Abstract
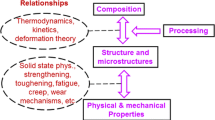
Physical metallurgy is a branch of materials science, especially focusing on the relationship between composition, processing, crystal structure and microstructure, and physical and mechanical properties. Because all properties are the manifestation of compositions, structure and microstructure, thermodynamics, kinetics, and plastic deformation, factors as encountered in processing control become very important to control phase transformation and microstructure and thus properties of alloys. All the underlying principles have been well built and physical metallurgy approaches mature. However, traditional physical metallurgy is based on the observations on conventional alloys. As composition is the most basic and original factor to determine the bonding, structure, microstructure, and thus properties to a certain extent, physical metallurgy principles might be different and need to be modified for HEAs which have entirely different compositions from conventional alloys. The most distinguished effects in HEAs are high-entropy, severe lattice distortion, sluggish diffusion, and cocktail effects. This chapter will present and discuss the corresponding subjects of physical metallurgy based on these effects.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reed-Hill RE, Abbaschian R (1994) Physical metallurgy principles, 3rd edn. PWS Publishing Company, Boston, pp xiii–xv
Cahn RW, Haasen P (eds) (1983) Physical metallurgy, 3rd revised and enlarged ed. Elsevier Science publishers BV, Amsterdam, pp 1–35
Yeh JW (2006) Recent progress in high-entropy alloys. Ann Chimie Sci Materiaux (Eur J Control) 31:633–648
Yeh JW (2013) Alloy design strategies and future trends in high-entropy alloys. JOM 65:1759–1771
Reed-Hill RE, Abbaschian R (1994) Physical metallurgy principles, 3rd edn. PWS Publishing Company, Boston, pp 353–358
Cullity BD, Stock SR (2001) Elements of X-ray diffraction, 3rd edn. Prentice-Hall Inc, Upper Saddle River, pp 327–340
Otto F, Yang Y, Bei H, George EP (2013) Relative effects of enthalpy and entropy on the phase stability of equiatomic high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater 61:2628–2638
Tsai KY, Tsai MH, Yeh JW (2013) Sluggish diffusion in Co-Cr-Fe-Mn-Ni high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater 61:4887–4898
Senkov ON, Scott JM, Senkova SV, Miracle DB, Woodward CF (2011) Microstructure and room temperature properties of a high-entropy TaNbHfZrTi alloy. J Alloys Compd 509:6043–6048
Tong CJ, Chen YL, Chen SK, Yeh JW, Shun TT, Tsau CH, Lin SJ, Chang SY (2005) Microstructure characterization of AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multi-principal elements. Metall Mater Trans A 36A:881–893
Hsu CY, Yeh JW, Chen SK, Shun TT (2004) Wear resistance and high-temperature compression strength of FCC CuCoNiCrAl0.5Fe alloy with boron addition. Metall Mater Trans A 35A:1465–1469
Zhang Y, Zhou YJ, Lin JP, Chen GL, Liaw PK (2008) Solid-solution phase formation rules for multi-component alloys. Adv Eng Mater 10:534–538
Guo S, Liu CT (2013) Phase selection rules for complex multi-component alloys with equiatomic or close-to-equiatomic compositions. Chin J Nat 35:85–96
Yeh JW (2009) Recent progress in high-entropy alloys, the 2009 cross-strait conference on metallic glasses. National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, Taipei
Chen ST, Yeh JW (2009) Effect of mixing enthalpy, mixing entropy and atomic size difference on the structure of multicomponent alloys. Master’s thesis, National Tsing Hua University
Yang X, Zhang Y (2012) Prediction of high-entropy stabilized solid-solution in multi-component alloys. Mater Chem Phys 132:233–238
Yeh JW, Chen SK, Gan JY, Lin SJ, Chin TS, Shun TT, Tsau CH, Chang SY (2004) Formation of simple crystal structures in solid-solution alloys with multi-principal metallic elements. Metall Mater Trans A 35A:2533–2536
Yeh JW, Chang SY, Hong YD, Chen SK, Lin SJ (2007) Anomalous decrease in X-ray diffraction intensities of Cu-Ni-Al-Co-Cr-Fe-Si alloy systems with multi-principal elements. Mater Chem Phys 103:41–46
Wang S (2013) Atomic structure modeling of multi-principal-element alloys by the principle of maximum entropy. Entropy 15:5536–5548
Huang PK, Yeh JW (2010) Inhibition of grain coarsening up to 1000 °C in (AlCrNbSiTiV)N superhard coatings. Scr Mater 62:105–118
Guo S, Liu CT (2011) Phase stability in high entropy alloys: formation of solid-solution phase or amorphous phase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 21:433–446
Meyers MA, Chawla KK (1984) Mechanical metallurgy: principles and applications. Prentice-Hall, Inc, Englewood Cliff, New Jersey, pp 188–199
Senkov ON, Wilks GB, Miracle DB, Chuang CP, Liaw PK (2010) Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 18:1758–1765
Kao YF, Chen SK, Chen TJ, Chu PC, Yeh JW, Lin SJ (2011) Electrical, magnetic, and hall properties of AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys. J Alloys Compd 509:1607–1614
Lu CL, Lu SY, Yeh JW, Hsu WK (2013) Thermal expansion and enhanced heat transfer in high-entropy alloys. J Appl Crystallogr 46:736–739
Swalin RA (1972) Thermodynamics of solid, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 263–266
Tsai CW, Chen YL, Tsai MH, Yeh JW, Shun TT, Chen SK (2009) Deformation and annealing behaviors of high-entropy alloy Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi. J Alloys Compd 486:427–435
Hsu CY, Juan CC, Wang WR, Sheu TS, Yeh JW, Chen SK (2011) On the superior hot hardness and softening resistance of AlCoCrxFeMo0.5Ni high-entropy alloys. Mater Sci Eng A 528:3581–3588
Senkov ON, Wilks GB, Scott JM, Miracle DB (2011) Mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20 refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 19:698–706
Tsai MH, Wang CW, Tsai CW, Shen WJ, Yeh JW, Gan JY, Wu WW (2011) Thermal stability and performance of NbSiTaTiZr high-entropy alloy barrier for copper metallization. J Electrochem Soc 158:H1161–H1165
Tsai MH, Yeh JW, Gan JY (2008) Diffusion barrier properties of AlMoNbSiTaTiVZr high-entropy alloy layer between copper and silicon. Thin Solid Films 516:5527–5530
Shun TT, Hung CH, Lee CF (2010) Formation of ordered/disordered nanoparticles in FCC high entropy alloys. J Alloys Compd 493:105–109
Liu WH, Wu Y, He JY, Nieh TG, Lu ZP (2013) Grain growth and the hall–petch relationship in a high-entropy FeCrNiCoMn alloy. Scr Mater 68:526–529
Juan CC, Hsu CY, Tsai CW, Wang WR, Sheu TS, Yeh JW, Chen SK (2013) On microstructure and mechanical performance of AlCoCrFeMo0.5Nix high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 32:401–407
Ranganathan S (2003) Alloyed pleasures: multimetallic cocktails. Curr Sci 85:1404–1406
Zhang Y, Zuo TT, Cheng YQ, Liaw PK (2013) High-entropy alloys with high saturation magnetization, electrical resistivity, and malleability. Sci Rep 3:1455
Mackay AL (2001) On complexity. Crystallogr Rep 46:524–526
Cahn RW, Haasen P (eds) (1983) Physical metallurgy, 3rd revised and enlarged ed. Elsevier Science publishers BV, Amsterdam, pp 219–248
Porter DA (1992) Phase transformations in metals and alloys. Chapman & Hall, New York, pp 1–59
Kittel C (1996) Introduction to solid state physics, 7th edn. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 3–26
Alonso JA, Simozar S (1980) Prediction of solid solubility in alloys. Phys Rev B 22:5583–5588
Hume-Rothery W (1967) Factors affecting the stability of metallic phases. In: Rudman PS, Stringer J, Jaffee RI (eds) Phase stability in metals and alloys. McGraw-Hill, New York
Hume-Rothery W, Smallman RE, Haworth CW (1969) Structure of metals and alloys, 5th edn. Institute of Metals, London
Smith WF, Hashemi J (2006) Foundations of materials science and engineering, 4th edn. McGraw-Hill, Inc., New York
De Boer FR, Boom R, Mattens WCM, Miedema AR, Niessen AK (1988) Cohesion in metals: transition metal alloys. North-Holland Physics Publishing/Elsevier Science Publisher B.V, Amsterdam
Chen HY, Tsai CW, Tung CC, Yeh JW, Shun TT, Chen HC, Chen SK (2006) The effect of the substitution of Co by Mn in Al-Cr-Cu-Fe-Co-Ni high-entropy alloys. Ann Chimie Sci Materiaux 31:685–698
Santodonato LJ, Zhang Y, Feygenson M, Parish CM, Gao MC, Weber RJK, Neuefeind JC, Tang Z, Liaw PK (2015) Deviation from high-entropy configurations in the atomic distributions of a multi-principal-element alloy. Nat Commun 6:5964:1–13. doi:10.1038/ncomms6964
Hsu CY, Juan CC, Chen ST, Sheu TS, Chen ST, Yeh JW, Chen SK (2013) Phase diagrams of high-entropy alloy system Al-Co-Cr-Fe-Mo-Ni. J Appl Meteorol 65:1829–1839
Chen YL, Hu YH, Tsai CW, Hsieh CA, Kao SW, Yeh JW, Chin TS, Chen SK (2009) Alloying behavior of binary to octonary alloys based on Cu-Ni-Al-Co-Cr-Fe-Ti-Mo during mechanical alloying. J Alloys Compd 477:696–705
Chen YL, Hu YH, Hsieh CA, Yeh JW, Chen SK (2009) Competition between elements during mechanical alloying in an octonary multi-principal-element alloy system. J Alloys Compd 481:768–775
Chen YL, Hu YH, Tsai CW, Yeh JW, Chen SK, Chang SY (2009) Structural evolutions during mechanical milling and subsequent annealing of Cu-Ni-Al-Co-Cr-Fe-Ti alloys. Mater Chem Phys 118:354–361
Chen YL, Tsai CW, Juan CC, Chuang MH, Yeh JW, Chin TS, Chen SK (2010) Amorphization of equimolar alloys with HCP elements during mechanical alloying. J Alloys Compd 506:210–215
Chang HW, Huang PK, Davison A, Yeh JW, Tsau CH, Yang CC (2008) Nitride films deposited from an equimolar Al-Cr-Mo-Si-Ti alloy target by reactive DC magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 516:6402–6408
Egami T (1996) The atomic structure of aluminum based metallic glasses and universal criterion for glass formation. J Non Cryst Solids 205–207:575–582
Egami T, Waseda Y (1984) Atomic size effect on the formability of metallic glasses. J Non Cryst Solids 64:113–134
Inoue A (2000) Stabilization of metallic supercooled liquid and bulk amorphous alloys. Acta Mater 48:279–306
Kao SW, Yeh JW, Chin TS (2008) Rapidly solidified structure of alloys with two to eight equal-molar elements – a simulation by molecular dynamics. J Phys Condens Matter 20:145214
Turnbull D (1977) On the gram-atomic volumes of metal-metalloid glass forming alloys. Scr Metall 11:1131–1136
Turnbull D (1981) Metastable structures in metallurgy. Metall Trans B 12B:217–230
Greer AL (1993) Confusion by design. Nature 366:303–304
Porter DA (1992) Phase transformations in metals and alloys. Chapman & Hall, New York, pp 110–142
Swalin RA (1972) Thermodynamics of solids, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 220–223
Swalin RA (1972) Thermodynamics of solids, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 267–289
Meyers MA, Chawla KK (1984) Mechanical metallurgy: principles and applications. Prentice-Hall, Inc, Englewood Cliff, New Jersey, pp 52–59, and 247–256
Humphreys FJ, Hatherly M (2004) Recrystallization and related annealing phenomena, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 102–104
Kittel C (1996) Introduction to solid state physics, 7th edn. Wiley, Hoboken, p 78
Lee C, Yeh JW (2013) Study on deformation behaviors of equimolar alloys from Ni to CoCrFeMnNi. Master’s thesis, National Tsing Hua University
Meyers MA, Chawla KK (1984) Mechanical metallurgy: principles and applications. Prentice-Hall, Inc, Englewood Cliff, New Jersey, pp 226–270
Weertman J, Weertman JR (1964) Elementary dislocation theory. Macmillan, New York, pp 22–83
Schramm RE, Reed RF (1975) Stacking fault energies of seven commercial austenitic stainless steels. Metall Trans A 6A:1345–1351
Gallagher PCJ (1970) The influence of alloying, temperature, and related effects on the stacking fault energy. Metall Trans 1:2429–2461
Humphreys FJ, Hatherly M (2004) Recrystallization and related annealing phenomena, 2nd edn. Elsevier Science Ltd, Oxford, pp 24–26
Zaddach AJ, Niu C, Kock CC, Irving DL (2013) Mechanical properties and stacking fault energies of NiFeCrCoMn high-entropy alloy. J Appl Meteorol 65:1780–1789
Morikawa T, Higashida K (2010) Deformation microstructure and texture in a cold-rolled austenitic steel with low stacking-fault energy. Mater Trans 51:620–624
Bhattacharjee PP, Sathiaraj GD, Zaid M, Gatti JR, Lee C, Tsai CW, Yeh JW (2014) Microstructure and texture evolution during annealing of equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. J Alloys Compd 587:544–552
Shewmon PG (1963) Diffusion in solids. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 164–178
Reed-Hill RE, Abbaschian R (1994) Physical metallurgy principles, 3rd edn. PWS Publishing Company, Boston, pp 390–394
Otto F, Dlouhy A, Somsen C, Bei H, Eggeler G, George EP (2013) The influences of temperature and microstructure on the tensile properties of a CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater 61:5743–5755
Gludovatz B, Hohenwarter A, Catoor D, Chang EH, George EP, Ritchie RO (2014) A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Science 345:1153–1158
Wu Z, Bei H, Pharr GM, George EP (2014) Temperature dependence of the mechanical properties of equiatomic solid solution alloys with face-centered cubic crystal structures. Acta Mater 81:428–441
Couzinié JP, Dirras G, Perrière L, Chauveau T, Leroy E, Champion Y, Guillot I (2014) Microstructure of a near-equimolar refractory high-entropy alloy. Mater Lett 126:285–287
Lin CM, Juan CC, Chang CH, Tsai CW, Yeh JW (2015) Effect of Al addition on mechanical properties and microstructure of refractory AlxHfNbTaTiZr alloys. J Alloys Compd 624:100–107
Couryney TH (1990) Mechanical behavior of materials, international ed. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 162–219 & 263–324
Tsai BS, Yeh JW (2015) Microstructure and mechanical properties of AlxCoCrFeMnNi (x = 0 ~ 1). Master’s thesis, National Tsing Hua University
Meyers MA, Chawla KK (1984) Mechanical metallurgy: principles and applications. Prentice-Hall, Inc, Englewood Cliff, New Jersey, pp 402–413, & 494–514
Chen CS, Yang CC, Chai HY, Yeh JW, Chau JLH (2014) Novel cermet material of WC/multi-element alloy. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 43:200–204
Lin CM, Tsai CW, Huang SM, Yang CC, Yeh JW (2014) New TiC/Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti0.5 cermet with slow TiC coarsening during sintering. J Appl Meteorol 66:2050–2056
Meyers MA, Chawla KK (1984) Mechanical metallurgy: principles and applications. Prentice-Hall, Inc, Englewood Cliff, New Jersey, pp 659–687
Dieter GE (1988) Mechanical metallurgy, SI metric ed. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 432–470
Reed RC (2006) The superalloys: fundamentals and applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 1–120
Mohamed FA, Langdon TG (1974) The transition from dislocation climb to viscous glide in creep of solid solution alloys. Acta Metall 30:779–788
He JY, Zhu C, Zhou DQ, Liu WH, Nieh TG, Lu ZP (2014) Steady state flow of the FeCoNiCrMn high entropy alloy at elevated temperatures. Intermetallics 55:9–14
Wang WR, Wang WL, Yeh JW (2014) Phases, microstructure and mechanical properties of AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys at elevated temperatures. J Alloys Compd 589:143–152
Khana KB, Kutty TRG, Surappa MK (2006) Hot hardness and indentation creep study on Al-5% Mg alloy matrix-B4C particle reinforced composites. Mater Sci Eng A 427:76–82
Kutty TRG, Jarvis T, Ganguly C (1997) Hot hardness and indentation creep studies on Zr-1Nb-lSn-0.1Fe alloy. J Nucl Mater 246:189–195
Wang WR, Wang WL, Wang SC, Tsai YC, Lai CH, Yeh JW (2012) Effects of Al addition on the microstructure and mechanical property of AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 26:44–51
Dieter GE (1988) Mechanical metallurgy, SI metric ed. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 336–337
Merchant HD, Murty GS, Bahadur SN, Dwivedi LT, Mehrotra Y (1973) Hardness-temperature relationships in metals. J Mater Sci 8:437–442
Kutty TRG, Ravi K, Ganguly C (1999) Studies on hot hardness of Zr and its alloys for nuclear reactors. J Nucl Mater 265:91–99
Acknowledgments
J.W.Y. would like to acknowledge all the financial supports from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Ministry of Economic Affairs, and National Tsing Hua University, R.O.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Yeh, JW. (2016). Physical Metallurgy. In: Gao, M., Yeh, JW., Liaw, P., Zhang, Y. (eds) High-Entropy Alloys. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-27013-5_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-27013-5_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-27011-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-27013-5
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)