Abstract
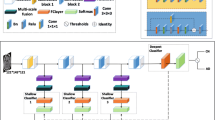
Deep learning models, such as convolutional neural networks and self-attention mechanisms, have been shown to be effective in computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) using structural magnetic resonance imaging (sMRI). Most of them use spatial convolutional filters to learn local information from the images. In this paper, we propose a 3D Global Fourier Network (GF-Net) to utilize global frequency information that captures long-range dependency in the spatial domain. The GF-Net contains three primary components: a 3D discrete Fourier transform, an element-wise multiplication between frequency domain features and learnable global filters, and a 3D inverse Fourier transform. The GF-Net is trained by a multi-instance learning strategy to identify discriminative features. Extensive experiments on two independent datasets (ADNI and AIBL) demonstrate that our proposed GF-Net outperforms several state-of-the-art methods in terms of accuracy and other metrics, and can also identify pathological regions of AD. The code is released at https://github.com/qbmizsj/GFNet.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knopman, D.S., et al.: Alzheimer disease. In: Nature reviews Disease Primers, vol. 7.1, pp. 1–21 (2021)
Damulina, A., et al.: Cross-sectional and longitudinal assessment of brain iron level in Alzheimer disease using 3-T MRI. Radiology 296(3), 619–626 (2020)
Wen, J., et al.: Convolutional neural networks for classification of Alzheimer’s disease: overview and reproducible evaluation. Med. Image Anal. 63, 101694 (2020)
Zeng, N., et al.: A new switching-delayed-PSO-based optimized SVM algorithm for diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurocomputing 320, 195–202 (2018)
Salvatore, C., et al.: Magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers for the early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: a machine learning approach. Front. Neurosci. 9, 307 (2015)
Cuingnet, R., et al.: Automatic classification of patients with Alzheimer’s disease from structural MRI: a comparison of ten methods using the ADNI database. Neuroimage 56(2), 766–781 (2011)
Eskildsen, S.F., et al.: Prediction of Alzheimer’s disease in subjects with mild cognitive impairment from the ADNI cohort using patterns of cortical thinning. Neuroimage 65, 511–521 (2013)
Cao, P., et al.: Nonlinearity-aware based dimensionality reduction and over-sampling for AD/MCI classification from MRI measures. Comput. Biol. Med. 91, 21–37 (2017)
Sørensen, L., Nielsen, M., Initiative, A.D.N., et al.: Ensemble support vector machine classification of dementia using structural MRI and mini-mental state examination. J. Neurosci. Methods 302, 66–74 (2018)
Tong, T., et al.: Multiple instance learning for classification of dementia in brain MRI. Med. Image Anal. 18(5), 808–818 (2014)
Khvostikov, A., et al.: 3D CNN-based classification using sMRI and MD-DTI images for Alzheimer disease studies. ar**v preprint ar**v:1801.05968 (2018)
Liu, M., et al.: Landmark-based deep multi-instance learning for brain disease diagnosis. Med. Image Anal. 43, 157–168 (2018)
Zhou, B., et al.: Learning deep features for discriminative localization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2921–2929 (2016)
Lian, C., et al.: Hierarchical fully convolutional network for joint atrophy localization and Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis using structural MRI. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 42(4), 880–893 (2018)
Zhu, W., et al.: Dual attention multi-instance deep learning for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis with structural MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 40(9), 2354–2366 (2021)
Qiu, S., et al.: Development and validation of an interpretable deep learning framework for Alzheimer’s disease classification. Brain 143(6), 1920–1933 (2020)
Li, H., Habes, M., Fan, Y.: Deep ordinal ranking for multi-category diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease using hippocampal MRI data. ar**v preprint ar**v:1709.01599 (2017)
Li, F., Liu, M., Initiative, A.D.N., et al.: Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis based on multiple cluster dense convolutional networks. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 70, 101–110 (2018)
Lin, W., et al.: Convolutional neural networks-based MRI image analysis for the Alzheimer’s disease prediction from mild cognitive impairment. Front. Neurosci. 12, 777 (2018)
Rao, Y., et al.: Global filter networks for image classification. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 980–993 (2021)
He, K., et al.: Masked autoencoders are scalable vision learners (2021). ar**v: 2111.06377 [cs.CV]
Couture, H.D., Marron, J.S., Perou, C.M., Troester, M.A., Niethammer, M.: Multiple instance learning for heterogeneous images: training a CNN for histopathology. In: Frangi, A.F., Schnabel, J.A., Davatzikos, C., Alberola-López, C., Fichtinger, G. (eds.) MICCAI 2018. LNCS, vol. 11071, pp. 254–262. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00934-2_29
Ashburner, J., Friston, K.J.: Voxel-based morphometry-the methods. Neuroimage 11(6), 805–821 (2000)
Kruthika, K.R. HD Maheshappa, Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative. CBIR System using Capsule Networks and 3D CNN for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Inf. Med. Unlocked 14, 59–68 (2019)
He, K., et al.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. ar**v preprint ar**v:2010.11929 (2020)
Gerischer, L.M., et al.: Combining viscoelasticity, diffusivity and volume of the hippocampus for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease based on magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage Clin. 18, 485–493 (2018)
Shao, W., et al.: Hypergraph based multi-task feature selection for multimodal classification of Alzheimer’s disease. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 80, 101663 (2020)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (20ZR1407800), Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project (No.2018SHZDZX01), and Fudan Univerisity startup fund (JIH2305006Y).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, S. et al. (2022). 3D Global Fourier Network for Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis Using Structural MRI. In: Wang, L., Dou, Q., Fletcher, P.T., Speidel, S., Li, S. (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2022. MICCAI 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13431. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16431-6_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16431-6_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-16430-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-16431-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)