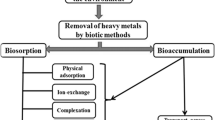
Abstract
Biosorption is a physicochemical process that allows certain microorganisms to passively bind contaminants onto their cellular structures. Mostly this process has been applied in the removal of heavy metals from contaminated water bodies. The technique is highly efficient and cost-effective and allows recovery of metal as well as the biomass. Among various organisms used for biosorption of heavy metals, such as bacteria, fungi, algae, higher plants, etc., cyanobacteria hold special position due to their unique structural properties and high metal sorption capabilities. Several cyanobacterial strains as live or dead cells have been used to remove heavy metals from contaminated sites. In view of its importance, this chapter discusses how cyanobacteria have been used in bioremediation of heavy metals. Attempts will be made to highlight the properties of cyanobacteria useful for biosorption and the process parameters responsible for enhancing the metal removal capability. In addition, mechanisms underlying sorption process are discussed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel -Aty AM, Ammar NS, Ghafar HHA, Ali RK (2013) Biosorption of cadmium and lead from aqueous solution by fresh water alga Anabaena sphaerica biomass. J Adv Res 4:367–374
Acharya C, Apte SK (2012) Marine cyanobacteria as suitable candidates for uranium recovery from aquatic environment. In: Indo-US Workshop on Cyanobacteria, Lonavala
Ahad RIA, Goswami S, Syiem MB (2017) Biosorption and equilibrium isotherms study of cadmium removal by Nostoc muscorum Meg 1: morphological, physiological and biochemical alterations. 3 Biotech 7:104–126
Ahmady-Asbchin S (2018) Biosorption of zinc from aqueous solution by cyanobacterium Fischerella ambigua ISC67: optimization, kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Water Sci Technol 78:1525–1534
Ahuja P, Gupta R, Saxena RK (1997) Oscillatoria anguistissima: a promising Cu2+ biosorbent. Curr Microbiol 35:151–154
Ahuja P, Gupta R, Saxena RK (1999a) Sorption and desorption of cobalt by Oscillatoria anguistissima. Curr Microbiol 39:49–52
Ahuja P, Gupta R, Saxena RK (1999b) Zn2+ biosorption by Oscillatoria anguistissima. Process Biochem 34:77–85
Al-Homaidan A, Al-Houri HJ, Al-Hazzani AA, Elgaaly G, Moubayed NMS (2014) Biosorption of copper ions from aqueous solutions by Spirulina platensis biomass. Arab J Chem 7:57–62
Al-Homaidan AA, Alabdullatif JA, Al-Hazzani AA, Al-Ghanayem AA, Alabbad AF (2015) Adsorptive removal of cadmium ions by Spirulina platensis dry biomass. Saudi J Biol Sci 22:795–800
Alidoust L, Soltani N, Modiri S, Haghighi O, Azarivand A, Khajeh K, Zahiri HS, Vali H, Noghabi KA (2016) Cadmium uptake capacity of an indigenous cyanobacterial strain, Nostoc entophytum ISC32: new insight into metal uptake in microgravity-simulating conditions. Microbiology 162:246–255
Aneja RK, Chaudhary G, Ahluwalia SS, Goyal D (2010) Biosorption of Pb2+ and Zn2+ by non-living biomass of Spirulina sp. Indian J Microbiol 50:438–442
Audiiolia S, Goyal D, Saxena RK (1993) Zinc tolerance in Phormidium uncinatum. Folia Microbiol 38:341–344
Awalina HA, Haryani GS, Setiadi T (2017) Equilibrium and kinetic modelling of cadmium (II) biosorption by Dried Biomass Aphanothece sp. From aqueous phase. Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 65:1–13
Balaji S, Kalaivani T, Rajasekaran C, Siva R, Shalini M, Das R, Madnokar V, Dhamorikar P (2015) Bioremediation potential of Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina) against chromium(VI). CLEAN Soil Air Water 43:1018–1024
Barakat MA (2011) New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arab J Chem 4:361–377
Bilal M, Rasheed T, Sosa-Hernández JE, Raza A, Nabeel F, Iqbal HMN (2018) Biosorption: an interplay between marine algae and potentially toxic elements—a review. Mar Drugs 65:1–16
Cain A, Vannela R, Woo LK (2008) Cyanobacteria as a biosorbent for mercuric ion. Bioresour Technol 99:6578–6586
Celekli A, Bozkurt H (2011) Bio-sorption of cadmium and nickel ions using Spirulina platensis: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Desalination 275:141–147
Çelekli A, Yavuzatmaca M, Bozkurt H (2010) An eco-friendly process: predictive modelling of copper adsorption from aqueous solution on Spirulina platensis. J Hazard Mater 173:123–129
Chojnacka K, Chojnacki A, Górecka H (2005) Biosorption of Cr3+, Cd2+ and Cu2+ ions by blue–green algae Spirulina sp.: kinetics, equilibrium and the mechanism of the process. Chemosphere 59:75–84
Clares ME, Guerrero MG (2015) Garcı’a-Gonza’lez M (2015). Cadmium removal by Anabaena sp. ATCC 33047 immobilized in polyurethane foam. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:1793–1798
Corder SL, Reeves M (1994) Biosorption of nickel in complex aqueous waste streams by cyanobacteria. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 45:847–859
De Philippis R, Paperi R, Sili C, Vincenzini M (2003) Assessment of the metal removal capability of two capsulated cyanobacteria, Cyanospira capsulata and Nostoc PCC7936. J Appl Phycol 15:155–161
Dixit S, Singh DP (2013) Phycoremediation of lead and cadmium by employing Nostoc muscorum as biosorbent and optimization of its biosorption potential. Int J Phytoremediation 15:801–813
El-Enany AE, Issa AA (2000) Cyanobacteria as a biosorbent of heavy metals in sewage water. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 8:95–101
Fang L, Zhou C, Cai P, Chen W, Rong X, Dai K, Liang W, Gu J, Huang Q (2011) Binding characteristics of copper and cadmium by cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis. J Hazard Mater 190:810–815
Fiore MF, Trevors JT (1994) Cell composition and metal tolerance in cyanobacteria. Biometals 7:83–103
Gadd GM (2009) Biosorption: critical review of scientific rationale environmental importance and significance for significance for pollution treatment. J Chem Biotechnol 84:13–28
Gardea-Torresdey JL, Arenas JL, Webb R, Tiemann KJ (1998) Effects of carboxyl group esterification on metal binding ability of Synechococcus sp. PCC 7942 (Cyanobacteria). In: Proceedings of the joint conference on the environment. Kansas State University, Manhattan, pp 105–109
Gong R, Ding Y, Liu H, Chen Q, Liu Z (2005) Lead biosorption and desorption by intact and pretreated Spirulina maxima biomass. Chemosphere 58:125–130
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2008) Sorption and desorption studies of chromium(VI) from nonviable cyanobacterium Nostoc muscorum biomass. J Hazard Mater 154:347–354
He J, Chen JP (2014) A comprehensive review on biosorption of heavy metals by algal biomass: materials, performances, chemistry, and modeling simulation tools. Bioresour Technol 160:67–78
Hoiczyk E, Hansel A (2000) Cyanobacterial cell walls: news from an unusual prokaryotic envelope. J Bacteriol 182:1191–1199
Incharoensakdi A, Kitjaharn P (2002) Zinc biosorption from aqueous solution by a halotolerant cyanobacterium Aphanothece halophytica. Curr Microbiol 45:261–264
Jiang J, Zhang N, Yang X, Song L, Yang S (2016) Toxic metal biosorption by macrocolonies of cyanobacterium Nostoc sphaeroides Kützing. J Appl Phycol 28:2265–2277
Kananarlapudi SLRK, Chintalpudi VK, Muddada S (2018) Application of biosorption for removal of heavy metals from wastewater. In: Derco J, Varna B (eds) Biosorption, pp 69–116
Karna RR, Uma L, Subramanian G, Mohan PM (1999) Biosorption of toxic metal ions by alkali-extracted biomass of a marine cyanobacterium, Phormidium valderianum BDU 30501. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 15:729–732
Katırcıoğlu H, Aslım B, Türker AR, Atıc T, Beyat Y (2008) Removal of cadmium(II) ion from aqueous system by dry biomass, immobilized live and heat-inactivated Oscillatoria sp. H1 isolated from freshwater (Mogan Lake). Bioresour Technol 99:4185–4191
Kim J, Dodbiba G, Tanimura Y, Mitsuhashi K, Fukuda N, Okaya K, Matsuo S, Fujita T (2011) Leaching of rare-earth elements and their adsorption by using blue-green algae. Mater Trans 52:1799–1806
Klimmek S, Stan HJ (2001) Comparative analysis of the biosorption of cadmium, lead, nickel, and zinc by algae. Environ Sci Technol 35:4283–4288
Kretschmer XC, Meitzner G, Gardea-Torresdey JL, Webb R (2004) Determination of Cu environments in the cyanobacterium Anabaena flos-aquae by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:771–780
Lou H, Cao X, Yan X, Wang L, Chen Z (2018) Adsorption performance of Cd(II), Cr(III), Cu(II), Ni(II), Pb(II) and Zn(II) by aminated solution-blown polyacrylonitrile micro/nanofibers. Water Sci Technol 2017:378–389
Michalak I, Chojnacka K, Witek-Krowiak A (2013) State of the art for the biosorption process—a review. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170:1389–1416
Micheletti E, Colica G, Viti C, Tamagnini P, De Philippis R (2008a) Selectivity in the heavy metal removal by exopolysaccharide-producing cyanobacteria. J Appl Microbiol 105:88–94
Micheletti E, Pereira S, Mannelli F, Moradas-Ferreira P, Tamagnini P, De Philippis R (2008b) Sheathless mutant of cyanobacterium Gloeothece sp. strain PCC 6909 with increased capacity to remove copper ions from aqueous solutions. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2797–2804
Mohammed AS, Kapri A, Goe R (2011) Heavy metal pollution: source, impact, and remedies. In: Khan MS, Zaidi A, Goel R, Musarrat J (eds) Biomanagement of metal-contaminated soils, pp 1–28
Morsy FM, Hassan SHA, Koutb M (2011) Biosorption of cd(II) and Zn(II) by Nostoc commune: isotherm and kinetics studies. CLEAN-Soil, Air, Water 36:680–687
Murugesan AG, Maheswari S, Bagirath G (2008) Biosorption of cadmium by live and immobilized cells of Spirulina Platensis. Int J Environ Res 2:307–312
Ozturk S, Aslim B, Suludere Z (2009) Evaluation of chromium (VI) removal behavior by two isolates of Synechocystis sp. in terms of exopolysaccharide (EPS) production and monomer composition. Bioresour Technol 100:5588–5593
Pandi M, Shashirekha V, Swamy M (2009) Bioabsorption of chromium from retan chrome liquor by cyanobacteria. Microbiol Res 164:420–428
Paperi R, Micheletti E, De Philippis R (2006) Optimization of copper sorbing–desorbing cycles with confined cultures of the exopolysaccharide-producing cyanobacterium Cyanospira capsulata. J Appl Microbiol 101:1351–1356
Pathak J, Rajneesh MPK, Singh SP, Häder DP, Sinha RP (2018) Cyanobacterial farming for environment friendly sustainable agriculture practices: innovations and perspectives. Front Environ Sci 6:1–13
Plude JL, Parker DL, Schommer OJ, Timmerman RJ, Hagstrom SA, Joers JM, Hnasko R (1991) Chemical characterization of polysaccharide from the slime layer of the cyanobacterium Microcystis flosaquae C3-40. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:1696–1700
Pradhan S, Rai LC (2000) Optimization of flow rate, initial metal ion concentration and biomass density for maximum removal of Cu2+ by immobilized Microcystis. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 16:579–584
Pradhan S, Rai LC (2001) Copper removal by immobilized Microcystis aeruginosa in continuous flow columns at different bed heights: study of the adsorption/desorption cycle. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 17:829–832
Prahan S, Singh S, Rai LC (2007) Characterization of various functional groups present in the capsule of Microcystis and study of their role in biosorption of Fe, Ni and Cr. Bioresour Technol 98:595–601
Rai PK, Tripathi BD (2007) Removal of heavy metals by the nuisance cyanobacteria Microcystis in continuous cultures: an eco-sustainable. Technol Environ Sci 4:53–59
Rangsayatorn N, Pokethitiyook P, Upatham ES, Lanza GR (2004) Cadmium biosorption by cells of Spirulina platensis TISTR 8217 immobilized in alginate and silica gel. Environ Int 30:57–63
Rezaei H (2016) Biosorption of chromium by using Spirulina sp. Arab J Chem 9:846–853
Rzymski P, Niedzielski P, Karczewski J, Poniedziałek B (2014) Biosorption of toxic metals using freely suspended Microcystis aeruginosa biomass. Cent Eur J Chem 12:1232–1238
Singh S (2014) A review on possible elicitor molecules of cyanobacteria: their role in improving plant growth and providing tolerance against biotic or abiotic stress. J Appl Microbiol 117:1364–5072
Solisio C, Lodi A, Soletto D, Converti A (2008) Cadmium biosorption on Spirulina platensis biomass. Bioresour Technol 99:5933–5937
Sun F, Wu F, Liao H, **ng B (2011) Biosorption of antimony(V) by freshwater cyanobacteria Microcystis biomass: chemical modification and biosorption mechanisms. Chem Eng J 171:1082–1090
Tease BE, Walker RW (1987) Comparative composition of the sheath of the cyanobacterium Gloeothece ATCC 27152 cultured with and without combined nitrogen. J Gen Microbiol 133:3331–3339
Verma R, Dwivedi P (2013) Heavy metal water pollution-a case study. Recent Res Sci Technol 5:98–99
Vijayaraghavan R, Ellappan V, Dharmar P, Lakshmanan U (2018) Preferential adsorption of uranium by functional groups of the marine unicellular cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus BDU130911. 3 Biotech 8:170
Wang J, Chen C (2009) Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnol Adv 27:195–226
Wang K, Liu Y, Li D (2010) Biosorption of copper by cyanobacterial bloom-derived biomass harvested from the eutrophic Lake Dianchi in China. Curr Microbiol 61:340–345
Weckesser J, Hofmann K, Jürgens UJ, Whitton BA, Raffelsberger B (1988) Isolation and chemical analysis of the sheaths of the filamentous cyanobacteria Calothrix parietina and C. scopulorum. J Gen Microbiol 134:629–634
WonKwak H, KonKim M, YunLee J, Yun H, HwaKim M, Park YH, Lee KH (2015) Preparation of bead-type biosorbent from water-soluble Spirulina platensis extracts for chromium (VI) removal. Algal Res 7:92–99
Yee N, Benning LG, Phoenix VR, Ferris FG (2004) Characterization of metal-cyanobacteria sorption reactions: a combined macroscopic and infrared spectroscopic investigation. Environ Sci Technol 38:775–782
Zhang D, Pan X, Zhao L, Mu G (2011) Biosorption of antimony (Sb) by the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. Pol J Environ Stud 20:1353–1358
Zinicovscaia I, Cepoi L, Valuta A, Rudi L, Culicov OA, Frontasyeva MV, Kirkesali EI, Pavlov SS, Tatiana M (2014) Nostoc Linckia as biosorbent of chromium and nickel from electroplating industry wastewaters. J Mater Sci Eng B 4:242–247
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Singh, S. (2020). Biosorption of Heavy Metals by Cyanobacteria: Potential of Live and Dead Cells in Bioremediation. In: Shah, M. (eds) Microbial Bioremediation & Biodegradation. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1812-6_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1812-6_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-1811-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-1812-6
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)