Abstract
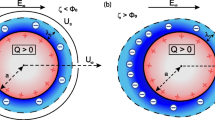
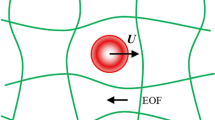
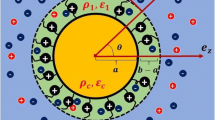
Electrophoresis is a process by which a charged colloid is propelled in a polar media under the action of an externally imposed electric field. This has been recognized as a useful tool to characterize macromolecules such as DNA, microorganisms, biocolloids or synthetic nanoparticles. Electrophoresis is also found to be an efficient method in separating, sorting and purification process. The microfluidic technology to address problems in biology, medical technology, such as controlled drug delivery and disease diagnostic are based on the electrophoresis phenomena. Thus, a correct relation between the electrostatic parameters and the electrophoretic velocity constitutes an important research topic. In this chapter, we have elaborated some of the existing simplified models for electrophoretic velocity. The shortcomings of these linear models or models based on weak-field consideration are illustrated in this chapter. An account of improved theory on electrophoresis is provided. The electrophoresis of a hydrophobic colloid is also addressed in the present chapter.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reuss, F.: Sur un nouvel effet de le électricité glavanique. Mémoires de la Societé Impériale des Naturalistes de Moscou 2, 327–337 (1809)
von Smoluchowski, M., Elektrische endosmose und strmungsstrme. In: Greatz E (ed) Handbuch der elektrizitt und des magnetismus. Band II Stationre strme, Barth, pp 366–428 (1921)
Huckel, E.: Die kataphorese der kugel. Physik. Z. 25, 204–210 (1924)
Henry, D., The cataphoresis of suspended particles. Part 1- The equation of cataphoresis. Proc. Roy. Soc. A, 133, 106–129 (1931)
Ohshima, H.: Electrophoretic mobility of soft particle. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 163, 474–483 (1994)
O’ Brien, R.W., White, Lee R., Electrophoretic mobility of a spherical colloidal particle. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 2: Molec. Chem. Phys. 74, 1607–1626 (1978)
Hsu, J.P., Ku, M.H.: Boundary effect on electrophoresis: finite cylinder in a cylindrical pore. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 283, 592–600 (2005)
Hsu, J.P., Chen, Z.S.: Electrophoresis of a sphere along the axis of a cylindrical pore: effects of double-layer polarization and electroosmotic flow. Langmuir 23, 6198–6204 (2007)
Sang, W., Joo, W.S., Hou, X., Zhao, H.: Electrophoretic motion of a spherical particle with a symmetric nonuniform surface charge distribution in a nanotube. Langmuir 24, 5332–5340 (2008)
Bhattacharyya, S., Gopmandal, P.P.: Migration of a charged sphere at an arbitrary velocity in an axial electric field. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 390, 86–94 (2011)
Khair, A.S.: Strong Deformation of the thick electric double layer around a charged particle during sedimentation or electrophoresis. Langmuir 34, 876–885 (2018)
Tretheway, D.C., Meinhart, C.D.: Apparent fluid slip at hydrophobic microchannel walls. Phys. Fluids 14, L9 (2002)
Moyano, D.F., Saha, K., Prakash, G., HaoKong, B., HaoKong, M., Vincent, M.R.: Fabrication of Corona-Free nanoparticles with tunable hydrophobicity. ACS NANO 8, 6748–6755 (2014)
Lauga, E., Brenner, M., Stone, H.A.: Handbook of Experimental Fluid Dynamics, pp. 1219–40. Springer, NY (2007)
Bocquet, L., Barrat, J.-L.: Flow boundary conditions from nano-to micro-scales. Soft Matter 3, 685–693 (2007)
Khair, A.S., Squires, T.M.: The influence of hydrodynamic slip on the electrophoretic mobility of a spherical colloidal particle. Phys. Fluids 21, 042001 (2009)
Park, H.M.: Electrophoresis of particles with Navier velocity slip. Electrophoresis 34, 651–661 (2013)
Bhattacharyya, S., Gopmandal, P.P., Ohshima, H.: On the similarity between the electrophoresis of a liquid drop and a spherical hydrophobic particle. Colloid Polym. Sci. 295, 2077–2082 (2017)
Bhattacharyya, S., Majee, P.S.: Electrophoresis of a polarizable charged colloid with hydrophobic surface: a numerical study. Phys. Rev. E 95, 042605 (2017)
Ohshima, H.: Electrokinetic phenomena in a dilute suspension of spherical solid colloidal particles with a hydrodynamically slip** surface in an aqueous electrolyte solution. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 272, 101996 (2019)
Hunter, R.J., Foundation of Colloid Science, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gopmandal, P.P., Maurya, S.K., Bhattacharyya, S. (2020). An Overview on Analytic Expressions for Electrophoretic Velocity of Rigid Colloids. In: Bhattacharyya, S., Kumar, J., Ghoshal, K. (eds) Mathematical Modeling and Computational Tools. ICACM 2018. Springer Proceedings in Mathematics & Statistics, vol 320. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3615-1_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3615-1_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-3614-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-3615-1
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)