Abstract
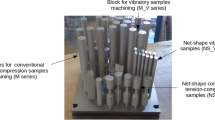
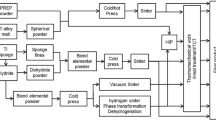
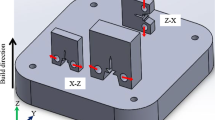
While static mechanical properties of Laser Powder Bed Fusion (L-PBF) processed titanium alloy Ti6Al4V Grade 5 are sufficient and comparable to classic production processes (DebRoy et al. in Prog Mater Sci 92:112–224 [1]; Vrancken et al. in J Alloys Compd 541:177–185 [2]) the fatigue properties of L-PBF lack behind (Leuders et al. in Int J Fatigue 48:300–307 [3]; Nicoletto in Int J Fatigue [4]). However, the reason for this issue are not completely clear and uniquely assignable as combination of (sub surface) porosity, microstructure and surface roughness. This work aims to investigate the influence of several factors on the fatigue properties of controlled, single powder patch of Ti6Al4V. The use of a single patch eliminates the influences of mechanical and chemical powder properties. The investigated factors comprise mechanical and electrochemical polishing (EP) surface treatment, heat treatment (stress relief SR, furnace annealing FA, hot isostatic pressing HIP), print orientation (vertical and horizontal) and load cases (R = −1, R = 0.1). Additionally, a set of tests is performed at 80 °C. For both load cases HIP and machining show a positive impact with a higher influence of machining. For load case R = 0.1 HCF (σaD, 50%) for HIP and machined is around 400 MPa while the same surface treatment but FA reach 218 MPa and SR/EP samples at just 111 MPa. Elevated environmental temperature and horizontal orientation have a minor positive impact. For R = −1 the overall gap narrows to 300 for HIP/machined and 175 MPa for SR/EP respectively.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DebRoy T, Wei HL, Zuback JS, Mukherejee T, Elmer JW, Milewski JO, Beese AM, Wilson-Heid A, De A, Zhang W (2018) Additive manufacturing of metallic components—process, structure and properties. Prog Mater Sci 92:112–224
Vrancken B, Thijs I, Kruth J-P, Van Humbeeck J (2012) Heat treatment of Ti6Al4V produced by selective laser melting: microstructure and mechanical properties. J Alloys Compd 541:177–185
Leuders S, Thöne M, Riemer A, Niendorf T, Tröster T, Ricahrd HA, Maier HJ (2013) On the mechanical behavior of titanium alloy Ti6Al4V manufactured by selective laser melting: fatigue and crack growth performance. Int J Fatigue 48:300–307
Nicoletto G (2016) Anisotropic HCF behavior of Ti6Al4V obtained by powder bed laser fusion. International Journal of Fatigue 94:255–262
Khalid Rafi H, Starr TL, Stucker BE (2013) A comparison of the tensile, fatigue, and fracture behavior of Ti–6Al–4V and 15-5 PH stainless steel parts made by selective laser melting. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 69:1299–1309
Meier B, Skalon M, Warchomicka F, Belei C, Görtler M, Kaindl R, Sommitsch C (2019) Effect of the reuse of powder on material properties of Ti6Al4V processed by SLM. In: Esaform conference proceedings
Król M, Tański T (2016) Surface quality research for selective laser melting of Ti 6Al 4V alloy. Arch Metall Mater 61:1291–1296
Yang L, Gu H, Lassell A (2014) Surface treatment of Ti6Al4V parts made by powder bed fusion additive manufacturing processes using electropolishing; Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, 268–277
Royer F, Bienvenu Y, Gaslain F (2015) EBSD observation of grains microstructures produced by selective laser melting. In: Conference proceedings Euro PM2015
MMPDS-6 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Meier, B., Warchomicka, F., Kaindl, R., Sommitsch, C., Waldhauser, W. (2022). Influence of Different Surface- and Heat Treatments; Elevated Temperature, Orientation on the Fatigue Properties of Ti6Al4V Processed by L-PBF for Controlled Powder Properties. In: Lesiuk, G., Duda, S., Correia, J.A.F.O., De Jesus, A.M.P. (eds) Fatigue and Fracture of Materials and Structures. Structural Integrity, vol 24. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97822-8_27
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97822-8_27
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-97821-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-97822-8
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)