Abstract
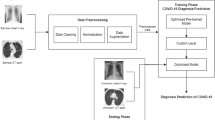
COVID-19 claimed 5 million lives worldwide so far, and the count is continuing. It also affected socio-economic life of almost everybody in the world. Due to COVID-19, mortality and morbidity are continuing, and it is necessary to find new methods and techniques to contain the infection. Every government is trying hard to implement a new strategy to minimize the spread of the virus. COVID-19 infection occurs due to the virus strain SARS-COV-2. Generally, death occurs due to COVID-19 because of suppurative pulmonary infection and subsequent septic shock or multiorgan failure. In the literature, there are some computational techniques which use deep learning models and reported fairly good performance. This paper proposes a new deep learning architecture inception v4 to automatically detect COVID-19 using the chart X-ray images. The proposed methodology provided improved performance of 98.7 and 94.8% of training and validation accuracy. The developed technology can be used to detect COVID-19 with a high performance; the same may be deployed by the various governments in the detection and the management of COVID-19 in an efficient manner.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kwekha-Rashid AS, Abduljabbar HN, Alhayani B (2021) Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) cases analysis using machine-learning applications
Asraf A, Islam MZ, Haque MR, Islam MM. Deep learning applications to combat novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic
Al-Turjman F (2021) Artificial intelligence and machine learning for COVID-19
Agrawal T, Choudhary P (2021) FocusCovid: automated COVID-19 detection using deep learning with chest X-ray images
Swapnarekha H, Behera HS, Roy D, Das S, Nayak J (2021) Competitive deep learning methods for COVID-19 detection using X-ray images. J Inst Eng (India) Ser B 102:1177–1190
Al Husaini MAS, Habaebi MH, Gunawan TS, Islam MR, Elsheikh EAA, Suliman FM (2021) Thermal-based early breast cancer detection using inception V3, inception V4, and modified inception MV4. Neural Comput Appl
Talo M, Yildirim O, Acharya UR (2019) Convolutional neural networks for multi-class brain disease detection using MRI images. Comput Med Imaging Graph 78:101673
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2015) Deep residual learning for image recognition
Pravin (2021) Computer vision, deep learning
Song H, Zhou Y, Jiang Z, Guo X, Yang Z. ResNet with global and local image features, stacked pooling block, for semantic segmentation
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Rachana, P.J., Kodipalli, A., Rao, T. (2023). Comparison Between ResNet 16 and Inception V4 Network for COVID-19 Prediction. In: Shetty, N.R., Patnaik, L.M., Prasad, N.H. (eds) Emerging Research in Computing, Information, Communication and Applications. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 928. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5482-5_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5482-5_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-5481-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-5482-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)