Abstract
Research on antimicrobial peptides is continuously growing because of the possibilities of applications they offer in different domains including food safety, human medicine, and plant biocontrol (phytosanitary).
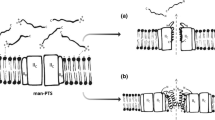
The present chapter is aiming to shed lights on diversity, function and structure of ribosomally synthesized antimicrobial peptides from Gram positive bacteria usually referred to as bacteriocins. In bacterial systems, competition is often driven by the production of bacteriocins; narrow spectrum proteinaceous toxins that serve to kill closely related species providing the producer better access to limited resources. Despite high levels of bacteriocin diversity, these proteins share many general characteristics. They are generally high molecular weight protein antibiotics that kill closely related strains or species. The bacteriocin gains entry into the target cell by recognizing specific cell surface receptors and then kills the cell by forming ion-permeable channels in the cytoplasmic membrane, by nonspecific degradation of cellular DNA, by inhibition of protein synthesis through the specific cleavage of 16s rRNA, or by cell lysis. In this chapter, the limits and performances of production will be presented. Further clear evidences on their aptitudes to master growth of microbes will be discussed as well as the main achievements and perspectives of their applications in food, environment and medical domains.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abriouel H, Valdivia E, Gálvez A, Maqueda M (1998) Response of Salmonella choleraesuis LT2 spheroplasts and permeabilized cells to the bacteriocin AS-48. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4623–4626
Acuña L, Morero RD, Bellomio A (2010) Development of wide spectrum hybrid bacteriocins for food biopreservation. Food Bioprocess Technol 4:1029–1049
Ananou S, Valdivia E, Martínez-Bueno M, Gálvez A, Maqueda M (2004) Effect of combined physico-chemical preservatives on enterocin AS-48 activity against the enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus CECT 976 strain. J Appl Microbiol 97:48–56
Ananou S, Garriga M, Hugas M, Maqueda M, Martínez-Bueno M, Gálvez A, Valdivia E (2005a) Control of Listeria monocytogenes in model sausages by enterocin AS-48. Int J Food Microbiol 103:179–190
Ananou S, Maqueda M, Martínez-Bueno M, Gálvez A, Valdivia E (2005b) Control of Staphylococcus aureus in sausages by enterocin AS-48. Meat Sci 71:549–576
Anastasiou R, Georgalaki M, Manolopoulou E, Kandarakis I, De Vuyst L, Tsakalidou E (2007) The performance of Streptococcus macedonicus ACA-DC 198 as starter culture in Kasseri cheese production. Int Dairy J 17:208–217
Angulo FJ, Getz J, Taylor JP, Hendricks KA, Hatheway CL, Barth SS, Solomon HM, Larson AE, Johnson EA, Nickey LN, Reis AA (1998) A large outbreak of botulism: the hazardous baked potato. J Infect Dis 178:172–177
Annamalai N, Manivasagan P, Balasubramanian T, Vijayalakshmi S (2009) Enterocin from Enterococcus faecium isolated from mangrove environment. Afr J Biotechnol 8:6311–6316
Aymerich MT, Garriga M, Ylla J, Vallier J, Monfort JM, Hugas M (2000) Application of enterocins as biopreservatives against Listeria innocua in meat products. J Food Prot 63:721–726
Aymerich MT, Garriga M, Costa S, Monfort JM, Hugas M (2002) Prevention of ropiness in cooked pork by bacteriocinogenic cultures. Int Dairy J 12:239–246
Balaban N, Rasooly A (2000) Staphylococcal enterotoxins. Int J Food Microbiol 61:1–10
Bari ML, Ukuku DO, Kawasaki T, Inatsu Y, Isshiki K, Kawamoto S (2005) Combined efficacy of nisin and pediocin with sodium lactate, citric acid, phytic acid, and potassium sorbate and EDTA in reducing the Listeria monocytogenes population of inoculated fresh-cut produce. J Food Prot 68:1381–1387
Ben Omar N, Abriouel H, Lucas R, Martínez-Cañamero M, Guyot JP, Gálvez A (2006) Isolation of bacteriocinogenic Lactobacillus plantarum strains from ben saalga, a traditional fermented gruel from Burkina Faso. Int J Food Microbiol 112:44–50
Benech RO, Kheadr EE, Lacroix C, Fliss I (2003) Impact of nisin producing culture and liposome-encapsulated nisin on ripening of Lactobacillus added-Cheddar cheese. J Dairy Sci 86:1895–1909
Benkerroum N, Sandine WE (1988) Inhibitory action of nisin against Listeria monocytogenes. J Dairy Sci 71:3237–3245
Benkerroum N, Oubel H, Mimoun LB (2002) Behavior of Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus in yogurt fermented with a bacteriocin-producing thermophilic starter. J Food Prot 65:799–805
Beuchat LR (1996) Pathogenic microorganisms associated with fresh produce. J Food Prot 59:204–216
Boziaris IS, Humpheson L, Adams MR (1998) Effect of nisin on heat injury and inactivation of Salmonella enteritidis PT4. Int J Food Microbiol 43:7–13
Branen JK, Davidson PM (2004) Enhancement of nisin, lysozyme, and monolaurin antimicrobial activities by ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and lactoferrin. Int J Food Microbiol 90:63–74
Breukink E, Wiedemann I, van Kraaij C, Kuipers OP, Sahl H, de Kruijff B (1999) Use of the cell wall precursor lipid II by a pore-forming peptide antibiotic. Science 5448:2361–2364
Brown JL, Ross T, McMeekin TA, Nichols PD (1997) Acid habituation of Escherichia coli and the potential role of cyclopropane fatty acids in low pH tolerance. Int J Food Microbiol 37:163–173
Buyong N, Kok J, Luchansky JB (1998) Use of a genetically enhanced, pediocin-producing starter culture, Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis MM217, to control Listeria monocytogenes in cheddar cheese. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4842–4845
Calderón-Miranda ML, Barbosa-Cánovas GV, Swanson BG (1999) Inactivation of Listeria innocua in skim milk by pulsed electric fields and nisin. Int J Food Microbiol 51:19–30
Callewaert R, Hugas M, De Vuyst L (2000) Competitiveness and bacteriocin production of enterococci in the production of Spanish-style dry fermented sausages. Int J Food Microbiol 57:33–42
Carneiro de Melo AM, Cassar CA, Miles RJ (1998) Trisodium phosphate increases sensitivity of gram-negative bacteria to lysozyme and nisin. J Food Prot 61:839–843
Carr FJ, Chill D, Maida N (2002) The lactic acid bacteria: a literature survey. Crit Rev Microbiol 28:281–370
Cheville AM, Arnold KW, Buchrieser C, Cheng CM, Kaspar CW (1996) rpoS regulation of acid, heat, and salt tolerance in Escherichia coli O157:H7. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1822–1824
Cintas LM, Casaus P, Håvarstein LS, Hernández PE, Nes IF (1997) Biochemical and genetic characterization of enterocin P, a novel sec-dependent bacteriocin from Enterococcus faecium P13 with a broad antimicrobial spectrum. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4321–4330
Cintas LM, Casaus P, Fernandez MF, Hernandez PE (1998) Comparative antimicrobial activity of enterocin L50, pediocin PA-1, nisin A and lactocin S against spoilage and food borne pathogenic bacteria. Food Microbiol 15:289–298
Coderre PE, Somkuti GA (1999) Cloning and expression of the pediocin operon in Streptococcus thermophilus and other lactic fermentation bacteria. Curr Microbiol 39:295–301
Cole K, Farnell MB, Donoghue AM, Stern NJ, Svetoch EA, Eruslanov BN, Volodina LI, Kovalev YN, Perelygin VV, Mitsevich EV, Mitsevich IP, Levchuk VP, Pokhilenko VD, Borzenkov VN, Svetoch OE, Kudryavtseva TY, Reyes-Herrera I, Blore PJ, Solis de los Santos F, Donoghue DJ (2006) Bacteriocins reduce Campylobacter colonization and alter gut morphology in turkey poults. Poult Sci 85:1570–1575
Cotter PD, Hill C, Ross RP (2005) Bacteriocins: develo** innate immunity for food. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:777–788
Cutter CN, Siragusa GR (1995) Treatments with nisin and chelators to reduce Salmonella and Escherichia coli on beef. J Food Prot 58:1028–1030
Davies EA, Delves-Broughton J (1999) Nisin. In: Robinson R, Batt C, Patel P (eds) Encyclopedia of food microbiology. Academic, London, pp 191–198
De Vuyst L, Leroy F (2007) Bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria: production, purification, and food applications. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 13:194–199
De Vuyst L, Vandamme EJ (1994) Bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria: microbiology, genetics and applications. Blackie Academic & Professional, London
Delves-Broughton J, Williams GC, Wilkinson S (1992) The use of bacteriocin, nisin, as a preservative in pasteurized liquid whole egg. Lett Appl Microbiol 15:133–136
Delves-Broughton J, Blackburn P, Evans RJ, Hugenholtz J (1996) Applications of the bacteriocin, nisin. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 69:193–202
Doan CH, Davidson PM (2000) Microbiology of potatoes and potato products: a review. J Food Prot 63:668–683
EFSA (2007) Introduction of a Qualified Presumption of Safety (QPS) approach for assessment of selected microorganisms referred to EFSA1. The EFSA J 587:1–16
EFSA (2010) The community summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses and zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in the European Union in 2008. J EFSA 8(1):1496 [pp. 410]. doi:10. 2903/j.efsa.2010.1496
Eijsink VG, Skeie M, Middelhoven PH, Brurberg MB, Nes IF (1998) Comparative studies of Class IIa bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3275–3281
Ennahar S, Assobhel O, Hasselmann C (1998) Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes in a smear-surface soft cheese by Lactobacillus plantarum WHE 92, a pediocin AcH producer. J Food Prot 61:186–191
Fang TJ, Lin LW (1994a) Growth of Listeria monocytogenes and Pseudomonas fragi on cooked pork in a modified atmosphere packaging/nisin combination system. J Food Prot 57:479–485
Fang TJ, Lin LW (1994b) Inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes on raw pork treated with modified atmosphere packaging and nisin. J Food Drug Anal 2:189–200
Farías ME, de Ruiz Holgado AP, Sesma F (1994) Bacteriocin production by lactic acid bacteria isolated from regional cheeses: inhibition of foodborne pathogens. J Food Prot 57:1013–1015
Farías ME, Nuñez de Kairuz M, Sesma F, Palacios J, de Ruiz Holgado AP, Oliver G (1999) Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes by the bacteriocin enterocin CRL35 during goat cheese making. Milchwissenschaft 54:30–32
Ferreira A, Canal N, Morales D, Fuentefria D, Corção G (2007) Characterization of enterocins produced by Enterococcus mundtii isolated from humans feces. Braz Arch Biol Technol 50:249–258
Foulquié Moreno MR, Sarantinopoulos P, Tsakalidou E, De Vuyst L (2006) The role and application of enterococci in food and health. Int J Food Microbiol 106:1–24
Gálvez A, Lucas-López R, Abriouel H, Valdivia E, Ben Omar N (2008) Application of bacteriocins in the control of foodborne pathogenic and spoilage bacteria. Crit Rev Biotechnol 28:125–152
Gálvez A, Valdivia E, Abriouel H, Camafeita E, Mendez E, Martinez-Bueno M, Maqueda M (1998) Isolation and characterization of enterocin EJ97, a bacteriocin produced by Enterococcus faecalis EJ97. Arch Microbiol 171(1):59–65
Gänzle MG, Weber S, Hammes WP (1999) Effect of ecological factors on the inhibitory spectrum and activity of bacteriocins. Int J Food Microbiol 46:207–217
García P, Rodríguez L, Rodríguez A, Martínez B (2010) Food biopreservation: promising strategies using bacteriocins, bacteriophages and endolysins. Trends Food Sci Technol 21:373–382
Ge J, ** W, Song G, Du C, Ling H, Sun X (2009) Paracin 1.7, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus paracasei HD1.7 isolated from Chinese cabbage sauerkraut, a traditional Chinese fermented vegetable food. Wei sheng wu xue bao. Acta Microbiol Sin 49:609–616
Georgalaki MD, Van den Berghe E, Kritikos D, Devreese B, Van Beeumen J, Kalantzopoulos G, De Vuyst L, Tsakalidou E (2002) Macedocin, a food-grade lantibiotic produced by Streptococcus macedonicus ACA-DC 198. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5891–5903
Gill AO, Holley RA (2000a) Inhibition of bacterial growth on ham and bologna by lysozyme, nisin and EDTA. Food Res Int 33:83–90
Gill AO, Holley RA (2000b) Surface application of lysozyme, nisin, and EDTA to inhibit spoilage and pathogenic bacteria on ham and bologna. J Food Prot 63:1338–1346
Giraffa G (1995) Enterococcal bacteriocins: their potential as anti- Listeria factors in dairy technology. Food Microbiol 12:291–299
Glass KA, Loeffelholz JM, Ford JP, Doyle MP (1992) Fate of Escherichia coli O157:H7 as affected by pH or sodium chloride and in fermented, dry sausage. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2513–2516
Gould GW (1995) Homeostatic mechanisms during food preservation by combined methods. In: Welti-Chanes J, Barbosa-Canovas G (eds) Food preservation by moisture control – fundamentals and applications. Technomic Publishing Co., Lancaster, pp 397–410
Grande MJ, Lucas R, Valdivia E, Abriouel H, Maqueda M, Martínez-Cañamero M, Ben Omar N, Gálvez A (2005) Stability of enterocin AS-48 in fruit and vegetable juices. J Food Prot 68:2085–2094
Grande MJ, Lucas R, Abriouel H, Valdivia E, Ben Omar N, Maqueda M, Martínez-Bueno M, Martínez-Cañamero M, Gálvez A (2006) Inhibition of toxicogenic Bacillus cereus in rice-based foods by enterocin AS-48. Int J Food Microbiol 106:185–194
Grande MJ, Lucas R, Abriouel H, Valdivia E, Ben Omar N, Maqueda M (2007) Treatment of vegetable sauces with enterocin AS-48 alone or in combination with phenolic compounds to inhibit proliferation of Staphylococcus aureus. J Food Prot 70:405–411
Hammami R, Zouhir A, Le Lay C, Ben Hamida J, Fliss I (2010) BACTIBASE second release: a database and tool platform for bacteriocin characterization. BMC Microbiol 10:22
Hampikyan H, Ugur M (2007) The effect of nisin on L. monocytogenes in Turkish fermented sausages (sucuks). Meat Sci 76:327–332
Hanlin MB, Kalchayanand N, Ray P, Ray B (1993) Bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria in combination have a greater antibacterial activity. J Food Prot 56:252–255
Helander IM, Mattila-Sandholm T (2000) Permeability barrier of the gram-negative bacterial outer membrane with special reference to nisin. Int J Food Microbiol 60:153–161
Hirsch A, Grinsted E, Chapman HR, Mattick ATR (1951) A note on the inhibition of an anaerobic spore former in Swiss-type cheese by a nisin-producing Streptococcus. J Dairy Res 18:205–206
Holck AL, Axelsson L, Huhme K, Krockel L (1994) Purification and cloning of sakacin 674, a bacteriocin from Lactobacillus sake Lb674. FEMS Microbiol Lett 115:143–150
Hugas M, Garriga M, Aymerich T (2003) Functionality of enterococci in meat products. Int J Food Microbiol 88:223–233
Jennes W, Dicks LM, Verwoerd DJ (2000) Enterocin 012, a bacteriocin produced by Enterococcus gallinarum isolated from the intestinal tract of ostrich. J Appl Microbiol 88:349–357
Jørgensen HJ, Maticen T, Løvseth A, Oboe K, Qvale KS, Loncarevic S (2005) An outbreak of staphylococcal food poisoning caused by enterotoxin H in mashed potato made with raw milk. FEMS Microbiol Lett 252:267–272
Kalchayanand N, Hanlin MB, Ray B (1992) Sublethal injury makes Gram-negative and resistant Gram-positive bacteria sensitive to the bacteriocins, pediocin AcH and nisin. Lett Appl Microbiol 15:239–243
Kang JH, Lee MS (2005) Characterization of a bacteriocin produced by Enterococcus faecium GM-1 isolated from an infant. J Appl Microbiol 98:1169–1176
Klaenhammer TR (1993) Genetics of bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 12:39–85
Knight KP, Bartlett FM, McKellar RC, Harris LJ (1999) Nisin reduces the thermal resistance of Listeria monocytogenes Scott A in liquid whole egg. J Food Prot 62:999–1003
Komitopoulou E, Boziaris IS, Davies EA, Delves-Broughton J, Adams MR (1999) Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris in fruit juices and its control by nisin. Int J Food Sci Technol 34:81–85
Lauková A, Czikková S (1999) The use of enterocin CCM 4231 in soy milk to control the growth of Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus. J Appl Microbiol 87:182–186
Lauková A, Czikková S (2001) Antagonistic effect of enterocin CCM 4231 from Enterococcus faecium on “bryndza”, a traditional Slovak dairy product from sheep milk. Microbiol Res 156:31–34
Lauková A, Czikková S, Burdova O (1999a) Anti-staphylococcal effect of enterocin in Sunar and yogurt. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 44:707–711
Lauková A, Czikková S, Dóbransky T, Burdova O (1999b) Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus by enterocin CCM4231 in milk products. Food Microbiol 16:93–99
Lauková A, Czikková S, Laczková S, Turek P (1999c) Use of enterocin CCM 4231 to control Listeria monocytogenes in experimentally contaminated dry fermented Horn’ad salami. Int J Food Microbiol 52:115–119
Lauková A, Vlaemynick G, Czikková S (2001) Effect of enterocin CCM 4231 on Listeria monocytogenes in Saint-Paulin cheese. Folia Microbiol 46:157–160
Le Loir Y, Baron F, Gautier M (2003) Staphylococcus aureus and food poisoning. Genet Mol Res 2:63–76
Leverentz B, Conway WS, Camp MJ, Janisiewicz WJ, Abuladze T, Yang M, Saftner R, Sulakvelidze A (2003) Biocontrol of Listeria monocytogenes on fresh-cut produce by treatment with lytic bacteriophages and a bacteriocin. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4519–4526
Leyer GJ, Wang LL, Johnson EA (1995) Acid adaptation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 increases survival in acidic foods. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3752–3755
Liang Z, Mittal GS, Griffiths MW (2002) Inactivation of Salmonella Typhimurium in orange juice containing antimicrobial agents by pulsed electric field. J Food Prot 65:1081–1087
Loessner M, Guenther S, Steffan S, Scherer S (2003) A pediocin-producing Lactobacillus plantarum strain inhibits Listeria monocytogenes in a multispecies cheese surface microbial ripening consortium. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1854–1857
Lucas R, Grande MJ, Abriouel H, Maqueda M, Ben Omar N, Valdivia E, Martínez-Cañamero M, Gálvez A (2006) Application of the broad-spectrum bacteriocin enterocin AS-48 to inhibit Bacillus coagulans in low-pH canned fruit and vegetable foods. Food Chem Toxicol 44:1774–1781
Lüders T, Birkemo GA, Fimland G, Nissen-Meyer J, Nes IF (2003) Strong synergy between a eukaryotic antimicrobial peptide and bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1797–1799
Lyon WJ, Glatz BA (1993) Isolation and purification of propionicin PLG-1, a bacteriocin produced by a strain of Propionibacterium thoenii. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:83–88
Lyon WJ, Sethi JK, Glatz BA (1993) Inhibition of psychrotrophic organisms by propionicin PLG-1, a bacteriocin produced by Propionibacterium thoenii. J Dairy Sci 76:1506–1513
Maisnier-Patin S, Deschamps N, Tatini SR, Richard J (1992) Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes in Camembert cheese made with a nisin-producing starter. Lait 72:249–263
Mathot AG, Beliard E, Thuault D (2003) Streptococcus thermophilus 580 produces a bacteriocin potentially suitable for inhibition of Clostridium tyrobutyricum in hard cheese. J Dairy Sci 86:3068–3074
Meindl K, Schmiederer T, Schneider K, Reicke A, Butz D, Keller S, Gühring H, Vértesy L, Wink J, Hoffmann H, Brönstrup M, Sheldrick GM, Süssmuth RD (2010) Labyrinthopeptins: a new class of carbacyclic lantibiotics. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 49:1151–1154
Messaoudi S, Kergourlay G, Rossero A, Ferchichi M, Prévost H, Drider D, Manai M, Dousset X (2011) Identification of lactobacilli residing in chicken ceca with antagonism against Campylobacter. Int Microbiol 14:103–110
Mills S, Stanton C, Hill C, Ross RP (2011) New developments and applications of bacteriocins and peptides in foods. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 2:299–329
Molinos AC, Abriouel H, López RL, Valdivia E, Ben Omar N, Gálvez A (2008) Combined physico-chemical treatments based on enterocin AS-48 for inactivation of Gram-negative bacteria in soybean sprouts. Food Chem Toxicol 46:2912–2921
Montville TJ, Winkowski K, Ludescherer RD (1995) Models and mechanisms for bacteriocin action and application. Int Dairy J 5:797–814
Morgan SM, Garvin M, Kelly J, Ross RP, Hill C (1999) Development of a lacticin 3147-enriched whey powder with inhibitory activity against foodborne pathogens. J Food Prot 62:1011–1016
Morgan SM, Ross RP, Beresford T, Hill C (2000) Combination of hydrostatic pressure and lacticin 3147 causes increased killing of Staphylococcus and Listeria. J Appl Microbiol 88:414–420
Morgan SM, Garvin M, Ross RP, Hill C (2001) Evaluation of a spray-dried lacticin 3147 powder for the control of Listeria monocytogenes and Bacillus cereus in a range of food systems. Lett Appl Microbiol 33:387–391
Morris SL, Walsh RC, Hansen JN (1984) Identification and characterization of some bacterial membrane sulfhydryl groups which are targets of bacteriostatic and antibiotic action. J Biol Chem 259:13590–13594
Mulet-Powell N, Lactoste-Armynot AM, Vinas M, Simeon De Buochberg M (1998) Interactions between pairs of bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria. J Food Prot 61:1210–1212
Muñoz A, Maqueda M, Gálvez A, Martínez-Bueno M, Rodríguez A, Valdivia E (2004) Biocontrol of psychrotrophic enterotoxigenic Bacillus cereus in a non fat hard type cheese by an enterococcal strain-producing enterocin AS-48. J Food Prot 67:1517–1521
Muñoz A, Ananou S, Gálvez A, Martínez-Bueno M, Rodríguez A, Maqueda M, Valdivia E (2007) Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus in dairy products by enterocin AS-48 produced in situ and ex situ: bactericidal synergism through heat and AS-48. Int Dairy J 17:760–769
Murdock CA, Cleveland J, Matthews KR, Chikindas ML (2007) The synergistic effect of nisin and lactoferrin on the inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli O157:H7. Lett Appl Microbiol 44:255–261
Muriana PM (1996) Bacteriocins for control ofListeria spp. in food. J Food Prot 59:S54–S63
Nazef L, Belguesmia Y, Tani A, Prévost H, Drider D (2008) Identification of lactic acid bacteria from poultry feces: evidence on anti-campylobacter and anti-listeria activities. Poult Sci 87:329–334
Nissen H, Holo H, Axelsson L, Blom H (2001) Characterization and growth of Bacillus spp. in heat-treated cream with and without nisin. J Appl Microbiol 90:530–534
O’Mahony T, Rekhif N, Cavadini C, Fitzgerald GF (2001) The application of a fermented food ingredient containing ‘variacin’, a novel antimicrobial produced by Kocuria varians, to control the growth of Bacillus cereus in chilled dairy products. J Appl Microbiol 90:106–114
Ortega E, Abriouel H, Lucas R, Gálvez A (2010) Multiple roles of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins: pathogenicity, superantigenic activity, and correlation to antibiotic resistance. Toxins 2:2117–2131
Parente E, Hill C (1992) Inhibition of Listeria in buffer, broth, and milk by enterocin 1146, a bacteriocin produced by Enterococcus faecium. J Food Prot 55:503–508
Pawar DD, Malik SVS, Bhilegaonkar KN, Barbuddhe SB (2000) Effect of nisin and its combination with sodium chloride on the survival of Listeria monocytogenes added to raw buffalo meat mince. Meat Sci 56:215–219
Pedersen MB, Iversen SL, Sørensen KI, Johansen E (2005) The long and winding road from the research laboratory to industrial applications of lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:611–624
Pettipher GL, Osmundson ME, Murphy JM (1997) Methods for the detection and enumeration of Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris and investigations of growth and taint in fruit juice and fruit-containing drinks. Lett Appl Microbiol 24:185–189
Pol IE, Mastwijk HC, Slump RA, Popa ME, Smith EJ (2001) Influence of food matrix on inactivation of Bacillus cereus by combinations of nisin, pulsed electric field treatment, and carvacrol. J Food Prot 64:1012–1018
Presser KA, Ross T, Ratkowsky DA (1998) Modelling the Angrowth limits (growth/no growth interface) of Escherichia coli as a function of temperature, pH, lactic acid concentration, and water activity. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1773–1779
Raccach M, Geshell DJ (1993) The inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes in milk by pediococci. Food Microbiol 10:181–186
Rayman K, Malik N, Hurst A (1983) Failure of nisin to inhibit outgrowth of Clostridium botulinum in a model cured meat system. Appl Environ Microbiol 46:1450–1452
Rea MC, Ross P, Cotter PD, Hill C (2011) Classifications of bacteriocins from Gram positive bacteria. In: Drider D, Rebuffat S (eds) Prokaryotic antimicrobial peptides: from Geenes to applications. Springer, New York, 29–53. doi:10. 1007/978-1-4419-7692-5_3
Reitsma CJ, Henning DR (1996) Survival of enterohemor- rhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 during the manufacture and curing of cheddar cheese. J Food Prot 59:460–464
Reviriego C, Fernández L, Rodríguez JM (2007) A food-grade system for production of pediocin PA-1 in nisin-producing and nonnisin- producing Lactococcus lactis strains: application to inhibit Listeria growth in a cheese model system. J Food Prot 70:2512–2517
Rilla N, Martinez B, Delgado T, Rodriguez A (2003) Inhibition of Clostridium tyrobutyricum in Vidiago cheese by Lactococcus lactis ssp. Lactis IPLA 729, a nisin Z producer. Int J Food Microbiol 85(1–2):23–33
Rodríguez JL, Gaya P, Medina M, Núñez M (1997) Bactericidal effect of enterocin 4 on Listeria monocytogenes in a model dairy system. J Food Prot 60:28–32
Rodríguez E, Calzada J, Arqués JL, Rodríguez JM, Núñez M, Medina M (2005) Antimicrobial activity of pediocin-producing, Lactococcus lactis on Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli O157:H7 in cheese. Int Dairy J 15:51–57
Rose NL, Sporns P, Stiles ME, McMullen LM (1999) Inactivation of nisin by glutathione in fresh meat. J Food Sci 64:759–762
Ross RP, Galvin M, McAuliffe O, Morgan S, Ryan M, Twomey DP, Meaney WJ, Hill C (1999) Develo** applications for lactococcal bacteriocins. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 76:337–346
Sabia C, de Niederhäusern S, Messi P, Manicardi G, Bondi M (2003) Bacteriocin-producing Enterococcus casseliflavus IM 416K1, a natural antagonist for control of Listeria monocytogenes in Italian sausages (“cacciatore”). Int J Food Microbiol 87:173–179
Şahingil D, Işlero lu H, Yildirim Z, Akçelik M, Yildirim M (2011) Characterization of lactococcin BZ produced by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis BZ isolated from boza. Turk J Biol 35:21–33
Scannell AGM, Hill C, Buckley DJ, Arendt EK (1997) Determination of the influence of organic acids and nisin on shelflife and microbiological safety aspects of fresh pork sausage. J Appl Microbiol 83:407–412
Scannell AG, Ross RP, Hill C, Arendt EK (2000a) An effective lacticin biopreservative in fresh pork sausage. J Food Prot 63:370–375
Scannell AGM, Hill C, Ross RP, Marx S, Hartmeier W, Arendt EK (2000b) Development of bioactive food packaging materials using immobilised bacteriocins lacticin 3147 and Nisaplin. Int J Food Microbiol 60:241–249
Schillinger U, Becker B, Vignolo G, Holzapfel WH (2001) Efficacy of nisin in combination with protective cultures against Listeria monocytogenes Scott A in tofu. Int J Food Microbiol 71:159–168
Schuman JD, Sheldon BW (2003) Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes in pH-adjusted pasteurized liquid whole egg. J Food Prot 66:999–1006
Schved F, Henis Y, Juven BJ (1994) Response of spheroplasts and chelator-permeabilized cells of Gram-negative bacteria to the action of the bacteriocins pediocin SJ-1 and nisin. Int J Food Microbiol 21:305–314
Seo KS, Bohach GA (2007) Staphylococcus aureus. In: Doyle MP, Beuchat LR (eds) Food microbiology: fundamentals and frontiers, 3rd edn. ASM Press, Washington, DC, pp 493–518
Shefet SM, Sheldon BW, Klaenhammer TR (1995) Efficacy of optimized nisin-based treatments to inhibit Salmonella typhimurium and extend shelf life of broiler carcasses. J Food Prot 58:1077–1082
Sivarooban T, Hettiarachchy NS, Johnson MG (2007) Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes using nisin with grape seed extract on turkey frankfurters stored at 4 and 10°C. J Food Prot 70:1017–1020
Small P, Blankenhorn D, Welty D, Zinser E, Slonczewski JL (1994) Acid and base resistance in Escherichia coli and Shigella flexneri: role of rpoS and growth pH. J Bacteriol 176:1729–1737
Smaoui S, Elleuch L, Bejar W, Karray-Rebai I, Ayadi I, Jaouadi B (2010) Inhibition of fungi and gram-negative bacteria by bacteriocin BacTN635 produced by Lactobacillus plantarum sp. TN635. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 162:1132–1146
Sobrino-López A, Martín Belloso O (2006) Enhancing inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus in skim milk by combining highintensity pulsed electric fields and nisin. J Food Prot 69:345–353
Solomakos N, Govaris A, Koidis P, Botsoglou N (2008) The antimicrobial effect of thyme essential oil, nisin, and their combination against Listeria monocytogenes in minced beef during refrigerated storage. Food Microbiol 25:120–127
Somkuti GA, Steinberg DH (2003) Pediocin production by recombinant lactic acid bacteria. Biotechnol Lett 25:473–477
Stergiou VA, Thomas LV, Adams MR (2006) Interactions of nisin with glutathione in a model protein system and meat. J Food Prot 69:951–956
Stern NJ, Svetoch EA, Eruslanov BV, Perelygin VV, Mitsevich EV, Mitsevich IP, Pokhilenko VD, Levchuk VP, Svetoch OE, Seal BS (2006) Isolation of a Lactobacillus salivarius strain and purification of its bacteriocin, which is inhibitory to Campylobacter jejuni in the chicken gastrointestinal system. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50:3111–3116
Stevens KA, Sheldon BW, Klapes NA, Klaenhammer TR (1991) Nisin treatment for inactivation of Salmonella species and other Gram-negative bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:3612–3615
Sulzer G, Busse M (1991) Growth inhibition of Listeria spp. On Camembert cheese by bacteria producing inhibitory substances. Int J Food Microbiol 14:287–296
Svetoch EA, Eruslanov BV, Perelygin VV, Mitsevich EV, Mitsevich IP, Borzenkov VN (2008) Diverse antimicrobial killing by Enterococcus faecium E 50–52 bacteriocin. J Agric Food Chem 56:1942–1948
Tagg JR, Dajani AS, Wannamaker LW (1976) Bacteriocins of gram-positive bacteria. Bacteriol Rev 40:722–7256
Tamarapu S, McKillip JL, Drake M (2001) Development of a multiplex polymerase chain reaction assay for detection and differentiation of Staphylococcus aureus in dairy products. J Food Prot 64:664–668
Thomas LV, Delves-Broughton J (2001) New advances in the application of the food preservative nisin. Adv Food Sci 2:11–22
Thomas LV, Clarkson MR, Delves-Broughton J (2000) Nisin. In: Naidu AS (ed) Natural food antimicrobial systems. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 463–524
Thomas LV, Ingram RE, Bevis HE, Davies EA, Milne CF, Delves-Broughton J (2002) Effective use of nisin to control Bacillus and Clostridium spoilage of a pasteurized mashed potato product. J Food Prot 65:1580–1585
Tichaczek PS, Vogel RF, Hammes WP (1994) Cloning and sequencing of sakP encoding sakacin P, the bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus sake LHT673. Microbiology+ 140:361–367
Tirado C, Schimdt K (2001) WHO surveillance programme for control of foodborne infections and intoxications: preliminary results and trends across greater Europe. J Infect 43:80–84
Tsakalidou E, Zoidou E, Pot B, Wassill L, Ludwig W, Devriese LA, Kalantzopoulos G, Schleifer KH, Kersters K (1998) Identification of streptococci from Greek Kasseri cheese and description of Streptococcus macedonicus sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:519–527
Ukuku DO, Fett WF (2004) Effect of nisin in combination with EDTA, sodium lactate, and potassium sorbate for reducing Salmonella on whole and fresh-cut cantaloupet. J Food Prot 67:2143–2150
Valenzuela AS, Ben Omar N, Abriouel H, Lucas Lopez R, Ortega E, Martinez Canamero M, Gálvez A (2008) Risk factors in enterococci isolated from foods in Morocco: determination of antimicrobial resistance and incidence of virulence traits. Food Chem Toxicol 46:2648–2652
Van den Berghe E, Skourtas G, Tsakalidou E, DeVuyst L (2006) Streptococcus macedonicus ACA-DC 198 produces the lantibiotic, macedocin, at temperature and pH conditions that prevail during cheese manufacture. Int J Food Microbiol 107:138–147
Veras JF, Carmo LS, Tong LC, Shupp JW, Cummings C, Santos DA (2008) A study of the enterotoxigenicity of coagulase negative and coagulase positive staphylococcal isolates from food poisoning outbreaks in Minas Gerais, Brazil. Int J Infect Dis 12:410–415
Vignolo G, Fadda S, de Kairuz MN, de Ruiz Holgado AA, Oliver G (1996) Control of Listeria monocytogenes in ground beef by ‘Lactocin 705’, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus casei CRL 705. Int J Food Microbiol 29:397–402
Vignolo G, Fadda S, de Kairuz MN, Holgado APR, Oliver O (1998) Effects of curing additives on the control of Listeria monocytogenes by lactocin 705 in meat slurry. Food Microbiol 15:259–264
Vignolo G, Palacios J, Farias ME, Sesma F, Schillinger U, Holzapfel W, Oliver G (2000) Combined effect of bacteriocins on the survival of various Listeria species in broth and meat system. Curr Microbiol 41:410–416
WHO (2002) Statistical information on food-borne disease in Europe. Microbiological and chemical hazards. In: FAO/WHO Pan-European conference on food quality and safety, Budapest. Springer, pp 29–53. ISBN 978-1-4419-7691-8
Yuste J, Fung DY (2004) Inactivation of Salmonella Typhimurium and Escherichia coli O157:H7 in apple juice by a combination of nisin and cinnamon. J Food Prot 67:371–377
Zamfir M, Callewaert R, Cornea PC, Savu L, Vatafu I, De Vuyst L (1999) Purification and characterization of a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus acidophilus IBB 801. J Appl Microbiol 87:923–931
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Omar, N.B., Abriouel, H., Fliss, I., Ferandez-Fuentes, M.Á., Galvez, A., Drider, D. (2013). Bacteriocins: Natural Weapons for Control of Food Pathogens. In: Malik, A., Grohmann, E., Alves, M. (eds) Management of Microbial Resources in the Environment. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-5931-2_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-5931-2_19
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-007-5930-5
Online ISBN: 978-94-007-5931-2
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)