Abstract
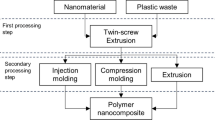
The disposal of plastic wares has been one of the most difficult challenges in the past few decades. High volume of used plastics have found their way to the oceans which is a threat to aquatic life. Recycling has been identified as one of the techniques to eliminate the incessant disposal of plastics. In this study, the influence of nanoparticles on the properties of recycled plastics was examined. Nine samples were prepared which were classified into three categories such as nano-based HDPE-sugarcane bagasse powder composite, nano-based HDPE composite and HDPE without nanoparticles and sugarcane bagasse powder. Samples of nanoparticles-recycled plastic composites were prepared by adding nanoparticles (iron oxide, copper oxide and aluminum oxide) to the high-density polyethylene. These samples were subjected to various tests, such as fatigue, compressive, and water absorption test. The sample containing 4.55% aluminum nanoparticles and 95.45% HDPE obtained the best performance in fatigue tests and water absorption tests. In compressive test, the sample with copper oxide nanoparticles and sugarcane bagasse powder had the highest compressive force and compressive strength. Among the three types of nanoparticles, aluminum oxide nanoparticles had the best performance. Results indicated that nanoparticles enhanced the properties of recycled high-density polyethylene. The study concluded with some recommendations for further studies.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geyer, R., Jambeck, R.J., Law, K.L.: Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 3(7), e1700782 (2017)
Tsakona, M., Rucevska, I.: UNEP Baseline report on plastic waste at Plastic Waste Partnership working group First meeting Beau Vallon, Seychelles, 2–5 March 2020 (2020)
Post, W., Susa, A., Blaauw, R., Molenveld, K., Knoop, R.J.I.: A review on the potential and limitations of recyclable thermosets for structural applications. Polym. Rev. 60(2020), 359–388 (2020)
Prata, J.C., et al.: Solutions and integrated strategies for the control and mitigation of plastic and microplastic pollution. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 16(2019), 1–19 (2019)
Henderson, L., Green, C.: Making sense of microplastics? Public understandings of plastic pollution. Marine Pollut. Bullet. 152, 110908 (2020)
Santos, J., Pham, A., Stasinopoulos, P., Giustozzi, F.: Recycling waste plastics in roads: a life-cycle assessment study using primary data. Sci. Total Environ. 751, 141842 (2021)
Shahrajabian, H., Sadeghian, F.: The investigation of alumina nanoparticles’ effects on the mechanical and thermal properties of HDPE/rPET/MAPE blends. Int. Nano Lett. 9(3), 213–219 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40089-019-0273-7
Bajracharya, M., Manolo, A.C., Karunasena, W., Lau, K.T.: An overview of mechanical properties and durability of glass-fibre reinforced recycled mixed plastic waste composites. Mater. Des. 62, 98–112 (2014)
Chong, W.K.O., Hermreck, C.: World’s first recycled plastic bridges. In: ICSDC 2011: Integrating Sustainability Practices in the Construction Industry, pp. 585–593. ASCE, USA (2011)
Wood, K.: Tough I-beam bridge for tank traffic. Composite Technology 15, 6 (2009)
Prochazkova, Z., Kralik, V., Nemecek, J., Sejnoha, M.: Recyled plastic material properties defined by nanoindentation. Adv. Mater. Lett. 7(1), 78–82 (2016)
Zdiri, K., Elamri, A., Hamdaoui, M., Harzallah, O., Khenoussi, N., Brendle, J.: Reinforcement of recycled PP polymers by nanoparticles incorporation. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 11(3), 296–311 (2018)
Mustafa Al Bakri, A.M., Liyana, J., Norazian, M.N., Kamarudin, H., Ruzaidi, C.M.: Mechanical properties of polymer composites with sugarcane baggase filler. Adv. Mater. Res. 740, 739–744 (2013)
Muñoz, E., García-Manrique, J.A.: Water absorption behaviour and its effect on the mechanical properties of flax fibre reinforced bioepoxy composites. Int. J. Polymer Sci. 2015, 16–18 (2015)
Khalili, P., Liu, X., Zhao, Z., Blinzler, B.: Fully biodegradable composites: Thermal, flammability, moisture absorption and mechanical properties of Natural fibre-reinforced composites with nano-hydroxyapatite. Materials 12(2019), 1–13 (2019)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Faculty of Engineering, Technology and Built Environment, UCSI University Malaysia and Faculty of Engineering and Technology, Liverpool John Moores University for support to conduct this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Han Sheng, K., Olugu, E.U., Binti Hassan, C.S., Karunamoothei, V., Teng, K.H. (2022). Influence of Nano-particles on the Properties of Recycled Plastics. In: Batako, A., Burduk, A., Karyono, K., Chen, X., Wyczółkowski, R. (eds) Advances in Manufacturing Processes, Intelligent Methods and Systems in Production Engineering. GCMM 2021. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 335. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90532-3_29
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90532-3_29
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-90531-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-90532-3
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)