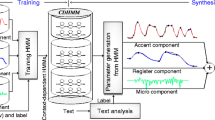
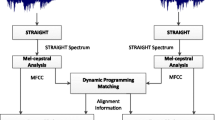
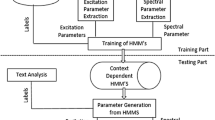
Abstract
Natural speech has diverse forms of expressiveness including emotions, speaking styles, and voice characteristics. Moreover, the expressivity changes depending on many factors at the phrase level, such as the speaker’s temporal emotional state, focus, feelings, and intention. Thus taking into account such variations in modeling of speech synthesis units is crucial to generating natural-sounding expressive speech. In this context, two approaches to HMM-based expressive speech synthesis are described: a technique for intuitively controlling style expressivity appearing in synthetic speech by incorporating subjective intensity scores in the model training and a technique for enhancing prosodic variations of synthetic speech using a newly defined phrase-level context for HMM-based speech synthesis and its unsupervised annotation for training data consisting of expressive speech.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anastasakos, T., J. McDonough, R. Schwartz, and J. Makhoul. 1996. A compact model for speaker adaptive training. Proceedings of ICSLP, 1137–1140.
Cowie, R., and R. R. Cornelius. 2003. Describing the emotional states that are expressed in speech. Speech Communication 40 (1–2): 5–32.
Doukhan, D., A. Rilliard, S. Rosset, M. Adda-Decker, and C. d’Alessandro. 2011. Prosodic analysis of a corpus of tales. Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, 3129–3132.
Erickson, D. 2005. Expressive speech: Production, perception and application to speech synthesis. Acoustical Science and Technology 26 (4): 317–325.
Eyben, F., S. Buchholz, N. Braunschweiler, J. Latore, V. Wan, M. J. F. Gales, and K. Knill. 2012. Unsupervised clustering of emotion and voice styles for expressive TTS. Proceedings of ICASSP, pp. 4009–4012.
Gales, M. J. F. 2000. Cluster adaptive training of hidden Markov models. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing 8 (4): 417–428.
Kawahara, H., I. Masuda-Katsuse, and A. de Cheveigne. 1999. Restructuring speech representations using a pitch-adaptive time–Frequency smoothing and an instantaneous-frequency-based F0 extraction: Possible role of a repetitive structure in sounds. Speech Communication 27 (3–4): 187–207.
Koriyama, T., T. Nose, and T. Kobayashi. 2011. On the use of extended context for HMM-based spontaneous conversational speech synthesis. Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, 2657–2660.
Maeno, Y., T. Nose, T. Kobayashi, Y. Ijima, H. Nakajima, H. Mizuno, and O. Yoshioka. 2011. HMM-based emphatic speech synthesis using unsupervised context labeling. Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, 1849–1852.
Maeno, Y., T. Nose, T. Kobayashi, T. Koriyama, Y. Ijima, H. Nakajima, H. Mizuno, and O. Yoshioka. 2013. HMM-based expressive speech synthesis based on phrase-level F0 context labeling. Proceedings of ICASSP, pp. 7859–7863.
Maeno, Y., T. Nose, T. Kobayashi, T. Koriyama, Y. Ijima, H. Nakajima, H. Mizuno, and O. Yoshioka. 2014. Prosodic variation enhancement using unsupervised context labeling for HMM-based expressive speech synthesis. Speech Communication 57:144–154.
Miyanaga, K., T. Masuko, and T. Kobayashi. 2004. A style control technique for HMM-based speech synthesis. Proceedings of INTERSPEECH-ICSLP, 1437–1440.
Nakajima, H., N. Miyazaki, A. Yoshida, T. Nakamura, and H. Mizuno. 2010. Creation and analysis of a Japanese speaking style parallel database for expressive speech synthesis. http://desceco.org/O-COCOSDA2010/proceedings/paper_30.pdf. Accessed 6 Dec 2014.
Nose, T., and T. Kobayashi. 2011a. Recent development of HMM-based expressive speech synthesis and its applications. Proceedings of APSIPA ASC. http://www.apsipa.org/proceedings_2011/pdf/APSIPA189.pdf. Accessed 6 Dec 2014.
Nose, T., and T. Kobayashi. 2011b. A perceptual expressivity modeling technique for speech synthesis based on multiple-regression HSMM. Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, 109–112.
Nose, T., and T. Kobayashi. 2013. An intuitive style control technique in HMM-based expressive speech synthesis using subjective style intensity and multiple-regression global variance model. Speech Communication 55 (2): 347–357.
Nose, T., J. Yamagishi, and T. Kobayashi. 2006. A style control technique for speech synthesis using multiple-regression HSMM. Proceedings of INTERSPEECH-ICSLP, 1324–1327.
Obin, N., A. Lacheret, and X. Rodet. 2011a. Stylization and trajectory modelling of short and long term speech prosody variations. Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, 2029–2032.
Obin, N., P. Lanchantin, A. Lacheret, and X. Rodet. 2011b. Discrete/continuous modelling of speaking style in HMM-based speech synthesis: Design and evaluation. Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, 2785–2788.
Schröder, M. 2009. Expressive speech synthesis: Past, present, and possible futures. In: Affective information processing, ed. J. H. Tao and T. N. Tan, 111–126. London: Springer.
Suni, A., T. Raitio, M. Vainio, and P. Alku. 2012. The GlottHMM Entry for Blizzard Challenge 2012: Hybrid Approach. Proceedings of Blizzard Challenge Workshop. http://festvox.org/blizzard/bc2012/HELSINKI_Blizzard2012.pdf. Accessed 6 Dec 2014.
Székely, E., J. Cabral, P. Cahill, and J. Carson-Berndsen. 2011. Clustering expressive speech styles in audiobooks using glottal source parameters. Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, 2409–2412.
Tachibana, M., J. Yamagishi, T. Masuko, and T. Kobayashi. 2005. Speech synthesis with various emotional expressions and speaking styles by style interpolation and morphing. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems E88-D (11): 2484–2491.
Vainio, M., A. Suni, and P. Sirjola. 2005. Accent and prominence in Finnish speech synthesis. Proceedings of International Conference on Speech and Computer (SPECOM), 309–312.
Yamagishi, J., K. Onishi, T. Masuko, and T. Kobayashi. 2003. Modeling of various speaking styles and emotions for HMM-based speech synthesis. Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, 2461–2464.
Yu, K., H. Zen, F. Mairesse, and S. Young. 2001. Context adaptive training with factorized decision trees for HMM-based statistical parametric speech synthesis. Speech Communication 53 (6): 914–923.
Yu, K., F. Mairesse, and S. Young. 2010. Word-level emphasis modelling in HMM-based speech synthesis. Proceedings of ICASSP, 4238–4241.
Zen, H., K. Tokuda, and A. Black. 2009. Statistical parametric speech synthesis. Speech Communication 51 (11): 1039–1064.
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank T. Nose, Y. Maeno, and T. Koriyama for their contributions to this study at Tokyo Tech. He would also like to thank O. Yoshioka, H. Mizuno, H. Nakajima, and Y. Ijima for their helpful discussions and providing expressive speech materials.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kobayashi, T. (2015). Prosody Control and Variation Enhancement Techniques for HMM-Based Expressive Speech Synthesis. In: Hirose, K., Tao, J. (eds) Speech Prosody in Speech Synthesis: Modeling and generation of prosody for high quality and flexible speech synthesis. Prosody, Phonology and Phonetics. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-45258-5_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-45258-5_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-45257-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-45258-5
eBook Packages: Humanities, Social Sciences and LawSocial Sciences (R0)