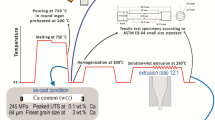
Abstract
Mg-Zn-Y system alloys have been a great interest because Mg-Zn-Y alloys with I-phase exhibited high ductility at room and elevated temperatures. According to our preliminary experiments, the addition of CaO improved strength, but the process window became narrow. Therefore, the aim of current work was to find optimum extrusion conditions for CaO added Mg-Zn-Y alloys by processing maps. The 0.3 wt.% of CaO added Mg-9.5Zn-2Y (Mg95.6Zn3.8Y0.6) alloy was prepared by casting into steel mold and homogenizing. Hot compression test were performed in the Gleeble machine at temperature range of 250–400 °C with various strain rates. The alloys were extruded with a reduction ratio of 20:1. To analyze the microstructure and texture, optical micrograph, scanning electron microscope and electron backscattered diffraction were used. Moreover, we investigated the effects of metallic Ca addition in this alloy to compare with the addition of CaO.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. J. Polmear, Metallurgy of the Light Metals, 3rd edn, Edward Arnold, London, 1995.
B. L. Mordike, T. Ebert, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 302 (2001) 37–45.
Q. Wang, J. Chen, Z. Zhao, S. He, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 528 (2010) 323–328.
D. H. Bae, S. H. Kim, D. H. Kim, W. T. Kim, Acta Mater., 50 (2002) 2343.
J. Y. Lee, D. H. Kim, H.K. Lim, D.H. Kim, Mater. Lett., 59 (2005)3801.
J. Y. Lee, H. K. Lim, D.-H. Kim, W.T. Kim, D.H. Kim, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 449–451 (2007) 987.
J. Y. Lee, D. -H. Kim, H. K. Lim, D. H. Kim, Mater. Lett., 59 (2005) pp. 3801–3805.
J. M. Dubois, P. Plaindoux, E. Berlin-Ferre, N. Tamura, D. J. Sordelet, Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Quasicrystals. Singapore: World Scientific; 1997.
Z.P. Luo, S.Q. Zhang, Y.L. Tang, D.S. Zhao, Scripta Metall. Mater., 28 (1993) 1513–1518.
E. Abe, H. Takakura, A. Singh, A.P. Tsai, J. Alloys Compd., 283 (1999) 169.
Alok Singh, M. Nakamura, M. Watanabe, A. Kato, A. P. Tsai, Scripta Materialia, 49 (2003) 417–422.
S. K. Kim, J. K. Lee, Y. O. Yoon, H. H. Jo, Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 187–188 (2007) 757–760.
J.K. Lee, S. H. Ha, Y. J. Kim, H. H. Jo, S. K. Kim, Journal of the Korean Foundrymen’s Society, vol. 27, No. 3, 2007, 131–134.
Y.V.R.K. Prasad, K.P. Rao, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 487 (2008) 316–327.
W. Peng, W. Zeng, Q. Wang, H. Yu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 571 (2013)116–122.
N. Srinivasan, Y.V.R.K. Prasad, Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 51 (1995) 171–192.
Y.V.R.K. Prasad, K.P. Rao, N. Hort, K.U. Kainer, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 502 (2009) 25–31.
Y.V.R.K. Prasad, S. Sasidhara, Hot Working Guide: A Compendium of Processing Maps, ASM International; 1997.
H. Ziegler, Progress in Solid Mechanics, Vol. 4, Eds. I.N. Sneddon and R. Hill, John Wiley and Sons New York (1963) 93.
Sun. H. F., Liang. S. J., Wang. E. D., Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 19 (2009) s349–s354
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 TMS (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society)
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kwak, Ty. et al. (2014). Effect of CaO on Hot Workability and Microstructure of Mg-9.5Zn-2Y Alloy. In: Alderman, M., Manuel, M.V., Hort, N., Neelameggham, N.R. (eds) Magnesium Technology 2014. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48231-6_57
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48231-6_57
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-48589-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-48231-6
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)