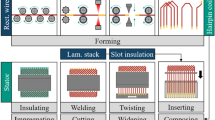
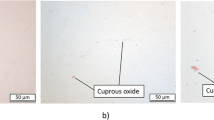
Abstract
The increasing demand for alternative drives in the mobility sector is continuously generating innovations in the development and production of electrical machines. The automotive industry relies more and more on traction machines with hairpin stators, as the process chain can be automated more easily and the copper filling factor can be increased. Enhancing the electrical copper filling factor in particular allows an improvement of the power density of the electrical machine. However, large conductor diameters lead to additional losses at high frequencies, as they occur in high-speed applications, due to eddy current effects. These operational disadvantages can be avoided by substituting the solid rectangular conductor by a litz-wire. Nevertheless, this semi-finished product requires a more complex manufacturing process. Within this paper the process chain for the production of a litz-wire hairpin-stator is illustrated and the challenges in the process chain of a stranded conductor compared to a solid conductor are presented. In this context, the manufacturing aspects for the production of the litz-wire hairpins are considered in detail.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Popescu, M., Goss, J., Staton, D.A., Hawkins, D., Chong, Y.C., Boglietti, A.: Electrical vehicles—practical solutions for power traction motor systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 54(3), 2751–2762 (2018). ISSN 0093-9994. Verfügbar unter: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2018.2792459
Riedel, A., et al.: Challenges of the hairpin technology for production techniques. In: 2018 21st International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), 7 Oktober 2018–10 Oktober 2018, S. 2471–2476. IEEE (2018). ISBN 978-89-86510-20-1
Kühl, A., Riedel, A., Gläßel, T., Masuch, M., Franke, J.: Robot-based production of electric motors with hairpin winding technology. In: LIMITED N, Hg. International Conference on Intelligent Automation and Robotics (ICIAR 2019), S. 257–262 (2019). ISBN 978-988-14048-7-9
Gläßel, T.: Prozessketten zum Laserstrahlschweißen von flachleiterbasierten Formspulenwicklungen für automobile Traktionsantriebe (2000)
Glaessel, T., Seefried, J., Franke, J.: Challenges in the manufacturing of hairpin windings and application opportunities of infrared lasers for the contacting process. In: 2017 7th International Electric Drives Production Conference (EDPC), 5 Dezember 2017–6 Dezember 2017, S. 1–7. IEEE (2017). ISBN 978-1-5386-1069-5
Stone, G.C.: Electrical insulation for rotating machines. Design, evaluation, aging, testing, and repair. IEEE Press, Piscataway (2004). IEEE Press Series on Power Engineering. 8. ISBN 0-471-44506-1
Butov, A., Verl, A.: Comparison of end of line tests for serial production of electric motors in hybrid truck applications. In: 2014 4th International Electric Drives Production Conference (EDPC), 30 September 2014–1 Oktober 2014, S. 1–4. IEEE (2014). ISBN 978-1-4799-5009-6
Bauer, D., Reuss, H.C., Nolle, E.: Einfluss von Stromverdrängung bei elektrischen Maschinen für Hybrid- und Elektrofahrzeugen, Juni 2015
Bauer, D.: Verlustanalyse bei elektrischen Maschinen für Elektro- und Hybridfahrzeuge zur Weiterverarbeitung in thermischen Netzwerkmodellen. Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden, Wiesbaden (2019). ISBN 978-3-658-24271-8
Albach, M., Fischer, J., Roßmanith, H., Exner, D., Stadler, A.: Optimale Wicklung = optimaler Wirkungsgrad. In: Elektronik Power, S. 38–46 (2010)
Sullivan, C.R., Zhang, R.Y.: Analytical model for effects of twisting on litz-wire losses. In: 2014 IEEE 15th Workshop on Control and Modeling for Power Electronics (COMPEL), 22 Juni 2014–25 Juni 2014, S. 1–10. IEEE (2014). ISBN 978-1-4799-2147-8
Biela, J.: Wirbelstromverluste in Wicklungen induktiver Bauelemente. ETZ (October 2021)
Sullivan, C.R., Zhang, R.Y.: Simplified design method for litz wire. In: 2014 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (2014)
Kühner, K.: Beitrag zur Beurteilung der Schädigung von Seilbahnseilen durch Drehung und Verdrehung im Betrieb: Universität Stuttgart (2017)
Stöck, M.: Steigerung der Leistungsdichte und der Wirtschaftlichkeit von Elektromotoren für atomotive Fahrantriebe (2016)
Riedel, A., Roessert, A., Kuehl, A., Franke, J.: Calculation of the copper filling factor of electric traction drives including graphical representation. In: 2019 22nd International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), 11 August 2019–14 August 2019, S. 1–6. ISBN 978-1-7281-3398-0
Hamalainen, H., Pyrhonen, J., Nerg, J., Talvitie, J.: AC resistance factor of litz-wire windings used in low-voltage high-power generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 61(2), 693–700 (2014). ISSN 0278-0046. Verfügbar unter: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2013.2251735W
Maschinenfabrik Niehoff Gmbh & Co. KG.: Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung von Litzen. Erfinder: H. LÄMMERMANN UND B. LOHMLLER. Deutschland. DE102013004592A1
Elektrisola Dr. Gerd Schildbach GmbH & Co. KG.: High frequency litz wires from Elektrisola. Ta**. Verfügbar unter. https://www.elektrisola.com/en/hf-litz-wire-litz/products/ta**.html. Zugriff am 17 Apr 2021
Acknowledgement
The corresponding author Andreas Riedel thanks Maximilian Kneidl, Johannes Seefried, Alexander Kuehl and Joerg Franke for supporting, counselling and reviewing the publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Riedel, A., Kneidl, M., Seefried, J., Kuehl, A., Franke, J. (2022). Comparison of Various Manufacturing Processes for Hairpin-Stators with Different Conductor Material. In: Behrens, BA., Brosius, A., Drossel, WG., Hintze, W., Ihlenfeldt, S., Nyhuis, P. (eds) Production at the Leading Edge of Technology. WGP 2021. Lecture Notes in Production Engineering. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-78424-9_44
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-78424-9_44
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-78423-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-78424-9
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)