Abstract
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) has been around for about six decades. Although in the early years it was more of a curiosity than an analytical method due to some technical complications, but since the 1990s it has evolved and spread slowly but steadily and by today it has become the established versatile and powerful analytical method known by many spectroscopists. Naturally, over the course of so many years, a lot of effort have been made, not unsuccessfully, to improve the analytical performance of LIBS. This chapter is dedicated to this progress as it attempts to briefly account for the main efforts and current state of the art of LIBS analytical performance.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Y, Tian D, Ding Y, Yang G, Liu K, Wang C, Han X. A review of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy signal enhancement. Appl Spectrosc. 2018;53:1.
Fu X, Li G, Dong D. Improving the detection sensitivity for laser induced breakdown spectroscopy: a review. Front Phys. 2020a;8:68.
Gornushkin IB, Stevenson CL, Galbács G, Smith BW, Winefordner JD. Measurement and modeling of ozone and nitrogen oxides produced by laser breakdown in oxygen-nitrogen atmospheres. Appl Spectrosc. 2003;57:1442.
Jianlong Y, Zongyu H, Yuanyuan M, Tianqi L, Yangting F, Yun W, Zheng L, Zhe W. Improvement of laser induced breakdown spectroscopy signal using gas mixture. Spectrochim Acta B. 2020;174:105992.
Joon-Gon S, Yonghoon L, Do-Kyeong K. Signal enhancement of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy by applying synchronized buffer gas pulses. Appl Phys Express. 2018;11:102401.
Effenberger JA, Scott JR. Effect of atmospheric conditions on LIBS spectra (review). Sensors. 2010;10:4907.
Jong-Il Yun Y, Reinhardt K, Jae-Il K. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for the on-line multielement analysis of highly radioactive glass melt. Part I: characterization and evaluation of the method. Appl Spectrosc. 2002;56:437.
Zeshan AU, Usman L, Rizwan A, Muhammad AB. Detection of lead in soil implying sample heating and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Appl Opt. 2021;60:452.
Kaimin G, Anmin C, Wanpeng X, Dan Z, Mingxing J. Effect of sample temperature on time-resolved laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. AIP Adv. 2019;9:065214.
Tavassoli SH, Gragossian A. Effect of sample temperature on laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Opt Laser Technol. 2009;41:481.
Gao X, Liu L, Song C, Lin J. The role of spatial confinement on nanosecond YAG laser-induced Cu plasma. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2015;48:175205.
Guo L, Li C, Hu W, Zhou Y, Zhang B, Cai Z, Zeng X, Lu Y. Plasma confinement by hemispherical cavity in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Appl Phys Lett. 2011;98:131501.
Li C, Guo L, He X, Hao Z, Li X, Shen M, Zeng X, Lu Y. Element dependence of enhancement in optics emission from laser-induced plasma under spatial confinement. J Anal At Spectrom. 2014;29:638.
Popov AM, Colao F, Fantoni R. Spatial confinement of laser-induced plasma to enhance LIBS sensitivity for trace elements determination in soils. J Anal At Spectrom. 2010;25:2491.
Yin H, Hou Z, Yuan T, Wang Z, Ni W, Li Z. Application of spatial confinement for gas analysis using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy to improve signal stability. J Anal At Spectrom. 2015;30:922.
Corsi M, Cristoforetti G, Hidalgo M, Iriarte D, Legnaioli S, Palleschi V, Salvetti A, Tognoni E. Effect of laser-induced crater depth in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy emission features. Appl Spectrosc. 2005;59:853.
Li K, Guo L, Li X, Hao Z, Zeng X, Shen M, Qingdong Z, Yongfeng L, **aoyan Z. Characteristics of spectral lines with crater development during laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Appl Opt. 2016a;55:7422.
Cheng L, Xun G, Qi L, Chao S, **gquan L. Spectral enhancement of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in external magnetic field. Plasma Sci Technol. 2015;17:919.
Hao Z, Guo L, Li CM, Shen M, Zou X, Li X, Lu Y, Zeng X. Sensitivity improvement in the detection of V and Mn elements in steel using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy with ring magnet confinement. J Anal At Spectrom. 2014;29:2309.
Mason KJ, Goldberg JM. Characterization of a laser plasma in a pulsed magnetic field. Part I: spatially resolved emission studies. Appl Spectrosc. 1991a;45:370.
Mason KJ, Goldberg JM. Characterization of a laser plasma in a pulsed magnetic field. Part II: time-resolved emission and absorption studies. Appl Spectrosc. 1991b;45:1444.
Shen XK, Lu YF, Gebre T, Ling H, Han YX. Optical emission in magnetically confined laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. J Appl Phys. 2006;100:3662.
Liu Y, Baudelet M, Richardson M. Elemental analysis by microwave-assisted laserinduced breakdown spectroscopy: evaluation on ceramics. J Anal At Spectrom. 2010;25:1316.
Al Shuaili AA, Al Hadhrami AM, Wakil MA, Alwahabi ZT. Improvement of palladium limit of detection by microwave-assisted laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2019;159:105666.
Wakila MA, Alwahabi ZT. Microwave-assisted laser induced breakdown molecular spectroscopy: quantitative chlorine detection. J Anal At Spectrom. 2019;34:1892.
Viljanen J, Sun Z, Alwahabi ZT. Microwave assisted laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy at ambient conditions. Spectrochim Acta B. 2016;118:29.
Tampo M, Miyabe M, Akaoka K, Oba M, Ohba H, Maruyama Y, Ikuo W. Enhancement of intensity in microwave-assisted laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for remote analysis of nuclear fuel recycling. J Anal At Spectrom. 2014;29:886.
Ayed Nassef O, Elsayed-Ali HE. Spark discharge assisted laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2005;60:1564.
Sobral H, Robledo-Martinez A. Signal enhancement in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy using fast square-pulse discharges. Spectrochim Acta B. 2016;124:67.
Tereszchuk KA, Vadillo JM, Laserna JJ. Glow-discharge-assisted laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy: increased sensitivity in solid analysis. Appl Spectrosc. 2008;62:1262.
De Giacomo A, Rifai RA, Gardette V, Salajková Z, Dell'Aglio M. Nanoparticle enhanced laser ablation and consequent effects on laser induced plasma optical emission. Spectrochim Acta B. 2020;166:105794.
Dell'Aglio M, Rifai RA, De Giacomo A. Nanoparticle enhanced laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (NELIBS), a first review. Spectrochim Acta B. 2018;148:105.
Jantzi SC, Motto-Ros V, Trichard F, Markushin Y, Melikechi N, De Giacomo A. Sample treatment and preparation for laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2016;115:52.
Palásti DJ, Albrycht P, Janovszky P, Paszkowska K, Geretovszky Z, Galbács G. Nanoparticle enhanced laser induced breakdown spectroscopy of liquid samples by using modified surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates. Spectrochim Acta B. 2020;166:105793.
Palásti DJ, Villy LP, Kohut A, Ajtai T, Geretovszky Z, Galbács G. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy signal enhancement effect for argon caused by the presence of gold nanoparticles. Spectrochim Acta B. 2022;193:106435.
Piepmeier EH, Malmstadt HV. Q-switched laser energy absorption in the plume of an aluminum alloy. Anal Chem. 1969;41:700.
Scott RH, Strasheim A. Time-resolved direct-reading spectrochemical analysis using a laser source with medium pulse-repetition rate. Spectrochim Acta. 1971;26B:707.
Cui M, Deguchi Y, Wang Z, Fujita Y, Liu R, Shiou F-J, Zhao S. Enhancement and stabilization of plasma using collinear long-short double-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2018;142:14.
Legnaioli S, Lorenzetti G, Pardini L, Cavalcanti GH, Palleschi V. Double and multiple pulse LIBS techniques. In: Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy: theory and applications. Series in optical sciences 182. Springer; 2014.
Babushok V, Delucia FC Jr, Gottfried JL, Munson CA, Miziolek AW. Double pulse laser ablation and plasma: laser induced breakdown spectroscopy signal enhancement. Spectrochim Acta B. 2006;61:999.
Scaffidi J, Angel SM, Cremers DA. Emission enhancement mechanisms in dual-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 2006;78:24.
Bogaerts A, Chen Z, Autrique D. Double pulse laser ablation and laser induced breakdown spectroscopy: a modeling investigation. Spectrochim Acta B. 2008;63:746.
Cristoforetti G, Tiberi M, Simonelli A, Marsili P, Giammanco F. Toward the optimization of double-pulse LIBS underwater: effects of experimental parameters on the reproducibility and dynamics of laser-induced cavitation bubble. Appl Opt. 2012;51:B30.
De Giacomo A, Dell'Aglio M, De Pascale O, Capitelli M. From single pulse to double pulse ns-laser induced breakdown spectroscopy under water: elemental analysis of aqueous solutions and submerged solid samples. Spectrochim Acta B. 2007;62:721.
Lazic V, Jovicevic S. Laser induced breakdown spectroscopy inside liquids: processes and analytical aspects. Spectrochim Acta B. 2014;101:288.
Galbács G, Budavári V, Geretovszky Z. Multi-pulse laser-induced plasma spectroscopy using a single laser source and a compact spectrometer. J Anal At Spectrom. 2005;20:974.
Galbács G, Jedlinszki N, Herrera K, Omenetto N, Smith BW, Winefordner JD. A study of ablation, spatial, and temporal characteristics of laser-induced plasmas generated bymultiple collinear pulses. Appl Spectrosc. 2010;64:161.
Jedlinszki N, Galbács G. An evaluation of the analytical performance of collinear multipulse laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Microchem J. 2011;97:255.
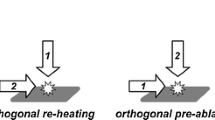
Prochazka D, Pořízka P, Novotný J, Hrdlička A, Novotný K, Šperka P, Kaiser J. Triple pulse LIBS: laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy signal enhancement by combination of pre-ablation and re-heating laser pulses. J Anal At Spectrom. 2020;35:293.
Chan SY, Cheung NH. Analysis of solids by laser ablation and resonance enhanced laserinduced plasma spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 2000;72:2087.
Lui S, Cheung NH. Resonance-enhanced laser-induced plasma spectroscopy for sensitive elemental analysis: elucidation of enhancement mechanisms. Appl Phys Lett. 2002;81:5114.
Lui SL, Cheung NH. Minimally destructive analysis of aluminum alloys by resonanceenhanced laser-induced plasma spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 2005;77:2617.
Goueguel C, Laville S, Vidal F, Chaker M, Sabsabi M. Resonant laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for analysis of lead traces in copper alloys. J Anal At Spectrom. 2011;26:2452.
Li J, Guo L, Zhao N, Yang X, Yi R, Li K, Zeng Q, Li X, Zeng X, Lu Y. Determination of cobalt in low-alloy steels using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with laser-induced fluorescence. Talanta. 2016b;151:234.
Li J, Hao Z, Zhao N, Zhou R, Yi R, Tang S, Guo L, Li X, Zeng X, Lu Y. Spatially selective excitation in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with laser-induced fluorescence. Opt Express. 2017;25:4945.
Loudyi H, Rifai K, Laville S, Vidal F, Chaker M, Sabsabi M. Improving laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) performance for iron and lead determination in aqueoussolutions with laser-induced fluorescence (LIF). J Anal At Spectrom. 2009;24:1421.
Akshaya K, Yueh FY, Miller T, Singh JP. Detection of trace elements in liquids by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy with a Meinhard nebulizer. Appl Opt. 2003;42:6040.
Cahoon EM, Almirall JR. Quantitative analysis of liquids from aerosols and microdrops using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 2012;84:2239.
Fang X, Rafi Ahmad S. Sample presentation considerations in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in aqueous solution. Appl Spectrosc. 2007;61:1021.
Nadir A, Semira ÜY, Dilek AA, Şerife Y. Ultrasonic nebulizationsample introduction system for quantitative analysis of liquid samples by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2012;74–75:87.
Jiang L, Sui M, Fan Y, Su H, Xue Y, Zhong S. Micro-gas column assisted laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (MGC-LIBS): a metal elements detection method for bulk water in-situ analysis. Spectrochim Acta B. 2021;177:106065.
Sobral H, Sanginés R, Trujillo-Vázquez A. Detection of trace elements in ice and water by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2012;78:62.
Metzinger A, Kovács-Széles É, Almási I, Galbács G. An assessment of the potential of laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) for the analysis of cesium in liquid samples of biological origin. Appl Spectrosc. 2014;68:789.
Metzinger A, Nagy A, Gáspár A, Márton Z, Kovács-Széles É, Galbács G. The feasibility of liquid sample microanalysis using polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic chips with in-channel and in-port laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy detection. Spectrochim Acta B. 2016;126:23.
Yang X, Hao Z, Shen M, Yi RX, Li J, Yu H, Guo L, **angyou L, **aoyan Z, Yongfeng L. Simultaneous determination of La, Ce, Pr, and Nd elements in aqueous solution using surfaceenhanced laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Talanta. 2017;163:127.
Choi D, Gong Y, Nam S-H, Han S-H, Yoo J, Lee Y. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) analysis of calcium ions dissolved in water using filter paper substrates: an ideal internal standard for precision improvement. Appl Spectrosc. 2014;68:198.
Zhichao Z, Wenbao J, Qing S, **aoyan Y, Daqian H, Zi W, Yu W, Yongsheng L. Determination of magnesium and sodium in brine by filter paper adsorption laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Anal Lett. 2022;55:1771.
Lin Q, Wei Z, Xu M, Wang S, Niu G, Liu K, Duan Y, Yang J. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for solution sample analysis using porous electrospun ultrafine fibers as a solid-phase support. RSC Adv. 2014;4:14392.
Guanhong W, Duixiong S, Maogen S, Chenzhong D. LIBS detection of heavy metal elements in liquid solutions by using wood pellet as sample matrix. Plasma Sci Technol. 2014;16:598.
Wang X, Shi L, Lin Q, Zhu X, Duan Y. Simultaneous and sensitive analysis of Ag(I), Mn(II), and Cr(III) in aqueous solution by LIBS combined with dispersive solid phase micro-extraction using nano-graphite as an adsorbent. J Anal At Spectrom. 2014;29:1098.
Díaz Pace DM, D'Angelo CA, Bertuccelli D, Bertuccelli G. Analysis of heavy metals in liquids using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy by liquid-to-solid matrix conversion. Spectrochim Acta B. 2006;61:929.
Nam S-H, Kwon S-W, Lee Y. Feasibility of separation and quantification of inorganic arsenic species using ion-exchange membranes and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Anal Lett. 2018;51:2835.
Schmidt NE, Goode SR. Analysis of aqueous solutions by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy of ion exchange membranes. Appl Spectrosc. 2002;56:370.
Wang X, Wei Y, Lin Q, Zhang J, Duan Y. Simple, fast matrix conversion and membrane separation method for ultrasensitive metal detection in aqueous samples by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 2015;87:5577.
Chen M, Yuan T, Hou Z, Wang Z, Wang Y. Effects of moisture content on coal analysis using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2015;112:23.
Eseller KE, Tripathi MM, Yueh F-Y, Singh JP. Elemental analysis of slurry samples with laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Appl Opt. 2010;49:C21.
Wisbrun R, Schechter I, Niessner R, Schroder H, Kompa K. Detector for trace elemental analysis of solid environmental samples by laser plasma spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 1994;66:2964.
Wu M, Wang X, Niu G, Zhao Z, Zheng R, Liu Z, Zhao Z, Duan Y. Ultrasensitive and simultaneous detection of multielements in aqueous samples based on biomimetic array combined with laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 2021;93:10196.
Dong D, Jiao L, Dua X, Zhao C. Ultrasensitive nanoparticle enhanced laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy using a super-hydrophobic substrate coupled with magnetic confinement. Chem Commun. 2017;53:4546.
Alvarez-Llamas C, Pisonero J, Bordel N. A novel approach for quantitative LIBS fluorine analysis. J Anal At Spectrom. 2017;32:162.
Anzano J, Cajal J, Lasheras R, Escudero M, Canudo J, Laguna M, Anwar J. Determination of lanthanides in fossil samples using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. J Chem Soc Pak. 2017;39:516.
Asimellis G, Michos N, Fasaki I, Kompitsas M. Platinum group metals bulk analysis in automobile catalyst recycling material by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2008;63:1338.
Bhatt CR, Yueh FY, Singh JP. Univariate and multivariate analyses of rare earth elements by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Appl Opt. 2017;56:2280.
Chinni RC, Cremers DA, Radziemski LJ, Bostian MB, Navarro-Northrup C. Detection of uranium using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Appl Spectrosc. 2009;63:1238.
Darwiche S, Benrabbah R, Benmansour M, Morvan D. Impurity detection in solid and molten silicon by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2012;74–75:115.
Davari SA, Taylor PA, Standley RW, Mukherjee D. Detection of interstitial oxygen contents in Czochralski grown silicon crystals using internal calibration in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). Talanta. 2019;193:192.
Díaz D, Hahn DW, Molina A. Quantification of gold and silver in minerals by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2017;136:106.
El-Deftar MM, Robertson J, Foster S, Lennard C. Evaluation of elemental profiling methods, including laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), for the differentiation of cannabis plant material grown in different nutrient solutions. Forensic Sci Int. 2015;251:95.
Fichet P, Mauchien P, Moulin C. Determination of impurities in uranium and plutonium dioxides by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Appl Spectrosc. 1999;53:1111.
Freedman A, Iannarilli FJ, Wormhoudt JC. Aluminum alloy analysis using microchip-laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2005;60:1076.
Fu X, Li G, Tian H, Dong D. Detection of cadmium in soils using laserinduced breakdown spectroscopy combined with spatial confinement and resin enrichment. RSC Adv. 2018;8:39635.
Fu X, Zhao C, Ma S, Tian H, Dong D, Li GL. Determining available potassium in soil by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with cation exchange membrane adsorption. J Anal At Spectrom. 2020b;35:2697.
Gao P, Yang P, Zhou R, Ma S, Zhang W, Hao Z, Tang S, Li X, Zeng X. Determination of antimony in soil using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy assisted with laser-induced fluorescence. Appl Opt. 2018;57:8942.
Gautier C, Fichet P, Menuta D, Lacour JL, Hermite DL, Dubessy J. Study of the double-pulse setup with an orthogonal beam geometry for laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2004;59:975.
Gondal MA, Hussain T. Determination of poisonous metals in wastewater collected from paint manufacturing plant using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Talanta. 2007;71:73.
Gornushkin IB, Kim JE, Smith BW, Baker SA, Winefordner JD. Determination of cobalt in soil, steel, and graphite using excited-state laser fluorescence induced in a laser spark. Appl Spectrosc. 1997a;51:1055.
Gornushkin IB, Baker SA, Smith BW, Winefordner JD. Determination of lead in metallic reference materials by laser ablation combined with laser excited atomic fluorescence. Spectroc Acta B. 1997b;52:1653.
Hemmerlin M, Meilland R, Falk H, Wintzens P, Pauleri L. Application of vacuum ultraviolet laser-induced breakdown spectrometry for steel analysiscomparison with spark-optical emissions spectrometry figures of merit. Spectrochim Acta B. 2001;56:661.
Hilbk-Kortenbruck F, Noll R, Wintjens P, Falk H, Becker C. Analysis of heavy metals in soils using laser-induced breakdown spectrometry combined with laser-induced fluorescence. Spectroc Acta B. 2001;56:933.
Idris N, Kurniawan H, Lie TJ. Characteristics of hydrogen emission in laser plasma induced by focusing fundamental Q-sw YAG laser on solid samples. Jpn J Appl Phys. 2004;43:4221.
Ishizuka T. Laser emission spectrography of rare earth elements. Anal Chem. 1973;45:538.
Jabbar A, Akhtar M, Mehmmod S, Iqbal M, Ahmed R, Baig MA. Quantification of copper remediation in the Allium cepa L. leaves using electric field assisted laser induced breakdown pectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2019;162:105719.
Jensen LC, Langford SC, Dickinson JT, Addleman RS. Mechanistic studies of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy of model environmental samples. Spectrochim Acta B. 1995;50:1501.
Jiang X, Hayden P, Costello JT, Kennedy ET. Double-pulse laser induced breakdown spectroscopy with ambient gas in the vacuum ultraviolet: optimization of parameters for detection of carbon and sulfur in steel. Spectrochim Acta B. 2014;101:106.
Kang J, Jiang Y, Li R, Chen Y. Sensitive elemental analysis with high repetition rate laser-ablation spark-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with lock-in signal detection. Spectrochim Acta B. 2019;155:50.
Khater MA, Costello JT, Kennedy ET. Optimization of the emission characteristics of laser-produced steel plasmas in the vacuum ultraviolet: significant improvements in carbon detection limits. Appl Spectrosc. 2002;56:970.
Knight AK, Scherbarth NL, Cremers DA, Ferris MJ. Characterization of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) for application to space exploration. Appl Spectrosc. 2000;54:331.
Labutin TA, Popov AM, Raikov SN, Zaytsev SM, Labutina NA, Zorov NB. Determination of chlorine in concrete by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in air. J Appl Spectrosc. 2013;80:315.
Labutin TA, Zaytsev SM, Popov AM, Zorov NB. A novel approach to sensitivity evaluation of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for rare earth elements determination. J Anal At Spectrom. 2016;31:2223.
Liu L, Hao Z. Quantitative determination of tantalum and niobium in tantalum–niobium ore using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Appl Opt. 2019;58:461.
Loebe K, Uhl A, Lucht H. Microanalysis of tool steel and glass with laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Appl Opt. 2003;42:6166.
Mei-Ting H, Yin-Hua J, Yu-Qi C, Run-Hua L. Quantitative analysis of trace elements in bismuth brass with high repetition rate laser-ablation spark-induced breakdown spectrum. Rhhz Test. 2021;70:10.
Pearce TJ, Martin J, Bromley B, Zigler A, Dix M (2000) Chemostratigraphy - the elemental solution using LIBS-OES. In: LIBS 2000 book of abstracts. First international conference on laser induced plasma spectroscopy and applications, Tirrenia, p 66.
Radziemski LJ, Cremers DA. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy: principles, applications and instruments. Proc SPIE. 1990;1318:71.
Radziemski LJ, Cremers DA, Benelli K, Khoo C, Harris RD. Use of the vacuum ultraviolet spectral region for LIBS-based Martian geology and exploration. Spectrochim Acta B. 2004;60:237.
Ramli M, Khumaeni A, Kurniawan KH, Tjia MO, Kagawa K. Spectrochemical analysis of Cs in water and soil using low pressure laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2017;132:8.
Sarkar A, Alamelu D, Aggarwal SK. Determination of thorium and uranium in solution by laser-induced breakdown spectrometry. Appl Opt. 2008;47:G58.
Senesia GS, Harmon RS. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy: a unique analytical tool for the geosciences. Spectrosc Eur. 2021;33:15.
Shen XK, Wang H, **e ZQ, Gao Y, Ling H, Lu YF. Detection of trace phosphorus in steel using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with laser-induced fluorescence. Appl Opt. 2009;48:2551.
Singh VK, Rai AK, Rai PK, **dal PK. Cross-sectional study of kidney stones by laserinduced breakdown spectroscopy. Lasers Med Sci. 2009;24:749.
Sun Q, Tran M, Smith BW, Winefordner JD. Direct determination of P, Al, Ca, Cu, Mn, Zn, Mg and Fe in plant materials by laser-induced plasma spectroscopy. Can J Anal Sci Spectrosc. 1999;44:164.
Tran M, Sun Q, Smith B, Winefordner JD. Direct determination of trace elements in terephthalic acid by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Anal Chim Acta. 2000;419:153.
Uhl A, Loebe K, Kreuchwig L. Fast analysis of wood preservers using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2001;56:795.
**ng P, Dong J, Yu P, Zheng H, Liu X, Hu S, Zhu Z. Uantitative analysis of lithium in brine by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy based on convolutional neural network. Anal Chim Acta. 2021;1178:338799.
Hahn DW, Omenetto N. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), part II: review of instrumental and methodological approaches to material analysis and applications to different fields. Appl Spectrosc. 2012;66:347.
Gornushkin IB, Anzano JM, King LA, Smith BW, Omenetto N, Winefordner JD. Curve of growth methodology applied to laser-induced plasma emission spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 1999a;54:491.
Tognoni E, Palleschi V, Corsi M, Cristoforetti G, Omenetto N, Gornushkin I, Smith BW, Winefordner JD. From sample to signal in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy: a complex route to quantitative analysis in laser induced breakdown spectroscopy, fundamentals and applications. Cambridge University Press; 2009.
Galbács G, Jedlinszki N, Cseh G, Galbács Z, Túri L. Accurate quantitative analysis of gold alloys using multi-pulse laser induced breakdown spectroscopy and a correlation-based calibration method. Spectrochim Acta B. 2008;63:591.
Galbács G. A critical review of recent progress in analytical laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015;407:7537.
Guezenoc J, Gallet-Budynek A, Bousquet B. Critical review and advices on spectral-based normalization methods for LIBS quantitative analysis. Spectrochim Acta B. 2019;160:105688.
Tognoni E, Cristoforetti G. Signal and noise in laser induced breakdown spectroscopy: an introductory review. Opt Laser Technol. 2016;79:164.
Zorov NB, Gorbatenko AA, Labutin TA, Popov AM. A review of normalization techniques in analytical atomic spectrometry with laser sampling: from single to multivariate correction. Spectrochim Acta B. 2010;65:642.
Runge EF, Minck RW, Brian FR. Spectrochemical analysis using a pulsed laser source. Spectrochim Acta B. 1964;20:733.
Juvé V, Portelli R, Boueri M, Baudelet M, Yu J. Space-resolved analysis of trace elements in fresh vegetables using ultraviolet nanosecond laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2008;63:1047.
Sarkar A, Mishra RK, Kaushik CP, Wattal PK, Alamelu D, Aggarwal SK. Analysis of barium borosilicate glass matrix for uranium determination by using ns-IR-LIBS in air and Ar atmosphere. Radiochim Acta. 2014;102:805.
Šindelářová A, Pořízka P, Modlitbová P, Vrlíková L, Kiss M, Kaška M, Prochazka D, Vrábel J, Buchtová M, Kaiser J. Methodology for the implementation of internal standard to laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy analysis of soft tissues. Sensors. 2021;21:900.
de Oliveira Borges F, Ospina JU, de Holanda Cavalcanti G, Farias EE, Rocha AA, Ferreira PILB, Gomes GC, Mello A. CF-LIBS analysis of frozen aqueous solution samples by using a standard internal reference and correcting the self-absorption effect. J Anal At Spectrom. 2018;33:629.
Kwak JH, Lenth C, Salb C, Ko EJ, Kim KW, Park K. Quantitative analysis of arsenic in mine tailing soils using double pulse-laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2009;64:1105.
Yan J, Shi Y, Liu K, Li H, Tang Z, Chen W, Jiang W, Li Q, Tang Y, Li X. The distribution of high-quality internal standard lines and their selection method based on the Q-value in portable laserinduced breakdown spectroscopy. Anal Methods. 2021;13:3829.
Yang J, Li X, Xu J, Ma X. A calibration-free laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (CFLIBS) quantitative analysis method based on the auto-selection of an internal reference line and optimized estimation of plasma temperature. Appl Spectrosc. 2018;72:129.
Russo R. Laser ablation. Appl Spectrosc. 1995;49:15A.
Yue Z, Sun C, Gao L, Zhang Y, Shabbir S, Xu W, Wu M, Zou L, Tan Y, Chen F, Yu J. Machine learning efficiently corrects LIBS spectrum variation due to change of laser fluence. Opt Express. 2020;28:14345.
Oh SY, Yueh FY, Singh JP, Herman CC, Zeigler K. Preliminary evaluation of laser induced breakdown spectroscopy for slurry samples. Spectrochim Acta B. 2009;64:113.
Huang F, Tian Y, Li Y, Ye W, Lu Y, Guo J, Zheng R. Normalization of underwater laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy using acoustic signals measured by a hydrophone. Appl Opt. 2021;60:1595.
Bolger JA. Semi-quantitative laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for analysis of mineral drill core. Appl Spectrosc. 2000;54:181.
Body D, Chadwick BL. Optimization of the spectral data processing in a LIBS simultaneous elemental analysis system. Spectrochim Acta B. 2001;56:725.
Fabre C, Cousin A, Wiens RC, Ollila A, Gasnault O, Maurice S, Sautter V, Forni O, Lasue J, Tokar R, Vaniman D, Melikechi N. In situ calibration using univariate analyses based on the onboard ChemCam targets: first prediction of Martian rock and soil compositions. Spectrochim Acta B. 2014;99:34.
Yu KG, Zhao YR, Liu F, He Y. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy coupled with multivariate chemometrics for variety discrimination of soil. Sci Rep. 2016;6:27574.
Kurniawan H, Suliyanti MM, Lie TJ, Kagawa K, Tjia MO. Application of primary plasma standardization to Nd-YAG laser-induced shock wave plasma spectrometry for quantitative analysis of high concentration Au–Ag–Cu alloy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2001;56:1407.
Xu L, Bulatov V, Gridin VV, Schechter I. Absolute analysis of particulate materials by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 1997;69:2103.
Galbács G, Kevei-Bárány I, Szőke E, Jedlinszki N, Gornushkin IB, Galbács MZ. A study of stalagmite samples from Baradla Cave (Hungary) by laser induced plasma spectrometry with automatic signal correction. Microchem J. 2011;99:406.
Fortes FJ, Cortés M, Simón MD, Cabalín LM, Laserna JJ. Chronocultural sorting of archaeological bronze objects using laser-induced breakdown spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta. 2005;554:136.
Lazic V, Fantoni R, Colao F, Santagata A, Morone A, Spizzichino V. Quantitative laser induced breakdown spectroscopy analysis of ancient marbles and corrections for the variability of plasma parameters and of ablation rate. J Anal At Spectrom. 2004;19:429.
Cabalín LM, González A, Ruiz J, Laserna JJ. Assessment of statistical uncertainty in the quantitative analysis of solid samples in motion using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2010;65:680.
De Giacomo A, Dell’Aglio M, De Pascale O, Gaudiuso R, Santagata A, Teghil R. Laserinduced breakdown spectroscopy methodology for the analysis of copper based alloys used in ancient artworks. Spectrochim Acta B. 2008;63:585.
Gornushkin IB, Smith BW, Potts GE, Omenetto N, Winefordner JD. Some considerations on the correlation between signal and background in laser induced breakdown spectroscopy using single-shot analysis. Anal Chem. 1999b;71:5447.
Chaléard C, Mauchien P, Andre N, Übbing J, Lacour JL, Geertsen C. Correction of matrix effects in quantitative elemental analysis with laser ablation optical emission spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom. 1997;12:183.
Chen G, Yeung ES. Acoustic signal as an internal standard for quantitation in lasergenerated plumes. Anal Chem. 1988;60:2258.
Palanco S, Laserna J. Spectral analysis of the acoustic emission of laserproduced plasmas. Appl Opt. 2003;42:6078.
Cheung NH, Yeung ES. Single-shot elemental analysis of liquids based on laser vaporization at fluences below breakdown. Appl Spectrosc. 1993;47:882.
Cheung NH, Ng CW, Ho WF, Yeung ES. Ultra-micro analysis of liquids and suspensions based on laser-induced plasma emissions. Appl Surf Sci. 1998;127:274.
Hrdlička A, Zaorálková L, Galiová M, Čtvrtníčková T, Kanický V, Otruba V, Novotný K, Krásenský P, Kaiser J, Malina R, Páleníková K. Correlation of acoustic and optical emission signals produced at 1064 and 532 nm laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) of glazed wall tiles. Spectrochim Acta B. 2009;64:74.
Feng J, Wang Z, Li Z, Ni W. Study to reduce laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy measurement uncertainty using plasma characteristic parameters. Spectrochim Acta B. 2010;65:549.
Panne U, Haisch C, Clara M, Niessner R. Analysis of glass and glass melts during the vitrification process of fly and bottom ashes by laser-induced plasma spectroscopy. Part I: normalization and plasma diagnostics. Spectrochim Acta B. 1998;53:1957.
Rammelkamp K. Investigation of LIBS and Raman data analysis methods in the context of insitu planetary exploration. Humboldt University; 2019.
Limbeck A, Brunnbauer L, Lohninger H, Pořízka P, Modlitbova P, Kaiser J, Janovszky P, Kéri A, Galbács G. Methodology and applications of elemental map** by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Anal Chim Acta. 2021;1147:72.
Jolivet L, Leprince M, Moncayo S, Sorbier L, Lienemann C-P, Motto-Ros V. Review of the recent advances and applications of LIBS-based imaging. Spectrochim Acta B. 2019;151:41.
Motto-Ros V, Moncayo S, Fabre C, Busser B. LIBS imaging applications, laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. 2nd ed. Elsevier; 2020.
Fabre C, Devismes D, Moncayo S, Pelascini F, Trichard F, Lecomte A, Bousquet B, Cauzid J, Motto-Ros V. Elemental imaging by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for the geological characterization of minerals. J Anal At Spectrom. 2018;33:1345.
Gimenez Y, Busser B, Trichard F, Kulesza A, Laurent JM, Zaun V, Lux F, Benoit JM, Panczer G, Dugourd P, Tillement O, Pelascini F, Sancey L, Motto-Ros V. 3D imaging of nanoparticle distribution in biological tissue by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Sci Rep. 2016;6:29936.
Menut D, Fichet P, Lacour JL, Rivoallan A, Mauchien P. Micro-laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy technique: a powerful method for performing quantitative surface map** on conductive and nonconductive samples. Appl Opt. 2003;42:6063.
Zorba V, Mao X, Russo RE. Femtosecond laser induced breakdown spectroscopy of Cu at the micron/sub-micron scale. Spectrochim Acta B. 2015;113:37.
Zorba V, Mao X, Russo RE. Ultrafast laser induced breakdown spectroscopy for high spatial resolution chemical analysis. Spectrochim Acta B. 2011;66:189.
Wang X, Liang Z, Meng Y, Wang T, Hang W, Huang B. Submicroanalysis of solid samples with near-field enhanced atomic emission spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2018;141:1.
Li W, Li X, Li X, Hao Z, Lu Y, Zeng X. A review of remote laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Appl Spectrosc Rev. 2020;55:1.
Narlagiri LM, Bharati MSS, Beeram R, Banerjee D, Soma VR. Recent trends in laser-based standoff detection of hazardous molecules. Trends Anal Chem. 2022;153:116645.
Sallé B, Mauchien P, Maurice S. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in open-path configuration for the analysis of distant objects. Spectrochim Acta B. 2007;62:739.
Chin SL. Femtosecond laser filamentation. Springer; 2010.
Rohwetter PH, Stelmaszczyk K, Wöste L, Ackermann R, Méjean G, Salmon E, Kasparian J, Yu J, Wolf JP. Filament-induced remote surface ablation for long range laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy operation. Spectrochim Acta B. 2005;60:1025.
Fobar DG, **ao X, Burger M, Le S, Berre A, Motta T, Jovanovic I. Robotic delivery of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for sensitive chlorine measurement in dry cask storage systems. Prog Nucl Energy. 2018;109:188.
Gottfried JL, De Lucia FC, Munson CA, Miziolek AW. Doublepulse standoff laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for versatile hazardous materials detection. Spectrochim Acta B. 2007;62:1405.
Barnett PD, Lamsal N, Angel SM. Standoff laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) using a miniature wide field of view spatial heterodyne spectrometer with sub-microsteradian collection optics. Appl Spectrosc. 2017;71:583.
Acknowledgments
The authors kindly acknowledge the financial support received from the National Research, Development and Innovation Office (Hungary) through project No. K 129063.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Galbács, G., Palásti, D.J., Janovszky, P.M. (2022). State-of-the-Art Analytical Performance. In: Galbács, G. (eds) Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy in Biological, Forensic and Materials Sciences. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-14502-5_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-14502-5_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-14501-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-14502-5
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)