Abstract
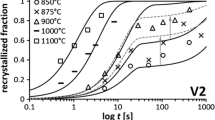
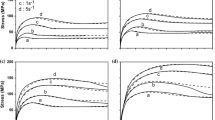
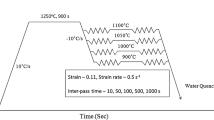
After and during hot rolling of steel, recrystallization can occur and impact severely on the resulting product properties. Recrystallization kinetics are, in particular, influenced by the addition of micro-alloying elements. On the one hand, micro-alloying elements in solid solution, such as Nb, Ti and V, exert a solute drag effect, which reduces the mobility of the grain boundaries. On the other hand, micro-alloying elements form precipitates, which exert a particle pinning force on the grain boundaries. In the present work, we formulate a physically-based recrystallization model with grain boundary mobilities that account simultaneously for the solute drag and Zener drag impact of Nb, Ti and V. We verify the model on numerous experiments on static recrystallization from literature, where good agreement is observed with a single set of simulation input parameters.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.F. Medina, a. Quispe, ISIJ Int. 41 (2001) 774–781.
C.S. Smith, Trans. AIME 175 (1948) 15–51.
M. Gomez, A. Quispe, S.F. Medina, Steel Res. Int. 85 (2014) 1440–1445.
H.L. Andrade, M.G. Akben, J.J. Jonas, Metall. Trans. A 14 (1983) 1967–1977.
M. Avrami, J. Chem. Phys. 8 (1940) 212–224.
M.K. Rehman, H.S. Zurob, Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 44 (2013) 1862–1871.
K. Rehman, H.S. Zurob, Mater. Sci. Forum 753 (2013) 417–422.
J.W. Cahn, Acta Metall. 10 (1962) 789–798.
H. Buken, P. Sherstnev, E. Kozeschnik, Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 24 (2016) 11pp.
J.E. Bailey, P.B. Hirsch, Proc. R. Soc. London A 267 (1962) 11–37.
Q. Zhu, C.M. Sellars, H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Mater. Sci. Technol. 23 (2007) 757–766.
H.S. Zurob, Y. Brechet, G. Purdy, Acta Mater. 49 (2001) 4183–4190.
E. Nes, Acta Metall. 24 (1976) 391–398.
D. Turnbull, Trans. AIME 191 (1951) 661–665.
G. Stechauner, E. Kozeschnik, Calphad 47 (2014) 92–99.
T. Zhou, R.J. O’Malley, H.S. Zurob, Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 41 (2010) 2112–2120.
H.O.K. Kirchner, Metall. Trans. 2 (1971) 2861–2864.
S.F. Medina, a. Quispe, ISIJ Int. 36 (1996) 1295–1300.
S.F. Medina, J.E. Mancilla, C. a. Hernández, ISIJ Int. 34 (1994) 689–696.
S.F. Medina, Scr. Metall. Mater. 32 (1995) 43–48.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 TMS (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society)
About this paper
Cite this paper
Buken, H., Zamberger, S., Kozeschnik, E. (2016). A Model for the Influence of Micro-Alloying Elements on Static Recrystallization of Austenite. In: Holm, E.A., et al. Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Recrystallization and Grain Growth (ReX&GG 2016). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48770-0_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48770-0_16
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-48626-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-48770-0
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)