Abstract
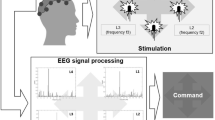
This paper proposed an automatic steady-state visual evoked potential (SSVEP) component selection (SCS) measure for a high-performance SSVEP-based brain-computer interface (SBCI) system. First, multi-electrode raw electroencephalogram signals are spatially pre-processed using a blind source separation technique resulting in multi-source components. The SCS measure of each component is then calculated by continuous wavelet transform (CWT), and the ensemble features that contain the weighted CWT energy of individual SSVEP harmonic are extracted. Second, the SSVEP component with maximal SCS measure is considered to have the highest signal-to-noise ratio. In our SBCI system, six stimulus frequencies served as the input patterns. Offline analyses were performed, through which the common electrode locations, the time window size, and the number of harmonics were defined. Thereafter the results of our method were compared with those of others. We next carried out an online test of the SBCI for 11 subjects using eight common electrode locations, a 1.5-s time window, and the first and second harmonics. The test results showed that our method achieved an average accuracy of 95.2 % and a practical bit rate of 68.2 bits/min.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolpaw JR, Birbaumer N, McFarland DJ, Pfurtscheller G, Vaughan TM (2002) Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control. Clin Neurophysiol 113:767–791
Lalor EC, Kelly SP, Finucane C, Burke R, Smith R, Reilly RB, McDarby G (2005) Steady-state VEP-based brain-computer interface control in an immersive 3D gaming environment. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process 2005(19):3156–3164
Müller-Putz GR, Scherer R, Brauneis C, Pfurtscheller G (2005) Steady-state visual evoked potential (SSVEP)-based communication: impact of harmonic frequency components. J Neural Eng 2:123–130
Shyu KK, Lee PL, Liu YJ, Sie JJ (2010) Dual-frequency steady-state visual evoked potential for brain computer interface. Neurosci Lett 483(1):28–31
Shyu KK, Lee PL, Lee MH, Lin MH, Lai RJ, Chiu YJ (2010) Development of a low-cost FPGA-based SSVEP BCI multimedia control system. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst 4(2):125–132
Lopez-Gordo MA, Prieto A, Pelayo F, Morillas C (2010) Use of phase in brain-computer interfaces based on steady-state visual evoked potentials. Neural Process Lett 32(1):1–9
Luo A, Sullivan TJ (2010) A user-friendly SSVEP-based brain-computer interface using a time-domain classifier. J Neural Eng 7(2)
Cheng M, Gao X, Gao S (2002) Design and implementation of a brain–computer interface with high transfer rates. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 49(10):1181–1186
Zhang ZM, Li XQ, Deng ZD (2010) A CWT-based SSVEP classification method for brain-computer interface system. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on intelligent control and information processing. Dalian, pp 43–48
Jia C, Gao X, Hong B, Gao S (2011) Frequency and phase mixed coding in SSVEP-based brain—computer interface. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 58(1):200–206
Brunner C, Allison BZ, Krusienski DJ, Kaiser V, Müller-Putz GR, Pfurtscheller G, Neuper C (2010) Improved signal processing approaches in an offline simulation of a hybrid brain-computer interface. J Neurosci Meth 188(1):165–173
Müller-Putz GR, Eder E, Wriessnegger SC, Pfurtscheller G (2008) Comparison of DFT and lock-in amplifier features and search for optimal electrode positions in SSVEP-based BCI. J Neurosci Meth 168(1):174–181
Wang YJ, Wang RP, Gao XR, Hong B, Gao SK (2006) A practical VEP-based brain-computer interface. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 14(2):234–239
Wu ZH, Yao DH (2008) Frequency detection with stability coefficient for steady-state visual evoked potential (SSVEP)-based BCIs. J Neural Eng 5(1):36–43
Friman O, Volosyak I, Graser A (2007) Multiple channel detection of steady-state visual evoked potentials for brain–computer interfaces. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 54(4):742–750
Bin G, Gao X, Yan Z, Hong B, Gao S (2009) An online multi-channel SSVEP-based brain-computer interface using a canonical correlation analysis method. J Neural Eng 6(4):046002
Pan J, Gao X, Duan F, Yan Z, Gao S (2011) Enhancing the classification accuracy of steady-state visual evoked potential-based brain—computer interfaces using phase. J Neural Eng 8(3):036027. doi:10.1088/1741-2560/8/3/036027
Yan Z, Gao X, Bin G, Hong B, Gao S (2009) A half-field stimulation pattern for SSVEP-based brain-computer interface. Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2009(2006):6461–6464
Peters BO, Pfurtscheller G, Flyvbjerg H (2001) Automatic differentiation of multichannel EEG signals. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 48(1):111–116
Regan D (1989) Human brain electrophysiology: evoked potentials and evoked magnetic fields in science and medicine. Elsevier, New York
Cichocki A, Amari S (2002) Adaptive blind signal and image processing: learning algorithms and applications (ch. 4). Wiley, Chichester
Belouchrani A, Abed-Meraim K, Cardoso J-F, Moulines E (1997) A blind source separation technique using second-order statistics. IEEE Trans Signal Process 45(2):434–444
Goupillaud P, Grossman A, Morlet J (1984) Cycle-octave and related transforms in seismic signal analysis. Geoexploration 23(1):85–102
Wang SY, Aziza TZ, Steina JF, Liu X (2005) Time–frequency analysis of transient neuromuscular events: dynamic changes in activity of the subthalamic nucleus and forearm muscles related to the intermittent resting tremor. J Neurosci Meth 145(1–2):151–158
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Support-vector network. Mach Learn 20:273–297
Vapnik VN (1995) The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer-Verlag, New York
Sanei S, Chambers JA (2007) EEG signal processing (ch. 2). Wiley, Chichester
Delorme A, Makeig S (2004) EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single trial eeg dynamics. J Neurosci Meth 134:9–21
Chatrian GE, Bergamini L, Dondey M, Klass DW, Lennox-Buchthal M, Petersén I (1974) A glossary of terms most commonly used by clinical electroencephalographers. Electroenceph Clin Neurophysiol 37:538–548
Townsend G, Lapallo BK, Boulay CB, Krusienski DJ, Frye GE, Hauser CK, Schwartz NE, Vaughan TM, Wolpaw JR, Sellers EW (2010) A novel P300-based brain-computer interface stimulus presentation paradigm: moving beyond rows and columns. Clin Neurophysiol 121(7):1109–1120
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant Nos. 90820305 and 60775040. The authors would like to thank all subjects for their participation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, Z., Deng, Z. (2014). An Automatic SSVEP Component Selection Measure for High-Performance Brain-Computer Interface. In: Sun, F., Hu, D., Liu, H. (eds) Foundations and Practical Applications of Cognitive Systems and Information Processing. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 215. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-37835-5_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-37835-5_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-37834-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-37835-5
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)