Abstract
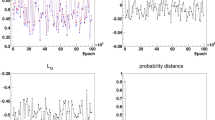
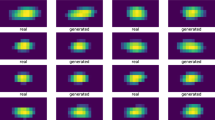
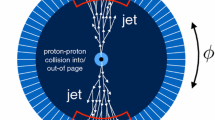
The recently proposed generative adversarial network (GAN)-based event generator, the Feature Augmented and Transformed GAN (FAT-GAN), has shown an impressive capability of reproducing inclusive electron–proton scattering events at given collision energy. In contrast, many practical applications require the event generator to have the flexibility of allowing users to specify the reaction energy as an input to produce the corresponding synthetic events. In this work, we extend the FAT-GAN framework by conditioning the component neural networks according to the given reaction energy. We demonstrate that this model, referred to as cFAT-GAN, can reliably produce inclusive event feature distributions and correlations for a continuous range of reaction energies by automatically interpolating and extrapolating from a set of trained energies. We employ a continuous energy feature representation to enable the networks to organically learn the distribution relationships between different reaction energies, laying the groundwork for accessing events at untrained energies. This continuous conditional energy provides a degree of versatility to the cFAT-GAN for its further development as a significant research tool in high-energy and nuclear physics.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alanazi, Y., Sato, N., Liu, T., W. Melnitchouk, M.P.K., Pritchard, E., Robertson, M., Strauss, R., Velasco, L., Li, Y.: Simulation of electron-proton scattering events by a feature-augmented and transformed generative adversarial network (fat-gan) (2020). ar**v:2001.11103
Bahr, M., et al.: Herwig++ physics and manual. Eur. Phys. J. C 58, 639–707 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-008-0798-9
Butter, A., Plehn, T., Winterhalder, R.: How to GAN LHC events. SciPost Phys. 7 (2019). https://doi.org/10.21468/SciPostPhys.7.6.075
Clark, A., Donahue, J., Simonyan, K.: Adversarial video generation on complex datasets (2019)
Donahue, D., Rumshisky, A.: Adversarial text generation without reinforcement learning (2018). CoRR ar**v:1810.06640
Gauthier, J.: Conditional generative adversarial nets for convolutional face generation (2015)
Gleisberg, T., Hoeche, S., Krauss, F., Schonherr, M., Schumann, S., Siegert, F., Winter, J.: Event generation with SHERPA 1.1. JHEP 02, 007 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/1126-6708/2009/02/007
Goodfellow, I.J., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., Bengio, Y.: Generative adversarial nets. In: Proceedings of NIPS’14, pp. 2672–2680. Cambridge, MA, USA (2014). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2969033.2969125
Gretton, A., Borgwardt, K., Rasch, M.J., Scholkopf, B., Smola, A.J.: A kernel method for the two-sample problem. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 19 (2007)
Gulrajani, I., Ahmed, F., Arjovsky, M., Dumoulin, V., Courville, A.C.: Improved training of Wasserstein GANs (2017). CoRR ar**v:1704.00028
Hashemi, B., Amin, N., Datta, K., Olivito, D., Pierini, M.: LHC analysis-specific datasets with generative adversarial networks (2019)
Isola, P., Zhu, J., Zhou, T., Efros, A.A.: Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks (2016). CoRR ar**v:1611.07004
Lu, Y., Tai, Y.W., Tang, C.K.: Attribute-guided face generation using conditional cyclegan (2018)
van der Maaten, L., Hinton, G.: Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9, 2579–2605 (2008). http://www.jmlr.org/papers/v9/vandermaaten08a.html
Michelsanti, D., Tan, Z.H.: Conditional generative adversarial networks for speech enhancement and noise-robust speaker verification. In: Interspeech 2017 (2017). https://doi.org/10.21437/interspeech.2017-1620
Mirza, M., Osindero, S.: Conditional generative adversarial nets (2014). CoRR ar**v:1411.1784
Musella, P., Pandolfi, F.: Fast and accurate simulation of particle detectors using generative adversarial networks. Comput. Softw. Big Sci. 2(1) (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41781-018-0015-y
de Oliveira, L., Paganini, M., Nachman, B.: Learning particle physics by example: location-aware generative adversarial networks for physics synthesis. Comput. Softw. Big Sci. 1(1) (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41781-017-0004-6
Paganini, M., de Oliveira, L., Nachman, B.: Accelerating science with generative adversarial networks: an application to 3d particle showers in multilayer calorimeters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120(4) (2018). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevlett.120.042003
Paganini, M., de Oliveira, L., Nachman, B.: Calogan simulating 3d high energy particle showers in multilayer electromagnetic calorimeters with generative adversarial networks. Phys. Rev. D 97(1) (2018). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevd.97.014021
Sjostrand, T., Mrenna, S., Skands, P.Z.: A brief introduction to PYTHIA 8.1. Comput. Phys. Commun. 178, 852–867 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2008.01.036
Winter, R., Clevert, D.: IVE-GAN: invariant encoding generative adversarial networks (2017). CoRR ar**v:1711.08646
Acknowledgements
We thank Jianwei Qiu for helpful discussions. This work was supported by the LDRD project No. LDRD19-13, No. LDRD20-18, and No. LDRD21-22.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Velasco, L. et al. (2022). cFAT-GAN: Conditional Simulation of Electron–Proton Scattering Events with Variate Beam Energies by a Feature Augmented and Transformed Generative Adversarial Network. In: Wani, M.A., Raj, B., Luo, F., Dou, D. (eds) Deep Learning Applications, Volume 3. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1395. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-3357-7_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-3357-7_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-3356-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-3357-7
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)