Abstract
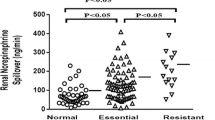
The contribution of sympathetic activation to the genesis and progression of hypertension has been well recognised for decades [1]. A step-up has been demonstrated in muscle sympathetic nerve activity from normal to high-normal blood pressure, white coat to borderline to established hypertension, with or without left ventricular hypertrophy [2]. These data are supported by other measures of sympathetic activation in man, specifically spillover of noradrenaline into plasma. A significant increase was noted in essential hypertension patients in comparison to normotensive controls [3] in a study of renal spillover. This increase was particularly prominent in younger hypertensives, aged 20–39 years.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krum H, Sobotka P, Mahfoud F, et al. Device-based antihypertensive therapy: therapeutic modulation of the autonomic nervous system. Circulation. 2011;123:209–15.
Smith PA, Graham LN, Mackintosh AF, et al. Relationship between central sympathetic activity and stages of human hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2004;17:217–22.
Esler M, Jennings G, Korner P, et al. Total, and organ-specific, noradrenaline plasma kinetics in essential hypertension. Am J Physiol. 1984;6:507–21.
DiBona GF, Kopp UC. Neural control of renal function. Physiol Rev. 1997;77:75–197.
DiBona GF. Sympathetic nervous system influences on the kidney: role in hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 1989;2:119S–24.
Katholi RE. Renal nerves in the pathogenesis of hypertension in experimental animals and humans. Am J Physiol. 1983;245:F1–14.
DiBona GF, Esler M. Translational medicine: the antihypertensive effect of renal denervation. Am J Physiol. 2010;298:R245–53.
Campese VM, Kogosov E. Renal afferent denervation prevents hypertension in rats with chronic renal failure. Hypertension. 1995;25:878–82.
Hausberg M, Kosch M, Harmelink P, et al. Sympathetic nerve activity in end-stage renal disease. Circulation. 2002;106:1974–9.
Converse Jr RL, Jacobsen TN, Toto RD, et al. Sympathetic overactivity in patients with chronic renal failure. N Engl J Med. 1992;327:1912–8.
Chapleau M. Arterial baroreflexes. In: Hypertension primer: the essentials of high blood pressure. 2nd ed. London: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 1999. p. 83.
Smithwick RH, Thompson JE. Splanchnicectomy for essential hypertension; results in 1,266 cases. J Am Med Assoc. 1953;152:1501–4.
Allen TR. Current status of lumbar sympathectomy. Am Surg. 1976;42:89–91.
Krum H, Schlaich M, Whitbourn R, Sobotka PA, Sadowski J, Bartus K, Kapelak B, Walton A, Sievert H, Thambar S, Abraham WT, Esler M. Catheter-based renal sympathetic denervation for resistant hypertension: a multicentre safety and proof-of-principle cohort study. Lancet. 2009;373:1275–81.
Symplicity HTN-2 Investigators, Esler MD, Krum H, Sobotka PA, Schlaich MP, Schmieder RE, Böhm M. Renal sympathetic denervation in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension (The Symplicity HTN-2 Trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;376:1903–9.
Schlaich MP, Sobotka PA, Krum H, Lambert E, Esler MD. Renal sympathetic-nerve ablation for uncontrolled hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:932–4.
Hering D, Lambert EA, Marusic P, Walton AS, Krum H, Lambert G, Esler M, Schlaich MP. Substantial reduction in single sympathetic nerve firing after renal denervation in patients with resistant hypertension. Hypertension. 2013;61:457–64.
Krum H, Schlaich MP, Sobotka PA, Böhm M, Mahfoud F, Rocha-Singh K, Katholi R, Esler MD. Percutaneous renal denervation in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension: final 3-year report of the Symplicity HTN-1 study. Lancet. 2014;383:622–9.
Esler MD, Krum H, Schlaich M, Schmieder RE, Böhm M, Sobotka PA. Renal sympathetic denervation for treatment of drug-resistant hypertension: one year results from the Symplicity HTN-2 randomized controlled trial. Circulation. 2012;126:2976–82.
Kandzari DE, Bhatt DL, Sobotka PA, O’Neill WW, Esler M, Flack JM, Katzen BT, Leon MB, Massaro JM, Negoita M, Oparil S, Rocha-Singh K, Straley C, Townsend RR, Bakris G. Catheter-based renal denervation for resistant hypertension: rationale and design of the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 Trial. Clin Cardiol. 2012;35:528–35.
Bhatt DL, Kandzari DE, O’Neill WW, D'Agostino R, Flack JM, Katzen BT, Leon MB, Liu M, Mauri L, Negoita M, Cohen SA, Oparil S, Rocha-Singh K, Townsend RR, Bakris GL, SYMPLICITY HTN-3 Investigators. A controlled trial of renal denervation for resistant hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1393–401.
Kaltenbach B, Id D, Franke JC, et al. Renal artery stenosis after renal sympathetic denervation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:2694–5.
Mabin T, Sapoval M, Cabane V, et al. First experience with endovascular ultrasound renal denervation for the treatment of resistant hypertension. EuroIntervention. 2012;8:57–61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Krum, H. (2015). Renal Sympathetic Denervation in the Management of Treatment-Resistant Hypertension. In: Goldsmith, D., Covic, A., Spaak, J. (eds) Cardio-Renal Clinical Challenges. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09162-4_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09162-4_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-09161-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-09162-4
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)