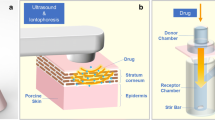
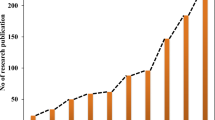
Abstract
Several strategies have been studied in the last decades in order to improve drug transport across the skin. Transdermal drug delivery systems represent a huge business opportunity for pharmaceutical industries. Although chemical enhancers have proven to be effective in promoting the transport of molecules throughout skin, the combination of chemical and physical/mechanical enhancers has shown a synergistic effect in most of the cases. This chapter reviews the enhancement effect of the combined use of sonophoresis, electroporation, and microneedles with chemical enhancers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander A, Dwivedi S, Ajazuddin, Giri TK, Saraf S, Saraf SH, Tripathi DK (2012) Approaches for breaking the barriers of drug permeation through transdermal drug delivery. J Control Release 164:26–40
Alvarez-Roman R, Merriono G, Kalia YN, Naik A, Guy R (2003) Skin permeability enhancement by low-frequency sonophoresis – lipid extraction and transport pathways. J Pharm Sci 92:1138–1146
Arora A, Prausnitz MR, Mitragotri S (2008) Micro-scale devices for transdermal drug delivery. Int J Pharm 364:227–236
Azagury A, Khoury L, Adato Y, Wolloch L, Ariel I, Hallak M, Kost J (2015) The synergistic effect of ultrasound and chemical penetration enhancers on chorioamnion mass transport. J Control Release 200:35–41
Badkar AV, Betageri GV, Hofmann GA, Banga AK (1999) Enhancement of transdermal iontophoretic delivery of a liposomal formulation of colchicine by electroporation. Drug Deliv 6(2):111–115
Badran MM, Kuntsche J, Fahr A (2009) Skin penetration enhancement by a microneedle device (Dermaroller) in vitro: dependency on needle size and applied formulation. Eur J Pharm Sci 36:511–523
Banga AK (2011) Skin electroporation and its applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Becker S, Zorec B, Miklavcic D, Pavselj N (2014) Transdermal transport pathway creation: electroporation pulse order. Math Biosci 257:60–68
Becker SM, Kuznetsov AV (2008) Thermal in vivo skin electroporation pore development and charged macromolecule transdermal delivery: a numerical study of the influence of chemically enhanced lower lipid phase transition temperatures. Int J Heat Mass Transf 51(7–8):2060–2074
Bonner MC, Barry BW (2006) Combined chemical and electroporation methods of skin penetration enhancement. In: Touitou E, Barry BW (eds) Enhancement in drug delivery. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Boucaud A (2004) Trends in the use of ultrasound-mediated transdermal drug delivery. Drug Discov Today 9:827–828
Brown MB, Martin GP, Jones SA, Akomeah FK (2006) Dermal and transdermal drug delivery systems: current and future prospects. Drug Deliv 13(3):175–187
Chen B, Wei J, Iliescu C (2010) Sonophoretic enhanced microneedles array (SEMA) – improving the efficiency of transdermal drug delivery. Sens Actuators B 145:54–60
Dahlan A, Alpar HO, Murdan S (2009) An investigation into the combination of low frequency ultrasound and liposomes on skin permeability. Int J Pharm 379:139–142
David N, Mahmood TA, Inventors, Kithera Biopharmaceuticals, Inc. Assignee (2010) Systems and methods for delivery of biologically active agents. WO 2010/056922 A2
Denet A-R, Vanbever R, Préat V (2004) Skin electroporation for transdermal and topical delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 56:659–674
Essa EA, Bonner MC, Barry BW (2003) Electroporation and ultradeformable liposomes; human skin barrier repair by phospholipid. J Control Release 92(1–2):163–172
Essa EA, Bonner MC, Barry BW (2004) Electrically assisted skin delivery of liposomal estradiol; phospholipid as damage retardant. J Control Release 95(3):535–546
Fang J-Y, Hwang T-L, Huang Y-B, Tsai Y-H (2002) Transdermal iontophoresis of sodium nonivamide acetate V. Combined effect of physical enhancement methods. Int J Pharm 235:95–105
Frenkel V (2008) Ultrasound mediated delivery of drugs and genes to solid tumors. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60:1193–1208
Gerstel MS, Place VA, Inventors, Alza Corporation (Palo Alto, CA) Assignee (1976) Drug delivery device. United States Patent US Patent 3 964 482
Haar G (2007) Therapeutic applications of ultrasound. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 93:111–129
Han T, Das DB (2013) Permeability enhancement for transdermal delivery of large molecule using low-frequency sonophoresis combined with microneedles. J Pharm Sci 102:3614–3622
Han T, Das DB (2015) Potential of combined ultrasound and microneedles for enhanced transdermal drug permeation: a review. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 89:312–328
Henry S, McAllister DV, Allen MG, Prausnitz MR (1998) Microfabricated microneedles: a novel approach to transdermal drug delivery. J Pharm Sci 87:922–925
Herwadkar A, Banga AK (2012) Peptide and protein transdermal drug delivery. Drug Discov Today Technol 9:e147–e154
Higaki K, Amnuaikit C, Kimura T (2003) Strategies for overcoming the stratum corneum. Am J Drug Deliv 1(3):187–214
Hosseinkhani H, Tabata Y (2005) Ultrasound enhances in vivo tumor expression of plasmid DNA by PEG-introduced cationized dextran. J Control Release 108:540–556
Husseini GA, Pitt WG (2008) Micelles and nanoparticles for ultrasonic drug and gene delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60:1137–1152
Ilic L, Gowrishankar TR, Vaughan TE, Herndon TO, Weaver JC (1999) Spatially constrained skin electroporation with sodium thiosulfate and urea creates transdermal microconduits. J Control Release 61(1–2):185–202
Ita K (2015) Transdermal delivery of heparin: physical enhancement techniques. Int J Pharm 496:240–249
Jiang G, Zhu D, Zan J, Ding F (2007) Transdermal drug delivery by electroporation: the effects of surfactants on pathway lifetime and drug transport. Chin J Chem Eng 15(3):397–402
Johnson M, Mitragotri S, Patel A, Blankschtein D, Langer R (1996) Synergistic effects of chemical enhancers and therapeutic ultrasound on transdermal drug delivery. J Pharm Sci 85:670–679
Joshi A, Raje J (2002) Sonicated transdermal transport. J Control Release 83:13–22
Kasetvatin Ch, Rujivipat S, Tiyaboonchai W (2015) Combination of elastic liposomes and low frequency ultrasound for skin permeation enhancement of hyaluronic acid. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 135:458–464
Khafagy E-S, Morishita M, Onuki Y, Takayama K (2007) Current challenges in non-invasive insulin delivery systems: a comparative review. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:1521–1546
Kim K, Choi SW, Kwak YH (2012) The effect of SonoPrep® on EMLA® cream application for pain relief prior to intravenous cannulation. Eur J Pediatr 171:985–988
Lavon I, Kost J (2004) Ultrasound and transdermal drug delivery. Drug Discov Today 9:670–676
Lavon I, Grossman N, Kost J (2005) The nature of ultrasound-SLS synergism during enhanced transdermal transport. J Control Release 107:484–494
Le L, Kost J, Mitragotri S (2000) Combined effect of low-frequency ultrasound and iontophoresis: applications for transdermal heparin delivery. Pharm Res 17:1151–1154
Lee SE, Choi KJ, Menon GK, Kim HJ, Choi EH, Ahn SK, Lee SH (2010) Penetration pathways induced by low-frequency sonophoresis with physical and chemical enhancers: iron oxide nanoparticles versus lanthanum nitrates. J Invest Dermatol 130:1063–1072
Liu H, Li S, Pan W, Wang Y, Han F, Yao H (2006) Investigation into the potential of low-frequency ultrasound facilitated topical delivery of Cyclosporine A. Int J Pharm 326(1–2):32–38
Lombry C, Dujardin N, Préat V (2000) Transdermal delivery of macromolecules using skin electroporation. Pharm Res 17(1):32–37
Lopez RFV, Seto JE, Blankschtein D, Langer R (2011) Enhancing the transdermal delivery of rigid nanoparticles using the simultaneous application of ultrasound and sodium lauryl sulfate. Biomaterials 32:933–941
Machet L, Boucaud A (2002) Phonophoresis: efficiency, mechanisms and skin tolerance. Int J Pharm 243:1–15
Mathur V, Satrawala Y, Rajput MS (2010) Physical and chemical penetration enhancers in transdermal drug delivery system. Asian J Pharm 4(3):173–183
Meidan VM, Walmsley AD, Irwin WJ (1995) Phonophoresis: is it a reality? Int J Pharm 118:129–149
Meidan V, Docker M, Wlamsley A, Irwin W (1998) Phonophoresis of hydrocortisone with enhancers: an acoustically defined model. Int J Pharm 170:157–168
Mitragotri S (2000) Synergistic effect of enhancers for transdermal drug delivery. Pharm Res 17(11):1354–1359
Mitragotri S (2004) Sonophoresis: a 50-year journey. Drug Discov Today 9:735–736
Mitragotri S (2013) Devices for overcoming biological barriers: the use of physical forces to disrupt the barriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65(1):100–103
Mitragotri S, Kost J (2004) Low-frequency sonophoresis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 56:589–601
Mitragotri S, Blankschtein D, Langer R (1995) Ultrasound-mediated transdermal protein delivery. Science 269:850–853
Mitragotri S, Blankschtein D, Langer R (1996) Transdermal drug delivery using low-frequency sonophoresis. Pharm Res 13:411–420
Mitragotri S, Ray D, Farrell J, Tang H, Yu B, Kost J, Blankschtein D, Langer R (2000) Synergistic effect of low-frequency ultrasound and sodium lauryl sulfate on transdermal transport. J Pharm Sci 89:892–900
Monti D, Giannelli R, Chetoni P, Burgalassi S (2001) Comparison of the effect of ultrasound and of chemical enhancers on transdermal permeation of caffeine and morphine through hairless mouse skin in vitro. Int J Pharm 229:131–137
Motlekar NA, Youan B-B (2006) The quest of non-invasive delivery of bioactive macromolecules: a focus on heparins. J Control Release 113:91–101
Murthy SN, Zhao Y-L, Sen A, Hui SW (2004a) Cyclodextrin enhanced transdermal delivery of piroxicam and carboxyfluorescein by electroporation. J Control Release 99:393–402
Murthy SN, Sen A, Hui SW (2004b) Surfactant-enhanced transdermal delivery by electroporation. J Control Release 98:307–315
Murthy SN, Zhao Y-L, Marlan K, Hui SW, Kazim AL, Sen A (2006) Lipid and electroosmosis enhanced transdermal delivery of insulin by electroporation. J Pharm Sci 95(9):2041–2050
Naik A, Kalia YN, Guy RH (2000) Transdermal drug delivery: overcoming the skin’s barrier function. Pharm Sci Technolo Today 3:318–326
Nava-Arzaluz MG, Calderón-Lojero I, Quintanar-Guerrero D, Villalobos-García R, Ganem-Quintanar A (2012) Microneedles as transdermal delivery systems: combination with other enhancing strategies. Curr Drug Deliv 9:57–73
Ogura M, Paliwal S, Mitragotri S (2008) Low-frequency sonophoresis: current status and future prospects. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60:1218–1223
Pamornpathomkul B, Duangjit S, Laohapatarapant S, Rojanarata T, Opanasopit P, Ngawhirunpat T (2015) Transdermal delivery of fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextrans using the combination of microneedles and low-frequency sonophoresis. Asian J Pharm Sci 10:415–424
Park D, Park H, Seo J, Lee S (2014) Sonophoresis in transdermal drug deliverys. Ultrasonics 54:56–65
Patel D, Kumar P, Thakkar HP (2015) Lopinavir metered-dose transdermal spray through microporated skin: permeation enhancement to achieve therapeutic needs. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 29:173–180
Pliquett U (1999) Mechanistic studies of molecular transdermal transport due to skin electroporation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 35(1):41–60
Polat BE, Blankschtein D, Langer R (2010) Low-frequency sonophoresis: application to the transdermal delivery of macromolecules and hydrophilic drugs. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 7:1415–1432
Polat BE, Figueroa PL, Blankschtein D, Langer R (2011a) Transport pathways and enhancement mechanisms within localized and non-localized transport regions in skin treated with low-frequency sonophoresis and sodium lauryl sulfate. J Pharm Sci 100:512–529
Polat BE, Hart D, Langer R, Blankschtein D (2011b) Ultrasound-mediated transdermal drug delivery: mechanisms, scope and emerging trends. J Control Release 152:330–348
Polat BE, Seto JE, Blankschtein D, Langer R (2011c) Application of the aqueous porous pathway model to quantify the effect of sodium lauryl sulfate on ultrasound-induced skin structural perturbation. J Pharm Sci 100:1387–1397
Polat BE, Deen WM, Langer R, Blankschtein D (2012) A physical mechanism to explain the delivery of chemical penetration enhancers into skin during transdermal sonophoresis – Insight into the observed synergism. J Control Release 158:250–260
Prausnitz MR, Langer R (2008) Transdermal drug delivery. Nat Biotechnol 26(11):1261–1268
Qiu Y, Gao Y, Hu K, Li F (2008) Enhancement of skin permeation of docetaxel: a novel approach combining microneedle and elastic liposomes. J Control Release 129:144–150
Sen A, Zhao Y, Hui SW (2002a) Saturated anionic phospholipids enhance transdermal transport by electroporation. Biophys J 83(4):2064–2073
Sen A, Zhao Y, Zhang L, Hui SK (2002b) Enhanced transdermal transport by electroporation using anionic lipids. J Control Release 82:390–405
Sen A, Daly ME, Hui SW (2002c) Transdermal insulin delivery using lipid enhanced electroporation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1564:5–8
Seto JE, Polat BE, Lopez RFV, Blankschtein D, Langer R (2010) Effects of ultrasound and sodium lauryl sulfate on the transdermal delivery of hydrophilic permeants: comparative in vitro studies with full-thickness and split-thickness pig and human skin. J Control Release 145:26–32
Shipton EA (2012) Advances in delivery systems and routes for local anaesthetics. Trends Anaesth Crit Care 2:228–233
Tezel A, Sanders A, Tuchscherer J, Mitragotri S (2002) Synergistic effect of low-frequency ultrasound and surfactants on skin permeability. J Pharm Sci 91:91–100
Thomas BJ, Finnin BC (2004) The transdermal revolution. Drug Discov Today 9:697–703
Tiwari S, Pai R, Udupa N (2004) Influence of ultrasound on the percutaneous absorption of ketorolac tromethamine in vitro across rat skin. Drug Deliv 11:47–51
Tokudome Y, Sugibayashi K (2003) The synergic effects of various electrolytes and electroporation on the in vitro skin permeation of calcein. J Control Release 92(1–2):93–101
Tokudome Y, Sugibayashi K (2004) Mechanism of the synergic effects of calcium chloride and electroporation on the in vitro enhanced skin permeation of drugs. J Control Release 95(2):267–274
Ueda H, Ogihara M, Sugibayashi K, Morimoto Y (1996) Change in the electrochemical properties of skin and the lipid packing in stratum corneum by ultrasonic irradiation. Int J Pharm 137:217–224
Vanbever R, Préat V (2000) Transdermal drug delivery by skin electroporation in the Rat. In: Jaroszeski MJ, Heller R, Gilbert R (eds) Electrochemotherapy, electrogenetherapy, and transdermal drug delivery. Electrically mediated delivery of molecules to cells. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 457–471
Vanbever R, Prausnitz MR, Préat V (1997) Macromolecules as novel transdermal transport enhancers for skin electroporation. Pharm Res 14(5):638–644
Vitorino C, Almeida A, Sousa J, Lamarche I, Gobin P, Marchand S, Couet W, Olivier JC, Pais A (2014) Passive and active strategies for transdermal delivery using co-encapsulating nanostructured lipid carriers: in vitro vs. in vivo studies. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 86:133–144
Watanabe S, Takagi S, Ga K, Yamamoto K, Aoyagi T (2009) Enhanced transdermal drug penetration by the simultaneous application of iontophoresis and sonophoresis. J Drug Del Sci Tech 19:185–189
Weaver JC, Chizmadzhev YA (1996) Theory of electroporation: a review. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg 41:135–160
Weaver JC, Vanbever R, Vaughan TE, Prausnitz MR (1997) Heparin alters transdermal transport associated with electroporation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 234(3):637–640
Weaver JC, Vaughan TE, Chizmadzhev Y (1999) Theory of electrical creation of aqueous pathways across skin transport barriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 35(1):21–39
Wong TW (2014) Electrical, magnetic, photomechanical and cavitational waves to overcome skin barrier for transdermal drug delivery. J Control Release 193:257–269
Wong T-W, Zhao Y-L, Sen A, Hui SW (2005) Pilot study of topical delivery of methotrexate by electroporation. Br J Dermatol 152(3):524–530
Yang Y, Kalluri H, Banga AK (2011) Effects of chemical and physical enhancement techniques on transdermal delivery of cyanocobalamin (Vitamin B12). Pharmaceutics 3:474–484
Zewert TE, Pliquett UF, Vanbever R, Langer R, Weaver JC (1999) Creation of transdermal pathways for macromolecule transport by skin electroporation and a low toxicity, pathway-enlarging molecule. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg 49:11–20
Zorec B, Jelenc J, Miklavcic D, Pavselj N (2016) Electroporation-enhanced transdermal delivery of patent blue using green skin pore device. IFMBE Proceedings 57:1030–1033
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Piñón-Segundo, E., Nava-Arzaluz, M.G., Ganem-Rondero, A. (2017). Effect of the Use of Chemical Enhancers Combined with Sonophoresis, Electroporation, or Microneedles on Transdermal Drug Delivery. In: Dragicevic, N., I. Maibach, H. (eds) Percutaneous Penetration Enhancers Physical Methods in Penetration Enhancement. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-53273-7_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-53273-7_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-53271-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-53273-7
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)