Abstract
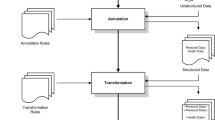
Electronic health care records (EHRs) are the main source of information between medical professionals. Therefore, EHRs would be a good source for advanced data analysis. However, the current data privacy laws complicate the utilization of patient data; due to the concern of evaluating personal information without consent. Since personal information is only partially useful for analysis, removing it from the documents is a reasonable solution that respects the patients privacy and makes patient data accessible for third parties. The electronic health care records anonymizer (EHR) is a BRAT-based application that can be used to tag personal information in EHRs and replace them with previously defined placeholders. In a first annotation step, machine learning (Stanford NER) and rule based approaches generate tags for potential personal information and prior user annotations are added to the document. The user can now add/edit/remove annotations until the annotations are adjusted. The performance of the automated tagging was evaluated on the basis of 10 example EHR input documents, and resulted in a F1 score of 0.72 and an accuracy of 0.96. Since the goal was to keep false negative (FN) tags at a low rate, the false negative rate (FNR) of 0.1 motivated the implementation of a ‘feedback loop’ that saves user annotations for future uses and therefore reduces FNs. Further, the moderate number of false positive (FP) tags results a low precision score of 0.6, which could be counteracted with the implementation of a ‘black list’ that saves tags that were deleted by the user. In combination the ‘feedback loop’ and ‘black list’ would boost the automatic annotation performance, yet in the end, the user has control.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Russ, M.L., Altman, B.: What is biomedical data science and do we need an annual review of it?. In: Vol. 1: i–iii, July (2018)
C. for Medicare & Medicaid Services: Centers for medicare & medicaid services (cms) (1965). [Online] https://www.cms.gov
Manning, C.D., Mihai, S., John, B., Jenny, F., J, B.S., David, M.: The stanford corenlp natural language processing toolkit. In: Proceedings of 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations, pp. 55–60 (2014)
Stenetorp, P., Pyysalo, S., Topić, G., Ohta, T., Ananiadou, S., Tsujii, J.: brat: a web-based tool for NLP-assisted text annotation. In: Proceedings of the Demonstrations Session at EACL 2012. Association for Computational Linguistics, Avignon, France (2012)
Apache: Apache poi (2019). [Online] https://poi.apache.org
Gupta, M.: A review of named entity recognition (ner) using automatic summarization of resumes (2018). [Online] https://towardsdatascience.com/a-review-of-named-entity-recognition-ner-using-automatic-summarization-of-resumes-5248a75de175
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Lordick, T., Hoch, A., Fransen, B. (2022). Anonymization of Electronic Health Care Records: The EHR Anonymizer. In: Dör**haus, J., Weil, V., Schaaf, S., Apke, A. (eds) Computational Life Sciences. Studies in Big Data, vol 112. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08411-9_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08411-9_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-08410-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-08411-9
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)