregulation of SOCS1 and SOCS3. J Virol 89(5):2672–2683. PMCID:PMC4325759
Peterhans E (1997) Oxidants and antioxidants in viral diseases: disease mechanisms and metabolic regulation. J Nutr 127(5 Suppl):962S–965S
Peterhans E (1997) Reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide in viral diseases. Biol Trace Elem Res 56(1):107–116
Moreno-Solis G, Dela Torre-Aguilar MJ, Torres-Borrego J, Llorente-Cantarero FJ, Fernandez-Gutierrez F, Gil-Campos M, Tunez-Finana I, Perez-Navero JL (2017) Oxidative stress and inflamatory plasma biomarkers in respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Clin Respir J 11(6):839–846
Martinez I, Garcia-Carpizo V, Guijarro T, Garcia-Gomez A, Navarro D, Aranda A, Zambrano A (2016) Induction of DNA double-strand breaks and cellular senescence by human respiratory syncytial virus. Virulence 7(4):427–442. PMCID:PMC4871660
Faden H, Kaul TN, Ogra PL (1983) Activation of oxidative and arachidonic acid metabolism in neutrophils by respiratory syncytial virus antibody complexes: possible role in disease. J Infect Dis 148(1):110–116
Kimpen JL, Garofalo R, Welliver RC, Ogra PL (1992) Activation of human eosinophils in vitro by respiratory syncytial virus. Pediatr Res 32(2):160–164
Kaul P, Singh I, Turner RB (2002) Effect of rhinovirus challenge on antioxidant enzymes in respiratory epithelial cells. Free RadicRes 36(10):1085–1089
Indukuri H, Castro SM, Liao SM, Feeney LA, Dorsch M, Coyle AJ, Garofalo RP, Brasier AR, Casola A (2006) Ikkepsilon regulates viral-induced interferon regulatory factor-3 activation via a redox-sensitive pathway. Virology 353(1):155–165
Pittaluga M, Parisi P, Sabatini S, Ceci R, Caporossi D, Valeria CM, Savini I, Avigliano L (2006) Cellular and biochemical parameters of exercise-induced oxidative stress: relationship with training levels. Free RadicRes 40(6):607–614
Stuehr DJ, Griffith OW (1992) Mammalian nitric oxide synthases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 65:287–346
Akaike T, Maeda H (2000) Nitric oxide and virus infection. Immunology 101(3):300–308. PMCID:PMC2327086
Asano K, Chee CB, Gaston B, Lilly CM, Gerard C, Drazen JM, Stamler JS (1994) Constitutive and inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression, regulation, and activity in human lung epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(21):10089–10093. PMCID:PMC44963
Belvisi M, Barnes PJ, Larkin S, Yacoub M, Tadjkarimi S, Williams TJ, Mitchell JA (1995) Nitric oxide synthase activity is elevated in inflammatory lung disease in humans. Eur J Pharmacol 283(1-3):255–258
Tsutsumi H, Takeuchi R, Ohsaki M, Seki K, Chiba S (1999) Respiratory syncytial virus infection of human respiratory epithelial cells enhances inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression. J Leukoc Biol 66(1):99–104
Akaike T (2001) Role of free radicals in viral pathogenesis and mutation. Rev Med Virol 11(2):87–101
Zaki MH, Akuta T, Akaike T (2005) Nitric oxide-induced nitrative stress involved in microbial pathogenesis. J Pharmacol Sci 98(2):117–129
Kao YJ, Piedra PA, Larsen GL, Colasurdo GN (2001) Induction and regulation of nitric oxide synthase in airway epithelial cells by respiratory syncytial virus. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163(2):532–539
Ali-Ahmad D, Bonville CA, Rosenberg HF, Domachowske JB (2003) Replication of respiratory syncytial virus is inhibited in target cells generating nitric oxide in situ. Front Biosci 8:a48–a53
Song W, Liu G, Bosworth CA, Walker JR, Megaw GA, Lazrak A, Abraham E, Sullender WM, Matalon S (2009) Respiratory syncytial virus inhibits lung epithelial Na+ channels by up-regulating inducible nitric-oxide synthase. J Biol Chem 284(11):7294–7306. PMCID:PMC2652346
Hacking D, Rockett K, Hull J, Kwiatkowski D (2002) Synergistic action of cytokines and purified respiratory syncytial virus in nitric oxide induction. J Leukoc Biol 71(4):729–730
Lopez-Guerrero JA, Carrasco L (1998) Effect of nitric oxide on poliovirus infection of two human cell lines. J Virol 72(3):2538–2540. PMCID:PMC109559
Majano PL, Garcia-Monzon C, Lopez-Cabrera M, Lara-Pezzi E, Fernandez-Ruiz E, Garcia-Iglesias C, Borque MJ, Moreno-Otero R (2005) Inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in chronic viral hepatitis. Evidence for a virus-induced gene upregulation. J Clin Invest 101(7):1343–1352. PMCID:PMC508711
Stark JM, Khan AM, Chiappetta CL, Xue H, Alcorn JL, Colasurdo GN (2005) Immune and functional role of nitric oxide in a mouse model of respiratory syncytial virus infection. J Infect Dis 191(3):387–395
Gentile DA, Doyle WJ, Belenky S, Ranck H, Angelini B, Skoner DP (2002) Nasal and oral nitric oxide levels during experimental respiratory syncytial virus infection of adults. Acta Otolaryngol 122(1):61–66
Gadish T, Soferman R, Merimovitch T, Fireman E, Sivan Y (2010) Exhaled nitric oxide in acute respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 164(8):727–731
Morichi S, Kawashima H, Ioi H, Ushio M, Yamanaka G, Kashiwagi Y, Takekuma K, Hoshika A, Watanabe Y (2009) Cerebrospinal fluid NOx (nitrite/nitrate) in RSV-infected children with CNS symptoms. J Infect 59(4):299–301
Hobson L, Everard ML (2008) Persistent of respiratory syncytial virus in human dendritic cells and influence of nitric oxide. Clin Exp Immunol 151(2):359–366. PMCID:PMC2276949
Stamler JS, Lamas S, Fang FC (2001) Nitrosylation. The prototypic redox-based signaling mechanism. Cell 106(6):675–683
Huang SH, Cao XJ, Wei W (2008) Melatonin decreases TLR3-mediated inflammatory factor expression via inhibition of NF-kappa B activation in respiratory syncytial virus-infected RAW264.7 macrophages. J. Pineal Res 45(1):93–100
Chen L, Song W, Davis IC, Shrestha K, Schwiebert E, Sullender WM, Matalon S (2009) Inhibition of Na+ transport in lung epithelial cells by respiratory syncytial virus infection. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 40(5):588–600. PMCID:PMC2677438
Kilani MM, Mohammed KA, Nasreen N, Hardwick JA, Kaplan MH, Tepper RS, Antony VB (2004) Respiratory syncytial virus causes increased bronchial epithelial permeability. Chest 126(1):186–191
Jamaluddin M, Garofalo R, Ogra PL, Brasier AR (1996) Inducible translational regulation of the NF-IL6 transcription factor by respiratory syncytial virus infection in pulmonary epithelial cells. J Virol 70(3):1554–1563. PMCID:PMC189977
Garofalo R, Sabry M, Jamaluddin M, Yu RK, Casola A, Ogra PL, Brasier AR (1996) Transcriptional activation of the interleukin-8 gene by respiratory syncytial virus infection in alveolar epithelial cells: nuclear translocation of the RelA transcription factor as a mechanism producing airway mucosal inflammation. J Virol 70(12):8773–8781. PMCID:PMC190974
Jamaluddin M, Casola A, Garofalo RP, Han Y, Elliott T, Ogra PL, Brasier AR (1998) The major component of IkappaBalpha proteolysis occurs independently of the proteasome pathway in respiratory syncytial virus-infected pulmonary epithelial cells. J Virol 72(6):4849–4857. PMCID:PMC110033
Bitko V, Velazquez A, Yang L, Yang YC, Barik S (1997) Transcriptional induction of multiple cytokines by human respiratory syncytial virus requires activation of NF-kappa B and is inhibited by sodium salicylate and aspirin. Virology 232(2):369–378
Tian B, Zhang Y, Luxon BA, Garofalo RP, Casola A, Sinha M, Brasier AR (2002) Identification of NF-kappaB-dependent gene networks in respiratory syncytial virus-infected cells. J Virol 76(13):6800–6814. PMCID:PMC136270
Liu P, Jamaluddin M, Li K, Garofalo RP, Casola A, Brasier AR (2007) Retinoic acid-inducible gene I mediates early antiviral response and Toll-like receptor 3 expression in respiratory syncytial virus-infected airway epithelial cells. J Virol 81(3):1401–1411. PMCID:PMC1797494
Rudd BD, Burstein E, Duckett CS, Li X, Lukacs NW (2005) Differential role for TLR3 in respiratory syncytial virus-induced chemokine expression. J Virol 79(6):3350–3357. PMCID:PMC1075725
Bao X, Indukuri H, Liu T, Liao SL, Tian B, Brasier AR, Garofalo RP, Casola A (2010) IKKepsilon modulates RSV-induced NF-kappaB-dependent gene transcription. Virology 408(2):224–231. PMCID:PMC2975836
Groskreutz DJ, Monick MM, Powers LS, Yarovinsky TO, Look DC, Hunninghake GW (2006) Respiratory syncytial virus induces TLR3 protein and protein kinase R, leading to increased double-stranded RNA responsiveness in airway epithelial cells. J Immunol 176(3):1733–1740
Koarai A, Sugiura H, Yanagisawa S, Ichikawa T, Minakata Y, Matsunaga K, Hirano T, Akamatsu K, Ichinose M (2010) Oxidative stress enhances toll-like receptor 3 response to double-stranded RNA in airway epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 42(6):651–660. PMCID:PMC2891495
Stewart MJ, Kulkarni SB, Meusel TR, Imani F (2006) c-Jun N-terminal kinase negatively regulates dsRNA and RSV induction of tumor necrosis factor- alpha transcription in human epithelial cells. J Interferon Cytokine Res 26(8):521–533
Dey N, Liu T, Garofalo RP, Casola A (2011) TAK1 regulates NF-KappaB and AP-1 activation in airway epithelial cells following RSV infection. Virology 418(2):93–101. PMCID:PMC3164748
Haeberle HA, Durrstein C, Rosenberger P, Hosakote YM, Kuhlicke J, Kempf VA, Garofalo RP, Eltzschig HK (2008) Oxygen-independent stabilization of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1 during RSV infection. PLoS One 3(10):e3352. PMCID:PMC2556398
Mochizuki H, Todokoro M, Arakawa H (2009) RS virus-induced inflammation and the intracellular glutathione redox state in cultured human airway epithelial cells. Inflammation 32(4):252–264
Smith LJ, Shamsuddin M, Sporn PH, Denenberg M, Anderson J (1997) Reduced superoxide dismutase in lung cells of patients with asthma. Free Radic Biol Med 22(7):1301–1307
Ghosh S, Janocha AJ, Aronica MA, Swaidani S, Comhair SA, Xu W, Zheng L, Kaveti S, Kinter M, Hazen SL et al (2006) Nitrotyrosine proteome survey in asthma identifies oxidative mechanism of catalase inactivation. J Immunol 176(9):5587–5597
Chung-man HJ, Zheng S, Comhair SA, Farver C, Erzurum SC (2001) Differential expression of manganese superoxide dismutase and catalase in lung cancer. Cancer Res 61(23):8578–8585
Cho HY, Imani F, Miller-DeGraff L, Walters D, Melendi GA, Yamamoto M, Polack FP, Kleeberger SR (2009) Antiviral activity of Nrf2 in a murine model of respiratory syncytial virus disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 179(2):138–150. PMCID:PMC2633060
Uchide N, Toyoda H (2011) Antioxidant therapy as a potential approach to severe influenza-associated complications. Molecules 16(3):2032–2052. PMCID:PMC6259602
Batinic-Haberle I, Reboucas JS, Spasojevic I (2010) Superoxide dismutase mimics: chemistry, pharmacology, and therapeutic potential. Antioxid Redox Signal 13(6):877–918. PMCID:PMC2935339
Wang MM, Lu M, Zhang CL, Wu X, Chen JX, Lv WW, Sun T, Qiu H, Huang SH (2018) Oxidative stress modulates the expression of tolllike receptor 3 during respiratory syncytial virus infection in human lung epithelial A549 cells. Mol Med Rep 18(2):1867–1877
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Young Clinical Scientist Award from the Flight Attendant Medical Research Institute (FAMRI) (grant I.D. number 123385), NIH/NIAID R21 AI35619, and Data Acquisition from the Institute for Human Infections and Immunity to YMH. We thank Drs. Linsey Yeager and Sherry Haller for manuscript editing.
Conflict of Interest Disclosure statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Hosakote, Y.M., Rayavara, K. (2020). Respiratory Syncytial Virus-Induced Oxidative Stress in Lung Pathogenesis. In: Chakraborti, S., Parinandi, N., Ghosh, R., Ganguly, N., Chakraborti, T. (eds) Oxidative Stress in Lung Diseases. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-32-9366-3_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-32-9366-3_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-32-9365-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-32-9366-3
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)