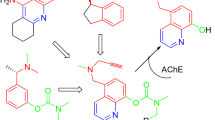
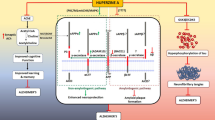
Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a multifactorial syndrome involving a complex array of different, while related factors in its progression. Accordingly, novel approaches that can simultaneously modulate several disease-related targets hold great promise for the effective treatment of AD. This review describes the development of novel multimodal compounds, as follows: the brain selective monoamine oxidase (MAO)-A and -B inhibitor with chelating and neuroprotective activity, M30; the chelating with neuroprotective activity, HLA20; the acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor with site-activated chelating and neuroprotective activity, HLA20A; the AChE-MAO-A and -B inhibitor with site-activated chelating and neuroprotective activity, M30D; and neuroprotective peptide NAPVSIPQ analogs. Among them, HLA20A and M30D act as pro-chelators and can be activated to liberate their respective active chelators HLA20 and M30 through pseudo inhibition of AChE. We first discuss the knowledge and structure-based strategy for the rational design of these novel compounds. Then, we review our recent studies on these drug candidates, regarding their wide range in vitro and in vivo activities, with emphasis on antioxidant-chelating potency, AchE and MAO-A and -B inhibitory activity, as well as neuroprotective/neurorescue effects. Finally, we discuss the diverse molecular mechanisms of action of these compounds with relevance to AD, including the major role of oxidative stress (OS) due to accumulation of iron in AD brains and formation of free oxygen radicals, modulation of amyloid-β (Aβ) and amyloid precursor protein expression/processing and tau, induction of cell cycle arrest; inhibition of neuronal death markers, upregulation of neurotrophic factors, as well as activation of protein kinase C and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdipranoto A, Wu S, Stayte S, Vissel B. The role of neurogenesis in neurodegenerative diseases and its implications for therapeutic development. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2008;7(2):187–210.
Anantharaman M, Tangpong J, Keller JN, Murphy MP, Markesbery WR, Kiningham KK, St Clair DK. Beta-amyloid mediated nitration of manganese superoxide dismutase: implication for oxidative stress in a APPNLH/NLH X PS-1P264L/P264L double knock-in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Pathol. 2006;168(5):1608–18. S0002-9440(10)62183-9 [pii]
Atri A, Shaughnessy LW, Locascio JJ, Growdon JH. Long-term course and effectiveness of combination therapy in Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2008;22(3):209–21. https://doi.org/10.1097/WAD.0b013e31816653bc.
Avramovich-Tirosh Y, Amit T, Bar-Am O, Zheng H, Fridkin M, Youdim MB. Therapeutic targets and potential of the novel brain- permeable multifunctional iron chelator-monoamine oxidase inhibitor drug, M-30, for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem. 2007a;100(2): 490–502. JNC4258 [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04258.x.
Avramovich-Tirosh Y, Reznichenko L, Mit T, Zheng H, Fridkin M, Weinreb O, Mandel S, Youdim MB. Neurorescue activity, APP regulation and amyloid-beta peptide reduction by novel multi-functional brain permeable iron- chelating- antioxidants, M-30 and green tea polyphenol, EGCG. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2007b;4(4):403–11.
Avramovich-Tirosh Y, Bar-Am O, Amit T, Youdim MB, Weinreb O. Up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and HIF-target genes in cortical neurons by the novel multifunctional iron chelator anti-Alzheimer drug, M30. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2010;7(4):300–6. CAR -54 [pii]
Bar-Am O, Weinreb O, Amit T, Youdim MB. Regulation of Bcl-2 family proteins, neurotrophic factors, and APP processing in the neurorescue activity of propargylamine. FASEB J. 2005;19(13):1899–901. 05-3794fje [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.05-3794fje.
Belluti F, Rampa A, Piazzi L, Bisi A, Gobbi S, Bartolini M, Andrisano V, Cavalli A, Recanatini M, Valenti P. Cholinesterase inhibitors: xanthostigmine derivatives blocking the acetylcholinesterase-induced beta-amyloid aggregation. J Med Chem. 2005;48(13):4444–56. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm049515h.
Blat D, Weiner L, Youdim MB, Fridkin M. A novel iron-chelating derivative of the neuroprotective peptide NAPVSIPQ shows superior antioxidant and antineurodegenerative capabilities. J Med Chem. 2008;51(1):126–34. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm070800l.
Borchardt T, Schmidt C, Camarkis J, Cappai R, Masters CL, Beyreuther K, Multhaup G. Differential effects of zinc on amyloid precursor protein (APP) processing in copper-resistant variants of cultured Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-Grand). 2000;46(4):785–95.
Borghi R, Patriarca S, Traverso N, Piccini A, Storace D, Garuti A, Gabriella C, Patrizio O, Massimo T. The increased activity of BACE1 correlates with oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2007;28(7):1009–14. S0197-4580(06)00145-X [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.05.004.
Brenneman DE, Spong CY, Hauser JM, Abebe D, Pinhasov A, Golian T, Gozes I. Protective peptides that are orally active and mechanistically nonchiral. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004;309(3):1190–7. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.103.063891. jpet.103.063891 [pii]
Bullock R, Dengiz A. Cognitive performance in patients with Alzheimer’s disease receiving cholinesterase inhibitors for up to 5 years. Int J Clin Pract. 2005;59(7):817–22. IJCP562 [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1368-5031.2005.00562.x.
Cavalli A, Bolognesi ML, Minarini A, Rosini M, Tumiatti V, Recanatini M, Melchiorre C. Multi-target-directed ligands to combat neurodegenerative diseases. J Med Chem. 2008;51(3):347–72. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm7009364.
Cheng SY, Trombetta LD. The induction of amyloid precursor protein and alpha-synuclein in rat hippocampal astrocytes by diethyldithiocarbamate and copper with or without glutathione. Toxicol Lett. 2004;146(2):139–49. S0378427403003588 [pii]
Chow VW, Savonenko AV, Melnikova T, Kim H, Price DL, Li T, Wong PC. Modeling an anti-amyloid combination therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Transl Med. 2010;2(13):13ra11. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3000337. 2/13/13ra1 [pii]
Correia SC, Moreira PI. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: a new hope to counteract neurodegeneration? J Neurochem. 2010;112(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06443.x. JNC6443 [pii]
Cuajungco MP, Faget KY. Zinc takes the center stage: its paradoxical role in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2003;41(1):44–56. S0165017302002199 [pii]
Diamant S, Podoly E, Friedler A, Ligumsky H, Livnah O, Soreq H. Butyrylcholinesterase attenuates amyloid fibril formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(23):8628–33. 0602922103 [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0602922103.
Drake J, Link CD, Butterfield DA. Oxidative stress precedes fibrillar deposition of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid beta-peptide (1-42) in a transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans model. Neurobiol Aging. 2003;24(3):415–20. S0197458002002257 [pii]
Duce JA, Bush AI. Biological metals and Alzheimer’s disease: implications for therapeutics and diagnostics. Prog Neurobiol. 2010;92(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.04.003. S0301-0082(10)00093-6 [pii]
Duce JA, Tsatsanis A, Cater MA, James SA, Robb E, Wikhe K, Leong SL, Perez K, Johanssen T, Greenough MA, Cho HH, Galatis D, Moir RD, Masters CL, McLean C, Tanzi RE, Cappai R, Barnham KJ, Ciccotosto GD, Rogers JT, Bush AI. Iron-export ferroxidase activity of beta-amyloid precursor protein is inhibited by zinc in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell. 2010;142(6):857–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.08.014. S0092-8674(10)00938-4 [pii]
Fowler JS, Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Logan J, Pappas N, Shea C, MacGregor R. Age-related increases in brain monoamine oxidase B in living healthy human subjects. Neurobiol Aging. 1997;18(4):431–5. S0197-4580(97)00037-7 [pii]
Gal S, Zheng H, Fridkin M, Youdim MB. Novel multifunctional neuroprotective iron chelator-monoamine oxidase inhibitor drugs for neurodegenerative diseases. In vivo selective brain monoamine oxidase inhibition and prevention of MPTP-induced striatal dopamine depletion. J Neurochem. 2005;95(1):79–88. JNC3341 [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03341.x.
Gal S, Zheng H, Fridkin M, Youdim MB. Restoration of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons in post-MPTP treatment by the novel multifunctional brain-permeable iron chelator-monoamine oxidase inhibitor drug, M30. Neurotox Res. 2010;17(1):15–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9070-9.
Geldenhuys WJ, Youdim MB, Carroll RT, Van der Schyf CJ. The emergence of designed multiple ligands for neurodegenerative disorders. Prog Neurobiol. 2011;94(4):347–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.04.010. S0301-0082(11)00061-X [pii]
Gozes I. NAP (davunetide) provides functional and structural neuroprotection. Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17(10):1040–4. BSP/CPD/E-Pub/000374 [pii]
Gozes I, Bardea A, Bechar M, Pearl O, Reshef A, Zamostiano R, Davidson A, Rubinraut S, Giladi E, Fridkin M, Brenneman DE. Neuropeptides and neuronal survival: neuroprotective strategy for Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1997;814:161–6.
Gozes I, Giladi E, Pinhasov A, Bardea A, Brenneman DE. Activity-dependent neurotrophic factor: intranasal administration of femtomolar-acting peptides improve performance in a water maze. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000;293(3):1091–8.
Gozes I, Divinsky I, Pilzer I, Fridkin M, Brenneman DE, Spier AD. From vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) through activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP) to NAP: a view of neuroprotection and cell division. J Mol Neurosci. 2003;20(3):315–22. JMN:20:3:315 [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:20:3:315.
Guglielmotto M, Giliberto L, Tamagno E, Tabaton M. Oxidative stress mediates the pathogenic effect of different Alzheimer’s disease risk factors. Front Aging Neurosci. 2010;2:3. https://doi.org/10.3389/neuro.24.003.2010.
Hamrick SE, McQuillen PS, Jiang X, Mu D, Madan A, Ferriero DM. A role for hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in desferoxamine neuroprotection. Neurosci Lett. 2005;379(2):96–100. S0304-3940(05)00009-1 [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2004.12.080.
Hegde ML, Bharathi P, Suram A, Venugopal C, Jagannathan R, Poddar P, Srinivas P, Sambamurti K, Rao KJ, Scancar J, Messori L, Zecca L, Zatta P. Challenges associated with metal chelation therapy in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2009;17(3):457–68. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2009-1068. Q3510L74N8003871 [pii]
Hensley K, Carney JM, Mattson MP, Aksenova M, Harris M, Wu JF, Floyd RA, Butterfield DA. A model for beta-amyloid aggregation and neurotoxicity based on free radical generation by the peptide: relevance to Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91(8):3270–4.
Hopkins AL. Network pharmacology: the next paradigm in drug discovery. Nat Chem Biol. 2008;4(11):682–90. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.118. nchembio.118 [pii]
Huang X, Atwood CS, Hartshorn MA, Multhaup G, Goldstein LE, Scarpa RC, Cuajungco MP, Gray DN, Lim J, Moir RD, Tanzi RE, Bush AI. The A beta peptide of Alzheimer’s disease directly produces hydrogen peroxide through metal ion reduction. Biochemistry. 1999a;38(24): 7609–16. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi990438f. bi990438f [pii]
Huang X, Cuajungco MP, Atwood CS, Hartshorn MA, Tyndall JD, Hanson GR, Stokes KC, Leopold M, Multhaup G, Goldstein LE, Scarpa RC, Saunders AJ, Lim J, Moir RD, Glabe C, Bowden EF, Masters CL, Fairlie DP, Tanzi RE, Bush AI. Cu(II) potentiation of alzheimer abeta neurotoxicity. Correlation with cell-free hydrogen peroxide production and metal reduction. J Biol Chem. 1999b;274(52):37111–6.
Inestrosa NC, Alvarez A, Perez CA, Moreno RD, Vicente M, Linker C, Casanueva OI, Soto C, Garrido J. Acetylcholinesterase accelerates assembly of amyloid-beta-peptides into Alzheimer’s fibrils: possible role of the peripheral site of the enzyme. Neuron. 1996;16(4):881–91. S0896-6273(00)80108-7 [pii]
Ito K, Ahadieh S, Corrigan B, French J, Fullerton T, Tensfeldt T. Disease progression meta-analysis model in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2010;6(1):39–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2009.05.665. S1552-5260(09)02013-5 [pii]
Jann MW. Rivastigmine, a new-generation cholinesterase inhibitor for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacotherapy. 2000;20(1):1–12.
Kaur D, Yantiri F, Rajagopalan S, Kumar J, Mo JQ, Boonplueang R, Viswanath V, Jacobs R, Yang L, Beal MF, DiMonte D, Volitaskis I, Ellerby L, Cherny RA, Bush AI, Andersen JK. Genetic or pharmacological iron chelation prevents MPTP-induced neurotoxicity in vivo: a novel therapy for Parkinson’s disease. Neuron. 2003;37(6):899–909. S0896627303001260 [pii]
Kayyali R, Pannala AS, Khodr H, Hider RC. Comparative radical scavenging ability of bidentate iron (III) chelators. Biochem Pharmacol. 1998;55(8):1327–32. S0006-2952(97)00602-3 [pii]
Kimura M, Akasofu S, Ogura H, Sawada K. Protective effect of donepezil against Abeta(1-40) neurotoxicity in rat septal neurons. Brain Res. 2005a;1047(1):72–84. S0006-8993(05)00516-0 [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2005.04.014.
Kimura M, Komatsu H, Ogura H, Sawada K. Comparison of donepezil and memantine for protective effect against amyloid-beta(1-42) toxicity in rat septal neurons. Neurosci Lett. 2005b;391(1–2):17–21. S0304-3940(05)00961-4 [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2005.08.036.
Kupershmidt L, Weinreb O, Amit T, Mandel S, Carri MT, Youdim MB. Neuroprotective and neuritogenic activities of novel multimodal iron-chelating drugs in motor-neuron-like NSC-34 cells and transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. FASEB J. 2009;23(11):3766–79. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.09-130047. fj.09-130047 [pii]
Kupershmidt L, Weinreb O, Amit T, Mandel S, Bar-Am O, Youdim MB. Novel molecular targets of the neuroprotective/neurorescue multimodal iron chelating drug M30 in the mouse brain. Neuroscience. 2011;189:345–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.03.040. S0306-4522(11)00322-8 [pii]
Lee HP, Zhu X, Casadesus G, Castellani RJ, Nunomura A, Smith MA, Lee HG, Perry G. Antioxidant approaches for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Rev Neurother. 2010;10(7):1201–8. https://doi.org/10.1586/ern.10.74.
Lin R, Chen X, Li W, Han Y, Liu P, Pi R. Exposure to metal ions regulates mRNA levels of APP and BACE1 in PC12 cells: blockage by curcumin. Neurosci Lett. 2008;440(3):344–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2008.05.070. S0304-3940(08)00733-7 [pii]
Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;46(1–3):3–26. S0169-409X(00)00129-0 [pii]
Luque FA, Jaffe SL. The molecular and cellular pathogenesis of dementia of the Alzheimer’s type an overview. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2009;84:151–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0074-7742(09)00408-5. S0074-7742(09)00408-5 [pii]
Mancini F, Naldi M, Cavrini V, Andrisano V. Multiwell fluorometric and colorimetric microassays for the evaluation of beta-secretase (BACE-1) inhibitors. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007;388(5–6): 1175–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-007-1356-2.
Marrazzo A, Caraci F, Salinaro ET, Su TP, Copani A, Ronsisvalle G. Neuroprotective effects of sigma-1 receptor agonists against beta-amyloid-induced toxicity. Neuroreport. 2005;16(11): 1223–6. 00001756-200508010-00018 [pii]
Massoud F, Gauthier S. Update on the pharmacological treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2010;8(1):69–80. https://doi.org/10.2174/157015910790909520.
Mechlovich D, Amit T, Mandel SA, Bar-Am O, Bloch K, Vardi P, Youdim MB. The novel multifunctional, iron-chelating drugs M30 and HLA20 protect pancreatic beta-cell lines from oxidative stress damage. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010;333(3):874–82. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.109.164269. jpet.109.164269 [pii]
Meunier J, Ieni J, Maurice T. The anti-amnesic and neuroprotective effects of donepezil against amyloid beta25-35 peptide-induced toxicity in mice involve an interaction with the sigma1 receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 2006a;149(8):998–1012. 0706927 [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0706927.
Meunier J, Ieni J, Maurice T. Antiamnesic and neuroprotective effects of donepezil against learning impairments induced in mice by exposure to carbon monoxide gas. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006b;317(3):1307–19. jpet.106.101527 [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.106.101527.
Morphy R. Selectively nonselective kinase inhibition: striking the right balance. J Med Chem. 2010;53(4):1413–37. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm901132v.
Munoz-Torrero D. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors as disease-modifying therapies for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(24):2433–55.
Olanow CW, Rascol O, Hauser R, Feigin PD, Jankovic J, Lang A, Langston W, Melamed E, Poewe W, Stocchi F, Tolosa E. A double-blind, delayed-start trial of rasagiline in Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(13):1268–78. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0809335. 361/13/1268 [pii]
Patil S, Sheng L, Masserang A, Chan C. Palmitic acid-treated astrocytes induce BACE1 upregulation and accumulation of C-terminal fragment of APP in primary cortical neurons. Neurosci Lett. 2006;406(1–2):55–9. S0304-3940(06)00708-7 [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2006.07.015.
Perez LR, Franz KJ. Minding metals: tailoring multifunctional chelating agents for neurodegenerative disease. Dalton Trans. 2010;39(9):2177–87. https://doi.org/10.1039/b919237a.
Piazzi L, Rampa A, Bisi A, Gobbi S, Belluti F, Cavalli A, Bartolini M, Andrisano V, Valenti P, Recanatini M. 3-(4-[[benzyl(methyl)amino]methyl]phenyl)-6,7-dimethoxy-2H-2-chromenone (AP2238) inhibits both acetylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase-induced beta-amyloid aggregation: a dual function lead for Alzheimer’s disease therapy. J Med Chem. 2003;46(12): 2279–82. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm0340602.
Querfurth HW, LaFerla FM. Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(4):329–44. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra0909142. 362/4/329 [pii]
Reinikainen KJ, Soininen H, Riekkinen PJ. Neurotransmitter changes in Alzheimer’s disease: implications to diagnostics and therapy. J Neurosci Res. 1990;27(4):576–86. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.490270419.
Reznichenko L, Amit T, Zheng H, Avramovich-Tirosh Y, Youdim MB, Weinreb O, Mandel S. Reduction of iron-regulated amyloid precursor protein and beta-amyloid peptide by (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in cell cultures: implications for iron chelation in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem. 2006;97(2):527–36. JNC3770 [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03770.x.
Rogers JT, Randall JD, Cahill CM, Eder PS, Huang X, Gunshin H, Leiter L, McPhee J, Sarang SS, Utsuki T, Greig NH, Lahiri DK, Tanzi RE, Bush AI, Giordano T, Gullans SR. An iron-responsive element type II in the 5′-untranslated region of the Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein transcript. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(47):45518–28. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M207435200. M207435200 [pii]
Sano M, Ernesto C, Thomas RG, Klauber MR, Schafer K, Grundman M, Woodbury P, Growdon J, Cotman CW, Pfeiffer E, Schneider LS, Thal LJ. A controlled trial of selegiline, alpha-tocopherol, or both as treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. The Alzheimer’s disease cooperative study. N Engl J Med. 1997;336(17):1216–22. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199704243361704.
Saura J, Luque JM, Cesura AM, Da Prada M, Chan-Palay V, Huber G, Loffler J, Richards JG. Increased monoamine oxidase B activity in plaque-associated astrocytes of Alzheimer brains revealed by quantitative enzyme radioautography. Neuroscience. 1994;62(1):15–30.
Sayre LM, Perry G, Smith MA. Oxidative stress and neurotoxicity. Chem Res Toxicol. 2008;21(1):172–88. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx700210j.
Schneider LS, Olin JT, Pawluczyk S. A double-blind crossover pilot study of l-deprenyl (selegiline) combined with cholinesterase inhibitor in Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Psychiatry. 1993;150(2): 321–3. https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.150.2.321.
Shachar DB, Kahana N, Kampel V, Warshawsky A, Youdim MB. Neuroprotection by a novel brain permeable iron chelator, VK-28, against 6-hydroxydopamine lession in rats. Neuropharmacology. 2004;46(2):254–63. S002839080300354X [pii]
Silvestri L, Camaschella C. A potential pathogenetic role of iron in Alzheimer’s disease. J Cell Mol Med. 2008;12(5A):1548–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00356.x. JCMM356 [pii]
Singh AT, Bhattacharyya RS, Radeff JM, Stern PH. Regulation of parathyroid hormone-stimulated phospholipase D in UMR-106 cells by calcium, MAP kinase, and small G proteins. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18(8):1453–60. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.8.1453.
Smith MA, Hirai K, Hsiao K, Pappolla MA, Harris PL, Siedlak SL, Tabaton M, Perry G. Amyloid-beta deposition in Alzheimer transgenic mice is associated with oxidative stress. J Neurochem. 1998;70(5):2212–5.
Soto C. Plaque busters: strategies to inhibit amyloid formation in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Med Today. 1999;5(8):343–50. S1357-4310(99)01508-7 [pii]
Tamagno E, Bardini P, Obbili A, Vitali A, Borghi R, Zaccheo D, Pronzato MA, Danni O, Smith MA, Perry G, Tabaton M. Oxidative stress increases expression and activity of BACE in NT2 neurons. Neurobiol Dis. 2002;10(3):279–88. S0969996102905152 [pii]
Tamagno E, Parola M, Bardini P, Piccini A, Borghi R, Guglielmotto M, Santoro G, Davit A, Danni O, Smith MA, Perry G, Tabaton M. Beta-site APP cleaving enzyme up-regulation induced by 4-hydroxynonenal is mediated by stress-activated protein kinases pathways. J Neurochem. 2005;92(3):628–36. JNC2895 [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02895.x.
van der Flier WM, Scheltens P. Epidemiology and risk factors of dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005;76(Suppl 5):v2–7. 76/suppl_5/v2 [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2005.082867.
Wang CY, Wang T, Zheng W, Zhao BL, Danscher G, Chen YH, Wang ZY. Zinc overload enhances APP cleavage and Abeta deposition in the Alzheimer mouse brain. PLoS One. 2010;5(12):e15349. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0015349.
Weinreb O, Amit T, Bar-Am O, Chillag-Talmor O, Youdim MB. Novel neuroprotective mechanism of action of rasagiline is associated with its propargyl moiety: interaction of Bcl-2 family members with PKC pathway. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1053:348–55. 1053/1/348 [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1344.030.
Weinreb O, Amit T, Bar-Am O, Youdim MB. Induction of neurotrophic factors GDNF and BDNF associated with the mechanism of neurorescue action of rasagiline and ladostigil: new insights and implications for therapy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1122:155–68. 1122/1/155 [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1403.011.
Weinreb O, Amit T, Bar-Am O, Youdim MB. Rasagiline: a novel anti-Parkinsonian monoamine oxidase-B inhibitor with neuroprotective activity. Prog Neurobiol. 2010;92(3): 330–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.06.008. S0301-0082(10)00120-6 [pii]
Weinreb O, Amit T, Bar-Am O, Youdim MB. A novel anti-Alzheimer’s disease drug, ladostigil neuroprotective, multimodal brain-selective monoamine oxidase and cholinesterase inhibitor. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2011;100:191–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-386467-3.00010-8. B978-0-12-386467-3.00010-8 [pii]
Wilkemeyer MF, Chen SY, Menkari CE, Brenneman DE, Sulik KK, Charness ME. Differential effects of ethanol antagonism and neuroprotection in peptide fragment NAPVSIPQ prevention of ethanol-induced developmental toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(14):8543–8. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1331636100. 1331636100 [pii]
Yamamoto A, Shin RW, Hasegawa K, Naiki H, Sato H, Yoshimasu F, Kitamoto T. Iron (III) induces aggregation of hyperphosphorylated tau and its reduction to iron (II) reverses the aggregation: implications in the formation of neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem. 2002;82(5):1137–47. 1061 [pii]
Yatin SM, Varadarajan S, Link CD, Butterfield DA. In vitro and in vivo oxidative stress associated with Alzheimer’s amyloid beta-peptide (1-42). Neurobiol Aging. 1999;20(3):325–30. discussion 339-342. S0197458099000561 [pii]
Yogev-Falach M, Bar-Am O, Amit T, Weinreb O, Youdim MB. A multifunctional, neuroprotective drug, ladostigil (TV3326), regulates holo-APP translation and processing. FASEB J. 2006;20(12):2177–9. fj.05-4910fje [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.05-4910fje.
Zheng H, Gal S, Weiner LM, Bar-Am O, Warshawsky A, Fridkin M, Youdim MB. Novel multifunctional neuroprotective iron chelator-monoamine oxidase inhibitor drugs for neurodegenerative diseases: in vitro studies on antioxidant activity, prevention of lipid peroxide formation and monoamine oxidase inhibition. J Neurochem. 2005a;95(1):68–78. JNC3340 [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03340.x.
Zheng H, Weiner LM, Bar-Am O, Epsztejn S, Cabantchik ZI, Warshawsky A, Youdim MB, Fridkin M. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of novel bifunctional iron-chelators as potential agents for neuroprotection in Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other neurodegenerative diseases. Bioorg Med Chem. 2005b;13(3):773–83. S0968-0896(04)00839-9 [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2004.10.037.
Zheng H, Blat D, Fridkin M. Novel neuroprotective neurotrophic NAP analogs targeting metal toxicity and oxidative stress: potential candidates for the control of neurodegenerative diseases. J Neural Transm Suppl. 2006;71:163–72.
Zheng H, Youdim MB, Fridkin M. Site-activated multifunctional chelator with acetylcholinesterase and neuroprotective-neurorestorative moieties for Alzheimer’s therapy. J Med Chem. 2009;52(14):4095–8. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm900504c.
Zheng H, Youdim MB, Fridkin M. Selective acetylcholinesterase inhibitor activated by acetylcholinesterase releases an active chelator with neurorescuing and anti-amyloid activities. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2010a;1(11):737–46. https://doi.org/10.1021/cn100069c.
Zheng H, Youdim MB, Fridkin M. Site-activated chelators targeting acetylcholinesterase and monoamine oxidase for Alzheimer’s therapy. ACS Chem Biol. 2010b;5(6):603–10. https://doi.org/10.1021/cb900264w.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Section Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Zheng, H., Amit, T., Bar-Am, O., Fridkin, M., Mandel, S.A., Youdim, M.B.H. (2020). From Anti-Parkinson’s Drug Rasagiline to Novel Multitarget Iron Chelators with Acetylcholinesterase and Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitory and Neuroprotective Properties for Alzheimer’s Disease. In: Riederer, P., Laux, G., Mulsant, B., Le, W., Nagatsu, T. (eds) NeuroPsychopharmacotherapy. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-56015-1_234-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-56015-1_234-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-56015-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-56015-1
eBook Packages: Springer Reference MedicineReference Module Medicine