Abstract
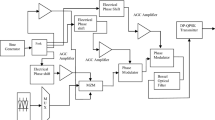
We propose a 4\( \times \)25-Gb/s intensity-modulated direct detection (IM/DD) duo-binary system with 50-GHz channel spacing. Both of the modulator and photodetector (PD) have 10-GHz 3-dB electrical bandwidth. At receiver, least mean square (LMS) algorithm is used to compensate the signal distortion after transmission. After 20-km standard single mode fiber (SSMF) transmission, LMS algorithm improves about 2-dB receive sensitivity at forward error correction (FEC) limit (BER = \({10^{ - 3}}\)) in duo-binary system. With LMS algorithm, duo-binary system has about 5-dB receive sensitivity improvement at FEC limit compared to on-off keying (OOK) system over 20-km SSMF transmission. This paper proposes a feasible scheme for future high-speed passive optical network (PON).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Veen, D., Houtsma, V., Winzer, P., Vetter, P.: 26-Gbps PON transmission over 40-km using duobinary detection with a low cost 7-GHz APD-based receiver. Paper Tu.3.B.1, European Conference and Exhibition on Optical Communications (2012)
Zhou, J., Qiao, Y.: Low-peak-to-average power ratio and low-complexity asymmetrically clipped optical orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing uplink transmission scheme for long-reach passive optical network. Opt. Lett. 40, 4034–4037 (2015)
Lender, A.: The duobinary technique for high-speed data transmission. IEEE Trans. Commun. Electron. 82, 214–218 (1963)
Yonenaga, K., Kuwano, S.: Dispersion-tolerant optical transmission system using duobinary transmitter and binary receiver. J. Lightwave Technol. 15, 1530–1537 (1997)
Zhou, J., Qiao, Y., Cai, Z., Ji, Y.: Asymmetrically clipped optical fast OFDM based on discrete cosine transform for IM/DD systems. J. Lightwave Technol. 33, 1920–1927 (2015)
Cvijetic, N.: OFDM for next-generation optical access networks. J. Lightwave Technol. 30, 384–398 (2012)
Zhou, J., Yan, Y., Cai, Z., Qiao, Y., Ji, Y.: A cost-effective and efficient scheme for optical OFDM in short-range IM/DD systems. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 26, 1372–1374 (2014)
Van Veen, D.T., Houtsma, V.E.: Symmetrical 25-Gb/s TDM-PON with 31.5-dB optical power budget using only off-the-shelf 10-Gb/s optical components. J. Lightwave Technol. 34, 1636–1642 (2016)
Ono, T., Yano, Y., Fukuchi, K., Ito, T., Yamazaki, H., Yamaguchi, M., Emura, K.: Characteristics of optical duobinary signals in terabit/s capacity, high-spectral efficiency WDM systems. J. Lightwave Technol. 16, 788–797 (1998)
Gu, X., Dodds, S.J., Blank, L.C., Spirit, D.M., Pycock, S.J., Ellis, A.D.: Duobinary technique for dispersion reduction in high capacity optical systems-modelling, experiment and field trial. IEEE Proc. Optoelectron. 143, 228–236 (1996)
Farhang-Boroujeny, B.: Signal Processing Techniques for Software Radios. Lulu Publishing House, Raleigh (2008)
Wang, Y., Yu, J., Chi, N.: Demonstration of 4 128-Gb/s DFT-S OFDM signal transmission over 320-km SMF with IM/DD. IEEE Photon. J. 8, 1–9 (2016)
Wang, Y., Huang, X., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Chi, N.: Enhanced performance of visible light communication employing 512-QAM N-SC-FDE and DD-LMS. Opt. Express 22, 15328–15334 (2014)
Hsu, D.Z., Wei, C.C., Chen, H.Y., Chen, J., Yuang, M.C., Lin, S.H., Li, W.Y.: 21-Gb/s after 100-km OFDM long-reach PON transmission using a cost-effective electro-absorption modulator. Opt. Express 18, 27758–27763 (2010)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61271192, 61427813, 61331010); National 863 Program of China (2013AA013401); Research Fund of ZTE Corporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Guo, M., Zhou, J., Tang, X., Qiao, Y. (2018). 4\( \times \)25-Gb/s Duo-Binary System over 20-km SSMF Transmission with LMS Algorithm . In: Chen, Q., Meng, W., Zhao, L. (eds) Communications and Networking. ChinaCom 2016. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 209. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66625-9_40
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66625-9_40
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-66624-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-66625-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)