Abstract
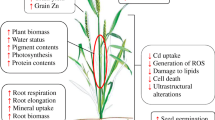
Heavy metals pollution is continuously increasing and posing threats to our environment. This heavy metals’ presence in soils accumulates in plants which become part of food supply. Heavy metals at their higher concentrations negatively affect plant growth parameters. Zn is one of the essential micronutrient which takes part in plant physiological functions and showed beneficial effects in plant growth, development processes and yield. Zn plays important role in cellular functions in all living organisms. Nevertheless, heavy metal concentrations are increasing in our agricultural soils through different anthropogenic activities which need to be discussed. Considering present scenario, this review was conducted to illustrate the promotive and beneficial role of Zn in alleviating heavy metals stress in various plants. It was observed that Zn not only ameliorate different metals’ toxic levels but also improve plant growth attributes by inhibiting heavy metals uptake in plant parts. Heavy metals induced oxidative stress and decline plant growth, biomass, chlorophyll contents, photosynthetic traits and many metabolic functions. Zn combat heavy metals toxicity by generating antioxidant defence system against oxidative damage and improved plant growth parameters by alleviating metals toxicity in different plants. However, Zn inadequate availability declined crop yield. Additionally, Zn deficiency disturbs plant growth and leaf chlorosis. Various techniques in the form of bio-fortification have been used to overcome Zn deficiency.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akay, A., & Koleli, N. (2007). Interaction between cadmium and zinc in barley (hordeum vulgare l.) grown under field conditions. Bangladesh Journal of Botany, 36, 13–19.
Alloway, B. J. (2004). Zinc in soils and crop nutrition. Publication of International Zinc Association. Retrieved October 4, 2010, from http://www.iza.com/Documents/Communications/Publications/ALLOWAY_PRINT.pdf\.
Alloway, B. J. (2008a). Zinc in soils and crop nutrition. Brussels, Belgium: International Zinc Association.
Alloway, B. J. (2008b). Copper and Zinc in soils: Too little or too much. New Zealand Trace Elements Group Conference 13–15th February 2008, University of the Waikato, Hamilton, New Zealand.
Alloway, B. J. (2008c). Zinc in soils and crop nutrition (2nd ed.). Brussels Belgium/Paris, France: International Zinc Association/International Fertilizer Industry Association.
Alloway, B. J. (2009). Soil factors associated with zinc deficiency in crops and humans. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 31, 537–548.
Alloway, B. J. (2013). Heavy metals and metalloids as micronutrients for plants and animals. In B. J. Alloway (Ed.), Heavy metals in soils (pp. 195–209). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer.
Andreini, C., Banci, L., Bertini, I., & Rosato, A. (2006). Zinc through the three domains of life. Journal of Proteome Research, 5, 3173–3178.
Appenroth, K. J. (2010). Definition of “heavy metals” and their role in biological systems. Soil Heavy Metals, 19, 19–29.
Arvind, P., & Prasad, M. N. V. (2003). Zinc alleviates cadmium-induced oxidative stressin Ceratophyllum demersum L.: A free floating freshwater macrophyte. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 41, 391–397.
Arvind, P., & Prasad, M. N. V. (2005a). Modulation of cadmium-induced oxidative stress in Ceratophyllum demersum by zinc involves ascorbate-glutathione cycle and glutathione metabolism. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 43, 107–116.
Arvind, P., & Prasad, M. N. V. (2005b). Cadmium-Zinc interactions in a hydroponic system using Ceratophyllum demersum L.: Adaptive Ecophysiology, biochemistry and molecular toxicology. Brazilian Journal of Plant Physiology, 17, 3–20.
Babu, N. G., Sarma, P. A., Attitalla, I. H., & Murthy, S. D. S. (2010). Effect of selected heavy metal ions on the photosynthetic electron transport and energy transfer in the thylakoid membrane of the cyanobacterium, Spirulina platensis. Academic Journal of Plant Sciences, 3, 46–49.
Bhutia, D. T. (2014). Protein energy malnutrition in India: The plight of our under five children. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care, 3, 63–70.
Bonnet, M., Camares, O., & Veisseire, P. (2000). Effects of zinc and influence of Acremonium lolii on growth parameters, chlorophyll a fluorescence and antioxidant enzyme activities of ryegrass (Lolium perene L. cv Apollo). Journal of Experimental Botany, 51, 945–953.
Bouain, N., Shahzad, Z., Rouached, A., Khan, G. A., Berthomieu, P., et al. (2014). Phosphate and zinc transport and signalling in plants: Toward a better understanding of their homeostasis interaction. Journal of Experimental Botany, 65(20), 5725–5741. doi:10.1093/jxb/eru314.
Brennan, R. F. (2005). Zinc application and its availability to plants. PhD dissertation, Division of Science and Engineering, School of Environmental Science, Murdoch University.
Broadley, M. R., White, P. J., Hammond, J. P., Zelko, I., & Lux, A. (2007). Zinc in plants. The New Phytologist, 173, 677–702.
Burleigh, S. H., Kristensen, B. K., & Bechmann, I. E. (2003). A plasma membrane zinc transporter from Medicago truncatula is upregulated in roots by Zn fertilization, yet down-regulated by arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization. Plant Molecular Biology, 52, 1077–1088.
Cakmak, I. (2000). Role of zinc in protecting plant cells from reactive oxygen species. The New Phytologist, 146, 185–205.
Cakmak, I. (2008). Enrichment of cereal grains with zinc: Agronomic or genetic bio-fortification? Plant and Soil, 302, 1–17.
Cakmak, I. (2009). Bio-fortification of cereal grains with zinc by applying zinc fertilizers. Biozoom, 1, 2–7.
Chandel, G., Datta, K., & Datta, S. K. (2010). Detection of genomic changes in transgenic Bt rice populations through genetic fingerprinting using amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP). GM Crops, 1, 327–336.
Cherif, J., Mediouni, C., Ammar, W. B., & Jemal, F. (2011). Interactions of zinc and cadmium toxicity in their effects on growth and in antioxidative systems in tomato plants (Solanum lycopersicum). Journal of Environmental Sciences, 23, 837–844.
Clabeaux, B. L., Navarro, D. A., Aga, D. S., & Bisson, M. A. (2013). Combined effects of cadmium and zinc on growth, tolerance, and metal accumulation in Chara australis and enhanced phytoextraction using EDTA. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 98, 236–243.
Clemens, S. (2009). Toxic metal accumulation, responses to exposure and mechanisms of tolerance in plants. Biochimie, 88, 1707–1719.
Cobbett, C., & Goldsbrough, P. (2002). Phytochelatins and metallothioneins: Roles in heavy metal detoxification and homeostasis. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 53, 159–182.
Colangelo, E. P., & Guerinot, M. L. (2006). Put the metal to the petal: Metal uptake and transport throughout plants. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 9, 322–330.
Dang, H. R., Li, Y., Sun, X., & Zhang, Y. L. (2010). Absorption, accumulation and distribution of zinc in highly-yielding winter wheat. Agricultural Sciences in China, 9, 965–973.
Dazy, M., Masfaraud, J. F., & Ferard, J. F. (2009). Induction of oxidative stress biomarkers associated with heavy metal stress in Fontinalis antipyretica Hedw. Chemosphere, 75, 297–302.
Deinlein, U., Weber, M., Schmidt, H., Rensch, S., Trampczynska, A., Hansen, T. H., Husted, S., Schjoerring, J. K., Talke, I. N., Kramer, U., & Clemens, S. (2012). Elevated nicotianamine levels in Arabidopsis halleri roots play a key role in Zn hyperaccumulation. Plant Cell, 24, 708–723.
Disante, K. B., Fuentes, D., & Cortina, J. (2010). Response to drought of Zn-stressed Quercus suber L. seedlings. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 70, 96–103.
Epstein, E., & Bloom, A. (2005). Mineral nutrition of plants: Principles and perspectives. Sunderland: Sinauer Associates.
Fageria, N. K. (2004). Dry matter yield and nutrient uptake by lowland rice at different growth stages. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 27, 947–958.
Foster, M., & Samman, S. (2012). Zinc and regulation of inflammatory cytokines: Implications for cardio-metabolic disease. Nutrients, 4, 676–694.
Freisinger, E. (2008). Plant MTs—Long neglected members of the metallothioneins superfamily. Dalton Transactions, 47, 6663.
Genc, Y., McDonald, G. K., & Graham, R. D. (2006). Contribution of different mechanisms to zinc efficiency in bread wheat during early vegetative stage. Plant and Soil, 281, 353–367.
Ghosh, M., & Singh, S. P. (2005). A review on phytoremediation of heavy metals and utilization of its byproducts. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 3, 1–18.
Gratao, P. L., Monteiro, C. C., Antunes, A. M., Peres, L. E. P., & Azevedo, R. A. (2008). Acquired tolerance of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum cv. Micro-Tom) plants to cadmium-induced stress. Annals of Applied Biology, 153, 321–333.
Hafeez, B., Khanif, Y. M., & Saleem, M. (2013). Role of zinc in plant nutrition—A review. American Journal of Experimental Agriculture, 3, 374–391.
Hall, J. L., & Williams, L. E. (2003). Transition metal transporters in plants. Journal of Experimental Botany, 54, 2601–2613.
Hansch, R., & Mendel, R. R. (2009). Physiological functions of mineral micronutrients (Cu, Zn, Mn, Fe, Ni, Mo, B, Cl). Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 12, 259–266.
Hao, H., Wei, Y., Yang, X., Feng, Y., & Wu, C. (2007). Effects of different nitrogen fertilizer levels on Fe, Mn, Cu and Zn concentrations in shoot and grain quality in rice (Oryza sativa). Rice Science, 14, 289–294.
Hart, J. J., Welch, R. M., Norvell, W. A., & Kochian, L. V. (2002). Transport interactions between cadmium and zinc in roots of bread and durum wheat seedlings. Physiologia Plantarum, 116, 73–78.
Haslett, B. S., Reid, R. J., & Rengel, Z. (2001). Zinc mobility in wheat: Uptake and distribution of zinc applied to leaves or roots. Annals of Botany, 87, 379–386.
Hassan, M. J., Zhang, G., Wu, F., Wei, K., & Chen, Z. (2005). Zinc alleviates growth inhibition and oxidative stress caused by cadmium in rice. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 168, 255–261.
Horton, S. (2006). The economics of food fortification. The Journal of Nutrition, 136, 1068–1071.
Ikenaka, Y., Nakayama, S. M. M., Muzandu, K., Choongo, K., Teraoka, H., Mizuno, N., & Ishizuka, M. (2010). Heavy metal contamination of soil and sediment in Zambia. African Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 4, 729–739.
Iqbal, N., Masood, A., Nazar, R., Syeed, S., & Khan, N. A. (2010). Photosynthesis, growth and antioxidant metabolism in mustard (Brassica juncea L.) cultivars differing in Cd tolerance. Agricultural Sciences in China, 9, 519–527.
Jarup, L. (2003). Hazards of heavy metal contamination. British Medical Bulletin, 68, 167–182.
Kabata-Pendias, A., & Pendias, H. (2001). Trace elements in soils and plants. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Kaya, C., Higgs, D., & Burton, A. (2000). Plant growth, phosphorus nutrition and acidphosphatase enzyme activity in three tomato cultivers grown hydroponically at different zinc concentrations. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 23, 569–579.
Khudsar, T., Mahmooduzzafar Iqbal, M., & Sairam, R. K. (2004). Zinc-induced changes inmorpho-physiological and biochemical parameters in Artemisia annua. Biologia Plantarum, 48, 255–260.
King, J. C., & Cousins, R. J. (2006). Zinc. In M. E. Shils, M. Shike, A. C. Ross, B. Caballero, & R. J. Cousins (Eds.), Modern nutrition in health and disease (10th ed., pp. 271–285). Baltimore: Lippincot Williams and Wilkins.
Koleli, N., Eker, S., & Cakmak, I. (2004). Effect of zinc fertilization on cadmium toxicity in durum and bread wheat grown in zinc-deficient soil. Environmental Pollution, 131, 453–459.
Latowski, D., Kuczyńska, P., & Strzałka, K. (2011). Xanthophyll cycle-a mechanism protecting plants against oxidative stress. Redox Report, 16, 78–90.
Lonnerdal, B. (2000). Dietary factors influencing zinc absorption. The Journal of Nutrition, 130, 1378–1383.
Maksymiec, W., Drazkiewicz, M., & Skorzynska-Polit, E. (2008). Responses of higher plants to heavy metal stress. Abiotic stress and plant responses (pp. 139–163). New Delhi: IK International Publishing House.
Maret, W., & Sandstead, H. H. (2006). Zinc requirements and the risks and benefits of zinc supplementation. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 20, 3–18.
Marschner, H. (2012). Mineral nutrition of higher plants (3rd ed.). London: Academic Press.
Martinez, C., & Motto, H. (2000). Solubility of lead, zinc and copper added to mineral soils. Environmental Pollution, 107, 153–158.
Mayer, J. E., Pfeiffer, W. H., & Beyer, P. (2008). Biofortified crops to alleviate micronutrient malnutrition. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 11, 166–170.
McCarty, M. F. (2012). Zinc and multi-mineral supplementation should mitigate the pathogenic impact of cadmium exposure. Medical Hypotheses, 79, 642–648.
Mousavi, S. R., Mohammad, G., & Goudarz, A. (2007). Effect of zinc and manganese foliar application on yield, quality and enrichment on potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) Asian Journal of Plant Sciences, 8, 1256–1260.
Moustakas, N. K., Akoumianaki-Ioannidou, A., & Barouchas, P. E. (2011). The effects of cadmium and zinc interactions on the concentration of cadmium and zinc in pot marigold (Calendula officinalis L.) Australian Journal of Crop Science, 5(3), 277.
Naik, S. K., & Das, D. K. (2008). Relative performance of chelated zinc and zinc sulphate for lowland rice (Oryza sativa L). Nutrition Cycle in Agroecosystem, 81, 219–227.
Overbeck, S., Rink, L., & Haase, H. (2008). Modulating the immune response by oral zinc supplementation: A single approach for multiple diseases. Archivum Immunologiae et Therapiae Experimentalis, 56, 15–30.
Palmgren, M. G., Clemens, S., Williams, L. E., Kramer, U., Borg, S., Schjorring, J. K., & Sanders, D. (2008). Zinc biofortification of cereals: Problems and solutions. Trends in Plant Science, 13, 464–473.
Peck, A. W., & McDonald, G. K. (2010). Adequate zinc nutrition alleviates the adverse effects of heat stress in bread wheat. Plant and Soil, 337, 355–374.
Phattarakul, N., Rarkasem, B., Li, L. J., LH, W., Zou, C. Q., Ram, H., Sohu, V. S., Kang, B. S., Surek, H., Kalayci, M., Yazici, A., Zhang, F. S., & Cakmak, I. (2012). Biofortificaiton of rice grain with zinc through zinc fertilization in different countries. Plant and Soil, 361, 131–141.
Pollard, A. J., Powell, K. D., Harper, F. A., & Smith, J. A. C. (2002). The genetic basis of metal hyperaccumulation in plants. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 21, 539–566.
Prasad, A. S. (2008). Zinc in human health: Effect of zinc on immune cells. Molecular Medicine, 14, 353–357.
Prasad, A. S. (2009). Zinc: Role in immunity, oxidative stress and chronic inflammation. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care, 12, 646–652.
Przedpelska, E., & Wierzbicka, M. (2007). Arabidopsis arenosa (Brassicaceae) from a lead-zinc waste heap in southern Poland- a plant with high tolerance to heavy metals. Plant and Soil, 299, 43–53.
Rascio, N., & Navari-Izzo, F. (2011). Heavy metal hyperaccumulating plants: How and why do they do it? And what makes them so interesting? Plant Science, 180, 169–181.
Roohani, N., Hurrell, R., Kelishadi, R., & Schullin, R. (2013). Zinc and its importance for human health: An integrative review. Journal of Research in Medical Sciences, 18, 144–157.
Shankar, A. H., & Prasad, A. S. (1998). Zinc and immune function: The biological basis of altered resistance to infection. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 68(suppl), 447–463.
Sinclair, S. A., & Kramer, U. (2012). The zinc homeostasis network of land plants. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1823(9), 1553–1567.
Singh, B., Natesan, S. K. A., Singh, B. K., & Usha, K. (2005). Improving zinc efficiency of cereals under zinc deficiency. Current Science, 88, 36–44.
Singh, V. P., Srivastava, P. K., & Prasad, S. M. (2012). Differential effect of UV-B radiation on growth, oxidative stress and ascorbate-glutathione in two cyanobacteria under copper stress. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 61, 61–70.
Tavallali, V., Rahemi, M., Eshghi, S., Kholdebarin, B., & Ramezanian, A. (2010). Zinc alleviates salt stress and increases antioxidant enzyme activity in the leaves of pistachio (Pistacia vera L. ‘Badami’) seedlings. Turkish Journal of Agriculture and Forestry, 34, 349–359.
Tewari, R. K., Kumar, P., & Sharma, P. N. (2008). Morphology and physiology of zinc-stressed mulberry plants. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 171, 286–294.
Thounaojam TC, Panda P, Choudhury S, Patra HK, Panda SK (2014) Zinc ameliorates copper-induced oxidative stress in develo** rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Protoplasma (251):61–69.
Tisdale, S. L., Nelson, W. L., & Beaten, J. D. (1984). Zinc in soil fertility and fertilizers (4th ed.pp. 382–391). New York: Macmillan.
Trampczynska, A., Kupper, H., Meyer-Klaucke, W., Schmidt, H., & Clemens, S. (2010). Nicotianamine forms complexes with Zn (II) in vivo. Metallomics, 2, 57–66.
Tsonev, T., & Lidon, F. J. C. (2012). Zinc in plants-An overview. Emirates Journal of Food & Agriculture, 24, 322–333.
Upadhyay, R., & Panda, S. K. (2009). Zinc reduced copper toxicity induced oxidative stress by promoting antioxidant defense in freshly grown duckweed Spirodela polyrhiza. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 175, 1081–1084.
Ventrella, A., Catucci, L., Piletska, E., Piletsky, S., & Agostiano, A. (2011). Interactions between heavy metals and photosynthetic materials studied by optical techniques. Bioelectrochemistry, 77, 19–25.
Vesely, T., Neuberg, M., Trakal, L., Szakova, J., & Tlustoa, P. (2011). Water lettuce Pistia stratiotes L. response to lead toxicity. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 223, 1847–1859.
Wang, C., Zhang, S. H., Wang, P. F., Qian, J., Hou, J., Zhang, W. J., & Lu, J. (2009). Excess Zn alters the nutrient uptake and induces the antioxidative responses in submerged plant Hydrilla verticillata (L.f) Royle. Chemosphere, 76, 938–945.
World Health Organization (WHO). (2002). The World Health Report 2002. Geneva: WHO.
WHO, FAO, & IAEA. (2002). Trace elements in human health and nutrition (pp. 230–245). Geneva: WHO.
Yadav, S. K. (2009). Heavy metals toxicity in plants: An overview on the role of glutathione and phytochelatins in heavy metal stress tolerance of plants. South Afr. Journal of Botany, 76, 167–179.
Yusuf, M., Fariduddin, Q., Varshney, P., & Ahmad, A. (2012). Salicylic acid minimizes nickel and/or salinity-induced toxicity in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) through an improved antioxidant system. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 19, 8–18.
Zhao, A. Q., Tian, X. H., WH, L., Gale, W. J., XC, L., & Cao, Y. X. (2011). Effect of zinc on cadmium toxicity in winter wheat. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 34, 1372–1385.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
ul Hassan, Z. et al. (2017). Role of Zinc in Alleviating Heavy Metal Stress. In: Naeem, M., Ansari, A., Gill, S. (eds) Essential Plant Nutrients. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-58841-4_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-58841-4_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-58840-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-58841-4
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)