Abstract
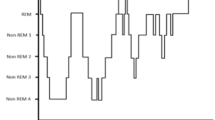
Sleep can be considered as a mechanism of self-regulation and resting that occurs in the majority of mammals in 24-hour cycles approximately, alternating with states of wakefulness. As a whole, sleep is a heterogeneous state presenting different stages. These stages can be identified through the recording and analysis of certain physiological parameters. From a medical point of view the analysis of the sleep is useful in the diagnosis of health problems that receive the generic name of “sleep disorders”. Sleep disorders can be grouped into four main categories: (a) problems to fall asleep and stay asleep, (b) problems to stay awake, (c) problems to maintain a regular schedule of sleep, and (d) unusual behaviors during sleep. This article presents an overview of the evolution of sleep research, with special attention to the most relevant milestones that have led to the systematic and automatic analysis of the sleep, and the establishment of standards for the construction of the so-called “Hypnograms”.
The original version of this chapter was inadvertently published with an incorrect chapter pagination 859–863 and DOI 10.1007/978-3-319-32703-7_168. The page range and the DOI has been re-assigned. The correct page range is 865–869 and the DOI is 10.1007/978-3-319-32703-7_169. The erratum to this chapter is available at DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-32703-7_260
An erratum to this chapter can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-32703-7_260
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loomis, A. L.; Harvey, E. N.; Hobart, G. A. (1937) Cerebral states during sleep, as studied by human brain potentials. Journal of Experimental Psychology, Vol 21(2), 127-144. doi:10.1037/h0057431
Loomis, A. L., Harvey, E. N. and Hobart, G. A. (1936) Electrical potentials of the human brain. J. Exp. Psychol., 19: 249–279.
Loomis, A. L., Harvey, E. N. and Hobart, G. A. (1938) Distribution of disturbance patterns in the human electroencephalogram, with special reference to sleep. J. Neurophysiol., 1: 413–430.
Liberson WT. (1944) Problem of sleep and mental disease. Digest Neurol Psychiat 12: 93-108.
Aserinsky E, Kleitman N (1953) Regularly Occurring Periods of Eye Motility, and Concomitant Phenomena, during Sleep. Science, New Series, Vol. 118, No. 3062., pp. 273-274.
Dement, W; Kleitman, N. (1957) Cyclic variations in EEG during sleep and their relation to eye movements, body motility, and dreaming. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology 9 (4): 673–690. doi:10.1016/0013-4694(57)90088-3. PMID 13480240.
Brazier, M. A. B. et al. (1961) Proposal for an LEG terminology by the terminology committee of the International Federation for Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology. Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol., 13: 646-650.
Reschtschaffen, A. and Kales, A. (1968) A Manual of Standarized Terminology, Techniques, and Scoring System for Sleep Stages of Human Subjects. Washington Public Health Service. US Government Printing Office, Washington DC.
Sleep Computing Committee of the Japanese Society of Sleep Research Society (JSSR). Tadao Hori et al. (2001) Proposed supplements and amendments to ‘A Manual of Standardized Terminology, Techniques and Scoring System for Sleep Stages of Human Subjects’, the Rechtschaffen & Kales (1968) standard. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 55, 305-310.
Task Force ‘Scoring of Polysomnographic Recordings’ of the German Sleep Society (DGSM): Hartmut Schulz et al. (2006) A Review of Sleep EEG Patterns. Part I: A Compilation of Amended Rules for Their Visual Recognition according to Rechtschaffen and Kales.
Iber C, Ancoli-Israel S, Chesson AL, Quan SF. (2007) The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events: Rules, terminology, and technical specification. Version 1. Westchester, IL: American Academy of Sleep Medicine. 0-4-X
Berry R, Brooks R, Gamaldo C, et al. (2012) The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events: rules, terminology, and technical specification, Version 2.0. Darien, IL: American Academy of Sleep.
Berry R, Brooks R, Gamaldo C, et al. (2014) The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events: rules, terminology, and technical specification, Version 2.1. Darien, IL: American Academy of Sleep.
Berry RB, Brooks R, Gamaldo CE, Harding SM, Lloyd RM, Marcus CL and Vaughn BV (2015) The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events: Rules, Terminology and Technical Specifications, Version 2.2. www.aasmnet.org.Darien, Illinois: American Academy of Sleep Medicine.
Khalighi S, Sousa T, Pires G, Nunes U (2013) Automatic sleep staging: A computer assisted approach for optimal combination of features and polysomnographic channels. Expert Systems with Applications 40, 7046-7059.
Nonclercq A, Urbain C, Verheulpen D, Decaestecker C, Van Bogaert P, Peigneux P (2013) Sleep spindle detection through amplitude–frequency normal modelling. Journal of Neuroscience Methods. Volume 214, Issue 2, pages 192–203, doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2013.01.015
Camilleri T.A., Camilleri K.P., Fabri S.G. (2014) Automatic detection of spindles and K-complexes in sleep EEG using switching multiple models. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control. Volume 10, pages 117–127, doi:10.1016/j.bspc.2014.01.010.
Hernández-Pereira E, Bolón-Canedo V, Sánchez-Maroño N, Ál-varez-Estévez D, Moret-Bonillo V, Alonso-Betanzos A (2016) A comparison of performance of K-complex classification methods using feature selection. Information Sciences. Volume 328, Pages 1–14.
Alvarez-Estevez, D., & Moret-Bonillo, V. (2011) Identification of electroencephalographic arousals in multichannel sleep recordings. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 58(1), 54–63. http://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2010.2075930
Alvarez-Estevez, D. et al. (2013) A method for the automatic analysis of the sleep macrostructure in continuum. Expert Systems with Applications, 40(5), 1796-1803.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fernández-Leal, Á., Moret-Bonillo, V., Cabrero-Canosa, M.J. (2016). Towards the Standardization of Hypnograms Construction for Sleep Analysis. In: Kyriacou, E., Christofides, S., Pattichis, C. (eds) XIV Mediterranean Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing 2016. IFMBE Proceedings, vol 57. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-32703-7_169
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-32703-7_169
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-32701-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-32703-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)