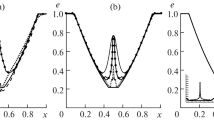
Abstract
Semi-lagrangian (or remeshed) particle methods are conservative particle methods where the particles are remeshed at each time-step. The numerical analysis of these methods show that their accuracy is governed by the regularity and moment properties of the remeshing kernel and that their stability is guaranteed by a lagrangian condition which does not rely on the grid size. Turbulent transport and more generally advection dominated flows are applications where these features make them appealing tools. The adaptivity of the method and its ability to capture fine scales at minimal cost can be further reinforced by remeshing particles on adapted grids, in particular through wavelet-based multi-resolution analysis.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
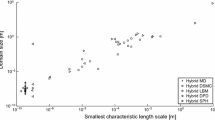
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Basdevant, M. Holschneider, V. Perrier, Methode des ondelettes mobiles. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris I 310, 647–652 (1990)
M. Berger, J. Oliger, Adaptive mesh refinement for hyperbolic partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 3, 484–512 (1984)
M. Bergdorf, G.-H. Cottet, P. Koumoutsakos, Multilevel adaptive particle methods for convection-diffusion equations. SIAM Multiscale Model. Simul. 4, 328–357 (2005)
M. Bergdorf, P. Koumoutsakos, A Lagrangian particle-wavelet method. SIAM Multiscale Model. Simul. 5(3), 980–995 (2006)
A. Cohen, I. Daubechies, J.C. Feauveau, Biorthogonal bases of compactly supported wavelets. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 45, 485–560 (1992)
G.-H. Cottet, A new approach for the analysis of vortex methods in 2 and 3 dimensions. Ann. Inst. Henri Poincaré 5, 227–285 (1988)
G.-H. Cottet, P. Koumoutsakos, Vortex Methods (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2000)
G.-H. Cottet, P. Koumoutsakos, M. Ould-Salihi, Vortex methods with spatially varying cores. J. Comput. Phys. 162, 164–185 (2000)
G.-H. Cottet, B. Michaux, S. Ossia, G. Vanderlinden, A comparison of spectral and vortex methods in three-dimensional incompressible flows. J. Comput. Phys. 175, 702–712 (2002)
G.-H. Cottet, J.-M. Etancelin, F. Perignon, C. Picard, High order Semi-Lagrangian particles for transport equations: numerical analysis and implementation issues. ESAIM: Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 48, 1029–1060 (2014)
M. Gazzola, B. Hejazialhosseini, P. Koumoutsakos, Reinforcement learning and wavelet adapted vortex methods for simulations of self-propelled swimmers. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 36, 622–639 (2014)
R.A. Kerr, Planetary origins: a quickie birth of jupiters and saturns. Science 298, 1698–1689 (2002)
P. Koumoutsakos, Inviscid axisymmetrization of an elliptical vortex. J. Comput. Phys. 138, 821–857 (1997)
P. Koumoutsakos, A. Leonard, High resolution simulations of the flow around an impulsively started cylinder using vortex methods. J. Fluid Mech. 296, 1–38 (1995)
R. Krasny, Desingularization of periodic vortex sheet roll-up. J. Comput. Phys. 65, 292–313 (1986)
J.-B. Lagaert, G. Balarac, G.-H. Cottet, Hybrid spectral particle method for the turbulent transport of a passive scalar. J. Comput. Phys. 260, 127–142 (2014)
F. Lossaso, J.O. Talton, N. Kwatra, R. Fedkiw, Two-way coupled SPH and particle level set fluid dynamics. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 14, 797–804 (2008)
A. Magni, G.-H. Cottet, Accurate, non-oscillatory remeshing schemes for particle methods. J. Comput. Phys. 231(1), 152–172 (2012)
J.E. Martin, E. Meiburg, Numerical investigation of three-dimensional evolving jets subject to axisymmetric and azimuthal perturbation. J. Fluid Mech. 230, 271 (1991)
J.J. Monaghan, Particle methods for hydrodynamics. Comput. Phys. Rep. 3, 71–124 (1985)
P. Ploumhans, G.S. Winckelmans, J.K. Salmon, A. Leonard, M.S. Warren, Vortex methods for direct numerical simulation of three-dimensional bluff body flows: application to the sphere at Re = 300, 500, and 1000. J. Comput. Phys. 165, 354–406 (2000)
D. Rossinelli, B. Hejazialhosseini, W. van Rees, M. Gazzola, M. Bergdorf, P. Koumoutsakos, MRAG-I2D: multi-resolution adapted grids for remeshed vortex methods on multicore architectures. J. Comput. Phys. 288, 1–18 (2015)
J. Sethian, A. Ghoniem, Validation study of vortex methods. J. Comput. Phys. 54, 425–456 (1984)
O. Vasilyev, Solving multi-dimensional evolution problems with localized structures using second generation wavelets. Int. J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 17(2), 151–168, 17, 151–168 (2003)
G. Winckelmans, A. Leonard, Contributions to vortex methods for the computation of three dimensional incompressible unsteady flows. J. Comput. Phys. 109, 247–273 (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Cottet, GH., Koumoutsakos, P. (2017). High Order Semi-Lagrangian Particle Methods. In: Bittencourt, M., Dumont, N., Hesthaven, J. (eds) Spectral and High Order Methods for Partial Differential Equations ICOSAHOM 2016. Lecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineering, vol 119. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-65870-4_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-65870-4_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-65869-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-65870-4
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)