Abstract
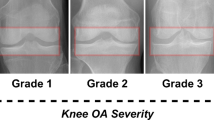
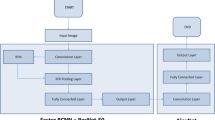
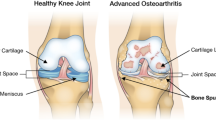
Knee osteoarthritis severity grading from plain radiographs and magnetic resonance (MR) images is of great significance in the diagnosis of osteoarthritis (OA). Recently, deep learning had a great impact on improving the Kellgren and Lawrence (KL) grading scheme of Knee osteoarthritis KOA using models that acquire the contextual features spontaneously without the need for any conventional high computational spatial configuration modeling. In this study, we review the state-of-the-art deep learning methods that enhanced the knee osteoarthritis severity KL grading. Pre-trained models such as Resnet18, VGG, DenseNet, Convolutional Siamese neural network, ResNet34, Squeeze-and-excitation ResNet (SE-ResNet) were found to be employed to extract valuable data for clinical images in the surveyed papers. The survey concludes that some very significant sophisticated deep learning methods were employed in some studies to grade KOA, which may also work on grading other diseases. Moreover, we show that applying Vision Transformer (ViT) for this specific task can be a better option than most of the convolutional neural networks (CNNs) based models.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braun, H.J., Gold, G.E.: Diagnosis of osteoarthritis: imaging. Bone 51(2), 278–288 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2011.11.019
Oka, H., et al.: Fully automatic quantification of knee osteoarthritis severity on plain radiographs. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 16(11), 1300–1306 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2008.03.011
Shamir, L., Ling, S.M., Scott, W., Hochberg, M., Ferrucci, L., Goldberg, I.G.: Early detection of radiographic knee osteoarthritis using computer-aided analysis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 17(10), 1307–1312 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2009.04.010
Yang, S.: Feature engineering in fine-grained image classification. Thesis, Jul. 2013. https://digital.lib.washington.edu:443/researchworks/handle/1773/23376. Accessed 17 Mar 2021
Ebrahimkhani, S., et al.: A review on segmentation of knee articular cartilage: from conventional methods towards deep learning. Artif. Intell. Med. 106, 101851 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2020.101851
Esteva, A., et al.: Deep learning-enabled medical computer vision. npj Digit. Med. 4(1), 5 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-020-00376-2
Serte, S., Akila, S.M, Almezhghwi, K.: Unsupervised classification of Covid-19 using chest X-rays with convolutional autoencoder. In: 4th International congress on Human-Computer Interaction, Optimization and robotic Applications, pp. 1–5 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/HORA55278.2022.9799880
Shen, D., Wu, G., Suk, H.-I.: Deep learning in medical image analysis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 19(1), 221–248 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071516-044442
Almezhghwi, K., Serte, S., Al-Turjman, F.: Convolutional neural networks for the classification of chest X-rays in the IoT era. Multimedia Tools Appl. 80(19), 29051–29065 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10907-y
Kaymak, S., Almezhghwi, K., Shelag, A.A.S.: Classification of diseases on chest X-rays using deep learning. In: Aliev, R.A., Kacprzyk, J., Pedrycz, W., Jamshidi, Mo., Sadikoglu, F.M. (eds.) ICAFS 2018. AISC, vol. 896, pp. 516–523. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04164-9_69
Giger, M.L.: Machine learning in medical imaging. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 15(3), 512–520 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacr.2017.12.028
Khumsi, A.F., Almezhghwi, K., Adweb, K.: Deep learning based analysis in oncological studies: colorectal cancer staging. In: Aliev, R.A., Kacprzyk, J., Pedrycz, W., Jamshidi, M., Babanli, M.B., Sadikoglu, F.M. (eds.) ICSCCW 2019. AISC, vol. 1095, pp. 573–579. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-35249-3_73
Almezhghwi, K.: Malaria detection using convolutional neural network. In: Aliev, R.A., Kacprzyk, J., Pedrycz, W., Jamshidi, M., Babanli, M., Sadikoglu, F.M. (eds.) ICSCCW 2021. LNNS, vol. 362, pp. 116–123. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92127-9_19
Kim, M., et al.: Deep learning in medical imaging. Neurospine 16(4), 657–668 (2019). https://doi.org/10.14245/ns.1938396.198
Abiyev, R.H., Ma’aitah, M.K.S.: Deep convolutional neural networks for chest diseases detection. J. Healthc. Eng. 2018 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4168538
Ravi, D., et al.: Deep learning for health informatics. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Inf. 21(1), 4–21 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2016.2636665
Ravishankar, H., et al.: Understanding the mechanisms of deep transfer learning for medical images. In: Carneiro, G., et al. (eds.) LABELS/DLMIA -2016. LNCS, vol. 10008, pp. 188–196. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46976-8_20
Ting, D.S.W., Liu, Y., Burlina, P., Xu, X., Bressler, N.M., Wong, T.Y.: AI for medical imaging goes deep. Nat. Med. 24(5), 539–540 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0029-3
Bush, I.J., Abiyev, R., Sallam Ma’aitah, M.K., Altıparmak, H.: Integrated artificial intelligence algorithm for skin detection. ITM Web Conf. 16, 02004.https://doi.org/10.1051/itmconf/20181602004
Currie, K.G., Hawk, E., Rohren, E., Vial, A., Klein, R.: Machine Learning and Deep Learning in Medical Imaging: Intelligent Imaging. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Sci. 50(4), 477–487 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmir.2019.09.005
Thomas, K.A., et al.: Automated classification of radiographic knee osteoarthritis severity using deep neural networks. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2(2), e190065 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1148/ryai.2020190065
Li, M.D., et al.: Siamese neural networks for continuous disease severity evaluation and change detection in medical imaging. npj Digit. Med. 3(1), 1–9 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-020-0255-1
Antony, J., McGuinness, K., O’Connor, N.E., Moran, K.: Quantifying radiographic knee osteoarthritis severity using deep convolutional neural networks. In: 2016 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Cancun, Mexico, pp. 1195–1200 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR.2016.7899799
Kim, D.H., Lee, K.J., Choi, D., Lee, J.I., Choi, H.G., Lee, Y.S.: Can additional patient information improve the diagnostic performance of deep learning for the interpretation of knee osteoarthritis severity. J. Clin. Med. 9(10), 3341 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103341
Nguyen, H.H., Saarakkala, S., Blaschko, M.B., Tiulpin, A.: Semixup: in- and out-of-manifold regularization for deep semi-supervised knee osteoarthritis severity grading from plain radiographs. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(12), 4346–4356 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2020.3017007
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16 × 16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. ar**v preprint ar**v (2020). https://doi.org/10.48550/ar**v.2010.11929
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Akila, S.M., Imanov, E., Almezhghwi, K. (2023). Analysis of Knee Osteoarthritis Grading Using Deep Learning. In: Aliev, R.A., Kacprzyk, J., Pedrycz, W., Jamshidi, M., Babanli, M.B., Sadikoglu, F. (eds) 15th International Conference on Applications of Fuzzy Systems, Soft Computing and Artificial Intelligence Tools – ICAFS-2022. ICAFS 2022. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 610. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25252-5_58
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25252-5_58
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-25251-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-25252-5
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)