Abstract
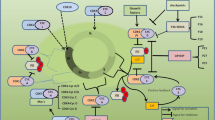
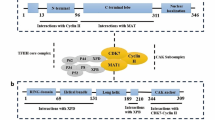
Cancer, a condition characterized by abnormal cell growth, is closely linked to the cell cycle. In reaction to mitogenic cues, all malignancies comprise an aberrant buildup of tumor tissues that are promoted toward uncontrollable cell multiplication and growth. Genetic or epigenetic alterations in cell cycle-regulating genes as well as other genes that govern the cell cycle are examples of oncogenic stimuli. This shows that cancer is caused by many, different paths of genetic changes. Oncogenes (such as CDKs and cyclins and CDKs) and tumor suppressor genes (such as CDK inhibitors) produce proteins that control cell cycle mechanism and stimulate or repress progression of cell cycle, respectively. The discovery of CDKs and cyclins aids in the explanation and comprehension of cell cycle system molecular pathways. Cyclins A, B, C, D1, and E, as well as CDKs and CDK-inhibitor molecules p21, p16, p53, and p27, are believed to have important functions in cell cycle management throughout breast cancer development and are strictly controlled in normal breast epithelium cells. These proteins are dysregulated in response to mitogenic stimulation, promoting neoplastic conversion of mammary epithelial cells. This chapter’s objective is to describe the functions of tumor-suppressive and oncogenic cell cycle elements in breast carcinoma growth and prognosis.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaltonen K, Amini R-M, Heikkilä P, Aittomäki K, Tamminen A, Nevanlinna H, Blomqvist C (2009) High cyclin b1 expression is associated with poor survival in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 100:1055–1060
Abou-Bakr AA, Eldweny HI (2013) P16 expression correlates with basal-like triple-negative breast carcinoma. Ecancermedicalscience 7:317
Abubakar M, Guo C, Koka H, Sung H, Shao N, Guida J, Deng J, Li M, Hu N, Zhou B (2019) Clinicopathological and epidemiological significance of breast cancer subtype reclassification based on p53 immunohistochemical expression. NPJ Breast Cancer 5:1–9
Ahnström M, Nordenskjöld B, Rutqvist LE, Skoog L, Stål O (2005) Role of cyclin d1 in erbb2-positive breast cancer and tamoxifen resistance. Breast Cancer Res Treat 91:145–151
Al-Joudi FS, Iskandar ZA, Rusli J (2008) The expression of p53 in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast: a study in the north-east states of Malaysia. Med J Malays 63:96–99
Albanese C, Johnson J, Watanabe G, Eklund N, Vu D, Arnold A, Pestell RG (1995) Transforming p21ras mutants and c-ets-2 activate the cyclin d1 promoter through distinguishable regions (∗). J Biol Chem 270:23589–23597
Alkarain A, Jordan R, Slingerland J (2004) P27 deregulation in breast cancer: prognostic significance and implications for therapy. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 9:67–80
Alle KM, Henshall SM, Field AS, Sutherland RL (1998) Cyclin d1 protein is overexpressed in hyperplasia and intraductal carcinoma of the breast. Clin Cancer Res 4:847–854
Androic I, Krämer A, Yan R, Rödel F, Gätje R, Kaufmann M, Strebhardt K, Yuan J (2008) Targeting cyclin b1 inhibits proliferation and sensitizes breast cancer cells to taxol. BMC Cancer 8:1–11
Arima Y, Hayashi N, Hayashi H, Sasaki M, Kai K, Sugihara E, Abe E, Yoshida A, Mikami S, Nakamura S (2012) Loss of p16 expression is associated with the stem cell characteristics of surface markers and therapeutic resistance in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Int J Cancer 130:2568–2579
Arnold A, Papanikolaou A (2005) Cyclin d1 in breast cancer pathogenesis. J Clin Oncol 23:4215–4224
Asghar U, Witkiewicz AK, Turner NC, Knudsen ES (2015) The history and future of targeting cyclin-dependent kinases in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 14:130–146
Assem M, Youssef EA, Rashad RM, Yahia MA-H (2017) Immunohistochemical expression of cyclin d1 in invasive ductal carcinoma of human breast. Onco Targets Ther 2:80–87
Ates C, Sevinçli S, Pohl T (2011) Electromagnetically induced transparency in strongly interacting Rydberg gases. Phys Rev A 83:041802
Bae SY, Lee JH, Bae JW, Jung SP (2020) Differences in prognosis by p53 expression after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Surg Treat Res 98:291
Baker SJ, Reddy EP (2012) Cdk4: a key player in the cell cycle, development, and cancer. Genes Cancer 3:658–669
Baldini E, Camerini A, Sgambato A, Prochilo T, Capodanno A, Pasqualetti F, Orlandini C, Resta L, Bevilacqua G, Collecchi P (2006) Cyclin A and E2F1 overexpression correlate with reduced disease-free survival in node-negative breast cancer patients. Anticancer Res 26:4415–4421
Barnes A, Pinder SE, Bell JA, Paish EC, Wencyk PM, Robertson JFR, Elston CW, Ellis IO (2003) Expression of p27kip1 in breast cancer and its prognostic significance. J Pathol 201:451–459
Barnes DM, Gillett CE (1998) Cyclin d1 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 52:1–15
Bertheau P, Lehmann-Che J, Varna M, Dumay A, Poirot B, Porcher R, Turpin E, Plassa L-F, De Roquancourt A, Bourstyn E (2013) P53 in breast cancer subtypes and new insights into response to chemotherapy. Breast 22:s27–s29
Boström P, Söderström M, Palokangas T, Vahlberg T, Collan Y, Carpen O, Hirsimäki P (2009) Analysis of cyclins a, b1, d1 and e in breast cancer in relation to tumour grade and other prognostic factors. BMC Res Notes 2:1–8
Brown I, Shalli K, McDonald SL, Moir SE, Hutcheon AW, Heys SD, Schofield AC (2004) Reduced expression of p27 is a novel mechanism of docetaxel resistance in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res 6:1–7
Buckley MF, Sweeney KJ, Hamilton JA, Sini RL, Manning DL, Nicholson RI, Watts CK, Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL (1993) Expression and amplification of cyclin genes in human breast cancer. Oncogene 8:2127–2133
Buolamwini JK (2000) Cell cycle molecular targets in novel anticancer drug discovery. Curr Pharm Des 6:379–392
Cao T, **ao T, Huang G, Xu Y, Zhu JJ, Wang K, Ye W, Guan H, He J, Zheng D (2017) Cdk3, target of mir-4469, suppresses breast cancer metastasis via inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget 8:84917
Cariou S, Donovan JCH, Flanagan WM, Milic A, Bhattacharya N, Slingerland JM (2000) Down-regulation of p21waf1/cip1 or p27kip1 abrogates antiestrogen-mediated cell cycle arrest in human breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97:9042–9046
Chen X, Danes C, Lowe M, Herliczek TW, Keyomarsi K (2000) Activation of the estrogen-signaling pathway by p21waf1/cip1 in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:1403–1413
Chu J-S, Huang C-S, Chang K-J (1999) P27 expression as a prognostic factor of breast cancer in Taiwan. Cancer Lett 141:123–130
Coates AS, Millar EKA, O’toole SA, Molloy TJ, Viale G, Goldhirsch A, Regan MM, Gelber RD, Sun Z, Castiglione-Gertsch M (2012) Prognostic interaction between expression of p53 and estrogen receptor in patients with node-negative breast cancer: results from IBCSG Trials VIII and IX. Breast Cancer Res 14:1–12
Coqueret O (2002) Linking cyclins to transcriptional control. Gene 299:35–55
Courjal F, Louason G, Speiser P, Katsaros D, Zeillinger R, Theillet C (1996) Cyclin gene amplification and overexpression in breast and ovarian cancers: evidence for the selection of cyclin d1 in breast and cyclin e in ovarian tumors. Int J Cancer 69:247–253
Crown J (2017) Cdk8: a new breast cancer target. Oncotarget 8:14269
Cui SP, Wang HL, Peng W, Liu HJ, Hou L, Zhang B (2012) Aberrant expression and correlative analysis of p16 in breast cancers. Bei**g Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 44:755–759
Dai M, Al-Odaini AA, Arakelian A, Rabbani SA, Ali S, Lebrun J-J (2012) A novel function for p21cip1 and acetyltransferase p/caf as critical transcriptional regulators of tgfβ-mediated breast cancer cell migration and invasion. Breast Cancer Res 14:1–22
Dai M, Al-Odaini AA, Fils-Aimé N, Villatoro MA, Guo J, Arakelian A, Rabbani SA, Ali S, Lebrun JJ (2013) Cyclin d1 cooperates with p21 to regulate tgfβ-mediated breast cancer cell migration and tumor local invasion. Breast Cancer Res 15:1–14
Davidoff AM, Herndon JE 2nd, Glover NS, Kerns BJ, Pence JC, Iglehart JD, Marks JR (1991) Relation between p53 overexpression and established prognostic factors in breast cancer. Surgery 110:259–264
Del Re M, Bertolini I, Crucitta S, Fontanelli L, Rofi E, De Angelis C, Diodati L, Cavallero D, Gianfilippo G, Salvadori B (2019) Overexpression of tk1 and cdk9 in plasma-derived exosomes is associated with clinical resistance to cdk4/6 inhibitors in metastatic breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 178:57–62
Diehl JA, Zindy F, Sherr CJ (1997) Inhibition of cyclin d1 phosphorylation on threonine-286 prevents its rapid degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Genes Dev 11:957–972
Domagala W, Welcker M, Chosia M, Karbowniczek M, Harezga B, Bartkova J, Bartek J, Osborn M (2001) P21/waf1/cip1 expression in invasive ductal breast carcinoma: relationship to p53, proliferation rate, and survival at 5 years. Virchows Arch 439:132–140
Donnellan R, Kleinschmidt I, Chetty R (2001) Cyclin E immunoexpression in breast ductal carcinoma: pathologic correlations and prognostic implications. Hum Pathol 32:89–94
Dorand RD, Nthale J, Myers JT, Barkauskas DS, Avril S, Chirieleison SM, Pareek TK, Abbott DW, Stearns DS, Letterio JJ (2016) Cdk5 disruption attenuates tumor pd-l1 expression and promotes antitumor immunity. Science 353:399–403
Dorée M, Galas S (1994) The cyclin-dependent protein kinases and the control of cell division. FASEB J 8:1114–1121
Dukelow T, Kishan D, Khasraw M, Murphy CG (2015) Cdk4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer. Anti-Cancer Drugs 26:797–806
Elsheikh S, Green AR, Aleskandarany MA, Grainge M, Paish CE, Lambros MBK, Reis-Filho JS, Ellis IO (2008) CCND1 amplification and cyclin D1 expression in breast cancer and their relation with proteomic subgroups and patient outcome. Breast Cancer Res Treat 109:325–335
Emig R, Magener A, Ehemann V, Meyer A, Stilgenbauer F, Volkmann M, Wallwiener D, Sinn HP (1998) Aberrant cytoplasmic expression of the p16 protein in breast cancer is associated with accelerated tumour proliferation. Br J Cancer 78:1661–1668
Fayed YM, El-Sheikh SA-M, Abulkheir ILH, Khorshed INA-H (2012) Immunohistochemical expression of p27 in ductal carcinoma of breast and its correlation with her2/neu expression and hormonal status. Egypt J Pathol 32:33–41
Fedele P, Sanna V, Fancellu A, Cinieri S (2019) A clinical evaluation of treatments that target cell cycle machinery in breast cancer. Expert Opin Pharmacother 20:2305–2315
Filipits M, Rudas M, Heinzl H, Jakesz R, Kubista E, Lax S, Schip**er W, Dietze O, Greil R, Stiglbauer W (2009) Low p27 expression predicts early relapse and death in postmenopausal hormone receptor–positive breast cancer patients receiving adjuvant tamoxifen therapy. Clin Cancer Res 15:5888–5894
Firestein R, Bass AJ, Kim SY, Dunn IF, Silver SJ, Guney I, Freed E, Ligon AH, Vena N, Ogino S (2008) Cdk8 is a colorectal cancer oncogene that regulates β-catenin activity. Nature 455:547–551
Foster JS, Henley DC, Bukovsky A, Seth P, Wimalasena J (2001) Multifaceted regulation of cell cycle progression by estrogen: regulation of Cdk inhibitors and Cdc25A independent of cyclin d1-Cdk4 function. Mol Cell Biol 21:794–810
Fredersdorf S, Burns J, Milne AM, Packham G, Fallis L, Gillett CE, Royds JA, Peston D, Hall PA, Hanby AM (1997) High level expression of p27kip1 and cyclin d1 in some human breast cancer cells: inverse correlation between the expression of p27kip1 and degree of malignancy in human breast and colorectal cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci 94:6380–6385
Fritah A, Saucier C, Mester J, Redeuilh G, Sabbah M (2005) P21 waf1/cip1 selectively controls the transcriptional activity of estrogen receptor α. Mol Cell Biol 25:2419–2430
Geradts J, Wilson PA (1996) High frequency of aberrant p16(ink4a) expression in human breast cancer. Am J Pathol 149:15–20
Göhring U-J, Schöndorf T, Kiecker VR, Becker M, Kurbacher C, Scharl A (1999) Immunohistochemical detection of H-ras protooncoprotein p21 indicates favorable prognosis in node-negative breast cancer patients. Tumor Biol 20:173–183
Graña X, Reddy EP (1995) Cell cycle control in mammalian cells: role of cyclins, cyclin dependent kinases (CDKs), growth suppressor genes and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CKIs). Oncogene 11:211–220
Guan X, Wang Y, **e R, Chen L, Bai J, Lu J, Kuo MT (2010) P27kip1 as a prognostic factor in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cell Mol Med 14:944–953
Guen VJ, Gamble C, Lees JA, Colas P (2017) The awakening of the cdk10/cyclin m protein kinase. Oncotarget 8:50174
Hall M, Peters G (1996) Genetic alterations of cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, and cdk inhibitors in human cancer. Adv Cancer Res 68:67–108
Han S, Park K, Bae BN, Kim KH, Kim HJ, Kim YD, Kim HY (2003) Prognostic implication of cyclin e expression and its relationship with cyclin d1 and p27kip1 expression on tissue microarrays of node negative breast cancer. J Surg Oncol 83:241–247
Harbhajanka A, Lamzabi I, Bitterman P, Reddy VB, Ghai R, Gattuso P (2019) Correlation of p16 expression on cancer and stromal cells with clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical features of lobular breast carcinoma. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 27:658–662
Heiss C, Schanz A, Amabile N, Jahn S, Chen Q, Wong ML, Rassaf T, Heinen Y, Cortese-Krott M, Grossman W (2010) Nitric oxide synthase expression and functional response to nitric oxide are both important modulators of circulating angiogenic cell response to angiogenic stimuli. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 30:2212–2218
Hodges LC, Cook JD, Lobenhofer EK, Li L, Bennett L, Bushel PR, Aldaz CM, Afshari CA, Walker CL (2003) Tamoxifen functions as a molecular agonist inducing cell cycle-associated genes in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 1:300–311
Horiuchi D, Kusdra L, Huskey NE, Chandriani S, Lenburg ME, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Creasman KJ, Bazarov AV, Smyth JW, Davis SE (2012) MYC pathway activation in triple-negative breast cancer is synthetic lethal with CDK inhibition. J Exp Med 209:679–696
Husdal A, Bukholm G, Bukholm IRK (2006) The prognostic value and overexpression of cyclin A is correlated with gene amplification of both cyclin A and cyclin E in breast cancer patient. Anal Cell Pathol 28:107–116
Hwang HC, Clurman BE (2005) Cyclin E in normal and neoplastic cell cycles. Oncogene 24:2776–2786
Jabbour-Leung NA, Chen X, Bui T, Jiang Y, Yang D, Vijayaraghavan S, McArthur MJ, Hunt KK, Keyomarsi K (2016) Sequential combination therapy of cdk inhibition and doxorubicin is synthetically lethal in p53-mutant triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 15:593–607
Jirström K, Stendahl M, Rydén L, Kronblad Å, Bendahl P-O, Stål O, Landberg G (2005) Adverse effect of adjuvant tamoxifen in premenopausal breast cancer with cyclin d1 gene amplification. Cancer Res 65:8009–8016
Joung YH, Lim EJ, Lee MY, Park J-H, Ye S-K, Park EU, Kim SY, Zhang Z, Lee KJ, Park DK (2005) Hypoxia activates the cyclin d1 promoter via the jak2/stat5b pathway in breast cancer cells. Exp Mol Med 37:353–364
Kato JY, Matsushime H, Hiebert SW, Ewen ME, Sherr CJ (1993) Direct binding of cyclin d to the retinoblastoma gene product (pRb) and pRb phosphorylation by the cyclin D-dependent kinase CDK4. Genes Dev 7:331–342
Kenny FS, Hui R, Musgrove EA, Gee JMW, Blamey RW, Nicholson RI, Sutherland RL, Robertson JFR (1999) Overexpression of cyclin d1 messenger rna predicts for poor prognosis in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 5:2069–2076
Keyomarsi K, Tucker SL, Buchholz TA, Callister M, Ding YE, Hortobagyi GN, Bedrosian I, Knickerbocker C, Toyofuku W, Lowe M (2002) Cyclin E and survival in patients with breast cancer. N Engl J Med 347:1566–1575
Khan N, Syed DN, Ahmad N, Mukhtar H (2013) Fisetin: a dietary antioxidant for health promotion. Antioxid Redox Signal 19:151–162
Khan SU, Fatima K, Malik F (2022a) Understanding the cell survival mechanism of anoikis-resistant cancer cells during different steps of metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 39:715
Khan SU, Pathania AS, Wani A, Fatima K, Mintoo MJ, Hamza B, Paddar MA, Bhumika W, Anand LK, Maqbool MS (2022b) Activation of lysosomal mediated cell death in the course of autophagy by mtorc1 inhibitor. Sci Rep 12:1–13
Kikuchi S, Nishimura R, Osako T, Okumura Y, Nishiyama Y, Toyozumi Y, Arima N (2013) Definition of p53 overexpression and its association with the clinicopathological features in luminal/her2-negative breast cancer. Anticancer Res 33:3891–3897
Kilker RL, Hartl MW, Rutherford TM, Planas-Silva MD (2004) Cyclin d1 expression is dependent on estrogen receptor function in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 92:63–71
Kilker RL, Planas-Silva MD (2006) Cyclin d1 is necessary for tamoxifen-induced cell cycle progression in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 66:11478–11484
Kim J-Y, Park K, Jung HH, Lee E, Cho EY, Lee KH, Bae SY, Lee SK, Kim SW, Lee JE (2016) Association between mutation and expression of tp53 as a potential prognostic marker of triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res Treat 48:1338
Lara JF, Thor AD, Dressler LG, Broadwater G, Bleiweiss IJ, Edgerton S, Cowan D, Goldstein LJ, Martino S, Ingle JN (2011) P53 expression in node-positive breast cancer patients: results from the cancer and leukemia group B 9344 trial (159905). Clin Cancer Res 17:5170–5178
Lebwohl DE, Muise-Helmericks R, Sepp-Lorenzino L, Serve S, Timaul M, Bol R, Borgen P, Rosen N (1994) A truncated cyclin D1 gene encodes a stable mRNA in a human breast cancer cell line. Oncogene 9:1925–1929
Lee D-S, Kim SH, Suh YJ, Kim S, Kim HK, Shim BY (2011) Clinical implication of p53 overexpression in breast cancer patients younger than 50 years with a triple-negative subtype who undergo a modified radical mastectomy. Jpn J Clin Oncol 41:854–866
Lee RJ, Albanese C, Stenger RJ, Watanabe G, Inghirami G, Haines GK, Webster M, Muller WJ, Brugge JS, Davis RJ (1999) pp60v-src induction of cyclin d1 requires collaborative interactions between the extracellular signal-regulated kinase, p38, and Jun kinase pathways: a role for camp response element-binding protein and activating transcription factor-2 in pp60v-src signaling in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 274:7341–7350
Leivonen M, Nordling S, Lundin J, Von Boguslawski K, Haglund C (2001) P27 expression correlates with short-term, but not with long-term prognosis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 67:15–22
Leng X, Connell-Crowley L, Goodrich D, Harper JW (1997) S-phase entry upon ectopic expression of g1 cyclin-dependent kinases in the absence of retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation. Curr Biol 7:709–712
Lengare PV, Sinai Khandeparkar SG, Joshi AR, Gogate BP, Solanke SG, Gore SH (2020) Immunohistochemical expression of cyclin d1 in invasive breast carcinoma and its correlation with clinicopathological parameters. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 63:376–381
Li B, Chonghaile TN, Fan Y, Madden SF, Klinger R, O’Connor AE, Walsh L, O’Hurley G, Udupi GM, Joseph J (2017) Therapeutic rationale to target highly expressed cdk7 conferring poor outcomes in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res 77:3834–3845
Li J-P, Zhang X-M, Zhang Z, Zheng L-H, **dal S, Liu Y-J (2019) Association of p53 expression with poor prognosis in patients with triple-negative breast invasive ductal carcinoma. Medicine 98:e15449
Li J, Poi MJ, Tsai M-D (2011) Regulatory mechanisms of tumor suppressor p16ink4a and their relevance to cancer. Biochemistry 50:5566–5582
Li Y, Dowbenko D, Lasky LA (2002) Akt/pkb phosphorylation of p21cip/waf1 enhances protein stability of p21cip/waf1 and promotes cell survival. J Biol Chem 277:11352–11361
Loden M, Stighall M, Nielsen NH, Roos G, Emdin SO, Östlund H, Landberg G (2002) The cyclin d1 high and cyclin E high subgroups of breast cancer: separate pathways in tumorogenesis based on pattern of genetic aberrations and inactivation of the prb node. Oncogene 21:4680–4690
Loo LWM, Gao C, Shvetsov YB, Okoro DR, Hernandez BY, Bargonetti J (2019) Mdm2, mdm2-c, and mutant p53 expression influence breast cancer survival in a multiethnic population. Breast Cancer Res Treat 174:257–269
Malumbres M, Barbacid M (2001) To cycle or not to cycle: a critical decision in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 1:222–231
Marais A, Ji Z, Child ES, Krause E, Mann DJ, Sharrocks AD (2010) Cell cycle-dependent regulation of the forkhead transcription factor foxk2 by cdk· cyclin complexes. J Biol Chem 285:35728–35739
Marchetti P, Cannita K, Ricevuto E, De Galitiis F, Di Rocco ZC, Tessitore A, Bisegna R, Porzio G, De Rubeis GP, Ventura T (2003) Prognostic value of p53 molecular status in high-risk primary breast cancer. Ann Oncol 14:704–708
Matutino A, Amaro C, Verma S (2018) Cdk4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer: beyond hormone receptor-positive her2-negative disease. Ther Adv Med Oncol 10:1758835918818346
Mehraj U, Dar AH, Wani NA, Mir MA (2021) Tumor microenvironment promotes breast cancer chemoresistance. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 87:147–158
Mehraj U, Aisha S, Sofi S, Mir MA (2022a) Expression pattern and prognostic significance of baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis repeat-containing 5 (birc5) in breast cancer: a comprehensive analysis. Adv Cancer Biol-Metastasis 4:100037
Mehraj U, Alshehri B, Khan AA, Bhat AA, Bagga P, Wani NA, Mir MA (2022b) Expression pattern and prognostic significance of chemokines in breast cancer: an integrated bioinformatics analysis. Clin Breast Cancer 22:567
Mehraj U, Qayoom H, Sofi S, Farhana P, Asdaq SMB, Mir MA (2022c) Cryptolepine targets top2a and inhibits tumor cell proliferation in breast cancer cells-an in vitro and in silico study. Anti Cancer Agents Med Chem 22:3025
Mehraj U, Sofi S, Alshehri B, Mir MA (2022d) Expression pattern and prognostic significance of cdks in breast cancer: an integrated bioinformatic study. Cancer Biomark 34:505–519
Mehta P, Nema S, Narang S (2019) Role of p53 and ki-67 in prognostication of carcinoma breast. Indian J Pathol Oncol 6:261–265
Michalides R, Van Tinteren H, Balkenende A, Vermorken JB, Benraadt J, Huldij J, Van Diest P (2002) Cyclin a is a prognostic indicator in early stage breast cancer with and without tamoxifen treatment. Br J Cancer 86:402–408
Mir MA, Sofi S, Aisha S (2022a) Role of cancer-associated fibroblasts in tumor microenvironment, chapter-3. In: Role of tumor microenvironment in breast cancer and targeted therapies. Elsevier, San Diego, pp 59–86; ISBN 978-0-443-18696-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-443-18696-7.00002-6
Mir MA, Mir AY, Jan U, Dar MA, Shah MZUH (2022b) Role of cancer-associated fibroblasts in tumor microenvironment, chapter-4. In: Role of tumor microenvironment in breast cancer and targeted therapies. Elsevier, San Diego, pp 87–112; ISBN 978-0-443-18696-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-443-18696-7.00004-x
Mir MA, Mir AY (2022) Role of regulatory t cells in cancer, chapter-5. In: Role of tumor microenvironment in breast cancer and targeted therapies. Elsevier, San Diego, pp 113–136; ISBN 978-0-443-18696-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-443-18696-7.00001-4
Mir MA, Mir AY, Mushtaq T (2022c) Role of tumor-associated macrophages in the breast tumor microenvironment, chapter-6. In: Role of tumor microenvironment in breast cancer and targeted therapies. Elsevier, San Diego, pp 137–170; ISBN 978-0-443-18696-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-443-18696-7.00003-8
Mir MA, Aisha S, Sofi S (2022d) Introduction to various types of cancers, chapter-1. In: Role of tumor microenvironment in breast cancer and targeted therapies. Elsevier, San Diego, pp 1–30; ISBN 978-0-443-18696-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-443-18696-7.00010-5
Mir MA, Mehraj U (2019) Double-crosser of the immune system: macrophages in tumor progression and metastasis. Curr Immunol Rev 15:172–184
Mir MA, Qayoom H, Mehraj U, Nisar S, Bhat B, Wani NA (2020) Targeting different pathways using novel combination therapy in triple negative breast cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 20:586–602
Mir MA, Aisha S, Sofi S, Rasheid S (2022e) The tumor microenvironment, chapter-2. In: Role of tumor microenvironment in breast cancer and targeted therapies. Elsevier, San Diego, pp 31–58; ISBN 978-0-443-18696-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-443-18696-7.00007-5
Mir M, Jan S, Mehraj U, Qayoom H, Nisar S (2022f) Immuno-onco-metabolism and therapeutic resistance. In: Immuno-oncology crosstalk and metabolism. Springer, Singapore, pp 45–89; ISBN 9789811662263. https://springer.longhoe.net/chapter/10.1007/978-981-16-6226-3_3
Mir MA, Aisha S, Mehraj U (2022g) Chapter 3 - Current therapeutics and treatment options in TNBC. In: Mir M (ed) Combinational therapy in triple negative breast cancer. Academic press, London, pp 61–94. ISBN: 978-0-323-96136-3. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-96136-3.00007-8
Mirchandani D, Roses DF, Inghirami G, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Cangiarella J, Guth A, Safyan RA, Formenti SC, Pagano M, Muggia F (2011) Loss of p27kip1 expression in fully-staged node-negative breast cancer: association with lack of hormone receptors in t1a/b, but not t1c infiltrative ductal carcinoma. Anticancer Res 31:4401–4405
Mohammadizadeh F, Hani M, Ranaee M, Bagheri M (2013) Role of cyclin d1 in breast carcinoma. J Res Med Sci 18:1021
Morgan DO (1997) Cyclin-dependent kinases: engines, clocks, and microprocessors. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 13:261
Muhammad EM, Ahmad AN, Guirguis MN, Ali A-EM (2012) Immunohistochemical p53 expression in breast carcinoma with correlation to clinico-pathological parameters. Med J Cairo Univ 80:179–189
Nahta R, Takahashi T, Ueno NT, Hung M-C, Esteva FJ (2004) P27kip1 down-regulation is associated with trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 64:3981–3986
Naidoo K, Wai PT, Maguire SL, Daley F, Haider S, Kriplani D, Campbell J, Mirza H, Grigoriadis A, Tutt A (2018) Evaluation of cdk12 protein expression as a potential novel biomarker for DNA damage response–targeted therapies in breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 17:306–315
Neganova I, Lako M (2008) G1 to s phase cell cycle transition in somatic and embryonic stem cells. J Anat 213:30–44
Newman L, **a W, Yang HY, Sahin A, Bondy M, Lukmanji F, Hung MC, Lee MH (2001) Correlation of p27 protein expression with her-2/neu expression in breast cancer. Mol Carcinog 30:169–175
Nie L, Wei Y, Zhang F, Hsu Y-H, Chan L-C, **a W, Ke B, Zhu C, Deng R, Tang J (2019) Cdk2-mediated site-specific phosphorylation of ezh2 drives and maintains triple-negative breast cancer. Nat Commun 10:1–15
Nielsen NH, Arnerlöv C, Emdin SO, Landberg G (1996) Cyclin E overexpression, a negative prognostic factor in breast cancer with strong correlation to oestrogen receptor status. Br J Cancer 74:874–880
Niméus-Malmström E, Koliadi A, Ahlin C, Holmqvist M, Holmberg L, Amini RM, Jirström K, Wärnberg F, Blomqvist C, Fernö M (2010) Cyclin b1 is a prognostic proliferation marker with a high reproducibility in a population-based lymph node negative breast cancer cohort. Int J Cancer 127:961–967
Nohara T, Ryo T, Iwamoto S, Gon G, Tanigawa N (2001) Expression of cell-cycle regulator p27 is correlated to the prognosis and er expression in breast carcinoma patients. Oncology 60:94–100
Oyama T, Kashiwabara K, Yoshimoto K, Arnold A, Koerner F (1998) Frequent overexpression of the cyclin d1 oncogene in invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast. Cancer Res 58:2876–2880
Pan Y, Yuan Y, Liu G, Wei Y (2017) P53 and ki-67 as prognostic markers in triple-negative breast cancer patients. PLoS One 12:e0172324
Patil VW, Singhai R, Patil AV, Gurav PD (2011) Triple-negative (ER, PgR, HER-2/neu) breast cancer in Indian women. Breast Cancer 3:9
Pérez-Tenorio G, Berglund F, Esguerra Merca A, Nordenskjöld B, Rutqvist LE, Skoog L, Stål O (2006) Cytoplasmic p21waf1/cip1 correlates with akt activation and poor response to tamoxifen in breast cancer. Int J Oncol 28:1031–1042
Pestell RG, Albanese C, Reutens AT, Segall JE, Lee RJ, Arnold A (1999) The cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors in hormonal regulation of proliferation and differentiation. Endocr Rev 20:501–534
Pines J (1995) Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases: theme and variations. Adv Cancer Res 66:181–212
Pohl G, Rudas M, Dietze O, Lax S, Markis E, Pirker R, Zielinski CC, Hausmaninger H, Kubista E, Samonigg H (2003) High p27kip1 expression predicts superior relapse-free and overall survival for premenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer receiving adjuvant treatment with tamoxifen plus goserelin. J Clin Oncol 21:3594–3600
Poikonen P, Sjöström J, Amini RM, Villman K, Ahlgren J, Blomqvist C (2005) Cyclin a as a marker for prognosis and chemotherapy response in advanced breast cancer. Br J Cancer 93:515–519
Porter PL, Barlow WE, Yeh IT, Lin MG, Yuan XP, Donato E, Sledge GW, Shapiro CL, Ingle JN, Haskell CM (2006) P27 kip1 and cyclin E expression and breast cancer survival after treatment with adjuvant chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst 98:1723–1731
Potemski P, Kusińska R, Pasz-Walczak G, Piekarski JH, Watała C, Płuciennik E, Bednarek AK, Kordek R (2009) Prognostic relevance of cyclin E expression in operable breast cancer. Med Sci Monit 15:40
Potemski P, Kusinska R, Watala C, Pluciennik E, Bednarek AK, Kordek R (2006) Cyclin e expression in breast cancer correlates with negative steroid receptor status, her2 expression, tumor grade and proliferation. Carcinogenesis 6:7
Pozo K, Castro-Rivera E, Tan C, Plattner F, Schwach G, Siegl V, Meyer D, Guo A, Gundara J, Mettlach G (2013) The role of cdk5 in neuroendocrine thyroid cancer. Cancer Cell 24:499–511
Qian X, Hulit J, Suyama K, Eugenin EA, Belbin TJ, Loudig O, Smirnova T, Zhou ZN, Segall J, Locker J (2013) P21cip1 mediates reciprocal switching between proliferation and invasion during metastasis. Oncogene 32:2292–2303
Ravazoula P, Batistatou A, Aletra C, Ladopoulos J, Kourounis G, Tzigounis B (2003) Immunohistochemical expression of glucose transporter glut 1 and cyclin d1 in breast carcinomas with negatine lymph nodes. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol 24:544–546
Ravikumar G, Ananthamurthy A (2014) Cyclin d1 expression in ductal carcinoma of the breast and its correlation with other prognostic parameters. J Cancer Res Ther 10:671
Robinson TJW, Liu JC, Vizeacoumar F, Sun T, Maclean N, Egan SE, Schimmer AD, Datti A, Zacksenhaus E (2013) Rb1 status in triple negative breast cancer cells dictates response to radiation treatment and selective therapeutic drugs. PLoS One 8:e78641
Rosendahl AH, Perks CM, Zeng L, Markkula A, Simonsson M, Rose C, Ingvar C, Holly JMP, Jernström H (2015) Caffeine and caffeic acid inhibit growth and modify estrogen receptor and insulin-like growth factor I receptor levels in human breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 21:1877–1887
Rudas M, Lehnert M, Huynh A, Jakesz R, Singer C, Lax S, Schip**er W, Dietze O, Greil R, Stiglbauer W (2008) Cyclin d1 expression in breast cancer patients receiving adjuvant tamoxifen-based therapy. Clin Cancer Res 14:1767–1774
Russell A, Thompson MA, Hendley J, Trute L, Armes J, Germain D (1999) Cyclin d1 and d3 associate with the SCF complex and are coordinately elevated in breast cancer. Oncogene 18:1983–1991
Salmani H, Hosseini A, Azarnezhad A, Ahmad H (2018) Pten and p53 gene expressions in breast cancer specimens and their clinicopathological significance. Middle East J Cancer 9:105–111
Santo L, Siu KT, Raje N (2015) Targeting cyclin-dependent kinases and cell cycle progression in human cancers. Semin Oncol 42:788–800
Schlafstein AJ, Withers AE, Rudra S, Danelia D, Switchenko JM, Mister D, Harari S, Zhang H, Daddacha W, Ehdaivand S (2018) Cdk9 expression shows role as a potential prognostic biomarker in breast cancer patients who fail to achieve pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Int J Breast Cancer 2018:6945129
Shan M, Zhang X, Liu X, Qin Y, Liu T, Liu Y, Wang J, Zhong Z, Zhang Y, Geng J (2013) P16 and p53 play distinct roles in different subtypes of breast cancer. PLoS One 8:e76408
Sherr CJ (1996) Cancer cell cycles. Science 274:1672–1677
Sherr CJ (2000) The pezcoller lecture: cancer cell cycles revisited. Cancer Res 60:3689–3695
Sieuwerts AM, Look MP, Meijer-Van Gelder ME, Timmermans M, Trapman AMAC, Garcia RR, Arnold M, Goedheer AJW, De Weerd V, Portengen H (2006) Which cyclin e prevails as prognostic marker for breast cancer? Results from a retrospective study involving 635 lymph node–negative breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 12:3319–3328
Simpson JF, Quan DE, O’Malley F, Odom-Maryon T, Clarke PE (1997) Amplification of ccnd1 and expression of its protein product, cyclin d1, in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Am J Pathol 151:161
Singh U, Chashoo G, Khan SU, Mahajan P, Nargotra A, Mahajan G, Singh A, Sharma A, Mintoo MJ, Guru SK (2017) Design of novel 3-pyrimidinylazaindole cdk2/9 inhibitors with potent in vitro and in vivo antitumor efficacy in a triple-negative breast cancer model. J Med Chem 60:9470–9489
Sofi S, Mehraj U, Qayoom H, Aisha S, Almilaibary A, Alkhanani M, Mir MA (2022a) Targeting cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (cdk1) in cancer: molecular docking and dynamic simulations of potential cdk1 inhibitors. Med Oncol 39:1–15
Sofi S, Mehraj U, Qayoom H, Aisha S, Asdaq SMB, Almilaibary A, Mir MA (2022b) Cyclin-dependent kinases in breast cancer: expression pattern and therapeutic implications. Med Oncol 39:1–16
Sofi S, Mehraj U, Qayoom H, Aisha S, Asdaq SMB, Almilaibary A, Mir MA (2022c) Cyclin-dependent kinases in breast cancer: expression pattern and therapeutic implications. Med Oncol 39:106
Sohn D, Essmann F, Schulze-Osthoff K, Jänicke RU (2006) P21 blocks irradiation-induced apoptosis downstream of mitochondria by inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase–mediated caspase-9 activation. Cancer Res 66:11254–11262
Solomon MJ (1993) Activation of the various cyclin/cdc2 protein kinases. Curr Opin Cell Biol 5:180–186
Spataro VJ, Litman H, Viale G, Maffini F, Masullo M, Golouh R, Martinez-Tello FJ, Grigolato P, Shilkin KB, Gusterson BA (2003) Decreased immunoreactivity for p27 protein in patients with early-stage breast carcinoma is correlated with her-2/neu overexpression and with benefit from one course of perioperative chemotherapy in patients with negative lymph node status: results from international breast cancer study group trial v. Cancer 97:1591–1600
Spring LM, Zangardi ML, Moy B, Bardia A (2017) Clinical management of potential toxicities and drug interactions related to cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer: practical considerations and recommendations. Oncologist 22:1039–1048
Stemke-Hale K, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Lluch A, Neve RM, Kuo W-L, Davies M, Carey M, Hu Z, Guan Y, Sahin A (2008) An integrative genomic and proteomic analysis of pik3ca, pten, and akt mutations in breast cancer. Cancer Res 68:6084–6091
Sun X, Zhangyuan G, Shi L, Wang Y, Sun B, Ding Q (2017) Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of cyclin b expression in patients with breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Medicine 96:e6860
Sutherland RL, Musgrove EA (2004) Cyclins and breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 9:95–104
Tassan J-P, Schultz SJ, Bartek J, Nigg EA (1994) Cell cycle analysis of the activity, subcellular localization, and subunit composition of human cak (cdk-activating kinase). J Cell Biol 127:467–478
Thu KL, Soria-Bretones I, Mak TW, Cescon DW (2018) Targeting the cell cycle in breast cancer: towards the next phase. Cell Cycle 17:1871–1885
Tobin NP, Bergh J (2012) Analysis of cyclin d1 in breast cancer: a call to arms. Curr Breast Cancer Rep 4:171–173
Traub F, Mengel M, Lück HJ, Kreipe HH, Von Wasielewski R (2006) Prognostic impact of skp2 and p27 in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 99:185–191
Tsuchiya A, Zhang GJ, Kanno M (1999) Prognostic impact of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27kip1 in node-positive breast cancer. J Surg Oncol 70:230–234
Umekita Y, Ohi Y, Sagara Y, Yoshida H (2002) Overexpression of cyclind1 predicts for poor prognosis in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer patients. Int J Cancer 98:415–418
Velasco-Velázquez MA, Li Z, Casimiro M, Loro E, Homsi N, Pestell RG (2011) Examining the role of cyclin d1 in breast cancer. Future Oncol 7:753–765
Vincent AJ, Ren S, Harris LG, Devine DJ, Samant RS, Fodstad O, Shevde LA (2012) Cytoplasmic translocation of p21 mediates nupr1-induced chemoresistance: nupr1 and p21 in chemoresistance. FEBS Lett 586:3429–3434
Wadhwa B, Paddar M, Khan S, Mir S, Clarke PA, Grabowska AM, Vijay DG, Malik F (2020) Akt isoforms have discrete expression in triple negative breast cancers and roles in cisplatin sensitivity. Oncotarget 11:4178
Wang C, Li Z, Lu Y, Du R, Katiyar S, Yang J, Fu M, Leader JE, Quong A, Novikoff PM (2006) Cyclin d1 repression of nuclear respiratory factor 1 integrates nuclear DNA synthesis and mitochondrial function. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:11567–11572
Wang L, Wang R, Ye Z, Wang Y, Li X, Chen W, Zhang M, Cai C (2018) Pvt1 affects EMT and cell proliferation and migration via regulating p21 in triple-negative breast cancer cells cultured with mature adipogenic medium. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 50:1211–1218
Wang TC, Cardiff RD, Zukerberg L, Lees E, Arnold A, Schmidt EV (1994) Mammary hyperplasia and carcinoma in mmtv-cyclin d1 transgenic mice. Nature 369:669–671
Wang Y, Zhang T, Kwiatkowski N, Abraham BJ, Lee TI, **e S, Yuzugullu H, Von T, Li H, Lin Z (2015) Cdk7-dependent transcriptional addiction in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell 163:174–186
Wei C-Y, Tan Q-X, Zhu X, Qin Q-H, Zhu F-B, Mo Q-G, Yang W-P (2015) Expression of cdkn1a/p21 and tgfbr2 in breast cancer and their prognostic significance. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:14619
Weinberg RA (1995) The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell 81:323–330
Westwick JK, Lee RJ, Lambert QT, Symons M, Pestell RG, Der CJ, Whitehead IP (1998) Transforming potential of Dbl family proteins correlates with transcription from the cyclin d1 promoter but not with activation of Jun NH2-terminal kinase, p38/mpk2, serum response factor, or c-jun. J Biol Chem 273:16739–16747
Wilcken NR, Prall OW, Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL (1997) Inducible overexpression of cyclin d1 in breast cancer cells reverses the growth-inhibitory effects of antiestrogens. Clin Cancer Res 3:849–854
Winters ZE, Hunt NC, Bradburn MJ, Royds JA, Turley H, Harris AL, Norbury CJ (2001) Subcellular localisation of cyclin b, cdc2 and p21waf1/cip1 in breast cancer: association with prognosis. Eur J Cancer 37:2405–2412
Yamamoto M, Tamakawa S, Yoshie M, Yaginuma Y, Ogawa K (2006) Neoplastic hepatocyte growth associated with cyclin d1 redistribution from the cytoplasm to the nucleus in mouse hepatocarcinogenesis. Mol Carcinog 45:901–913
Yang P, Du CW, Kwan M, Liang SX, Zhang GJ (2013) The impact of p53 in predicting clinical outcome of breast cancer patients with visceral metastasis. Sci Rep 3:1–6
Yde CW, Issinger O-G (2006) Enhancing cisplatin sensitivity in mcf-7 human breast cancer cells by down-regulation of bcl-2 and cyclin d1. Int J Oncol 29:1397–1404
You Y, Li H, Qin X, Zhang Y, Song W, Ran Y, Gao F (2015) Decreased cdk10 expression correlates with lymph node metastasis and predicts poor outcome in breast cancer patients-a short report. Cell Oncol 38:485–491
Yu Z-K, Gervais JLM, Zhang H (1998) Human cul-1 associates with the skp1/skp2 complex and regulates p21cip1/waf1 and cyclin d proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:11324–11329
Yu Z, Wang L, Wang C, Ju X, Wang M, Chen K, Loro E, Li Z, Zhang Y, Wu K (2013) Cyclin d1 induction of dicer governs microrna processing and expression in breast cancer. Nat Commun 4:1–10
Zhang P (1999) The cell cycle and development: redundant roles of cell cycle regulators. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11:655–662
Zhang S-Y, Caamano J, Cooper F, Guo X, Klein-Szanto AJP (1994) Immunohistochemistry of cyclin d1 in human breast cancer. Am J Clin Pathol 102:695–698
Zhang Z, Huang A, Zhang A, Zhou C (2017) Hur promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and survival via binding to cdk3 mrna. Biomed Pharmacother 91:788–795
Zhong Z, Yeow W-S, Zou C, Wassell R, Wang C, Pestell RG, Quong JN, Quong AA (2010) Cyclin d1/cyclin-dependent kinase 4 interacts with filamin A and affects the migration and invasion potential of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 70:2105–2114
Zilfou JT, Lowe SW (2009) Tumor suppressive functions of p53. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1:a001883
Zukerberg LR, Yang W-I, Gadd M, Thor AD, Koerner FC, Schmidt EV, Arnold A (1995) Cyclin d1 (prad1) protein expression in breast cancer: approximately one-third of infiltrating mammary carcinomas show overexpression of the cyclin d1 oncogene. Mod Pathol 8:560–567
Zwijsen RM, Klompmaker R, Wientjens EB, Kristel PM, Van Der Burg B, Michalides RJ (1996) Cyclin d1 triggers autonomous growth of breast cancer cells by governing cell cycle exit. Mol Cell Biol 16:2554–2560
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Mir, M.A., Khan, S.U., Aisha, S. (2023). Cell Cycle Dysregulation in Breast Cancer. In: Mir, M. (eds) Therapeutic potential of Cell Cycle Kinases in Breast Cancer. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-8911-7_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-8911-7_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-8910-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-8911-7
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)