Abstract
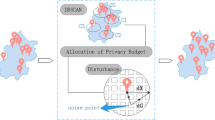
Location-Based Service (LBS) is one of basic services in collaborative applications. However, LBS applications may disclose user’s location privacy, which receives considerable concerns. Many methods have been proposed to protect privacy in LBS. Planar Isotropic Mechanism (PIM) is a typical location privacy preservation method in the scenario of continuous location data release. However, the method is complicated, since it requires two convex hull transformations and one isotropic position transform. To solve the problem, we propose a Staircase Mechanism (SM) based location privacy preservation method for the scenario of continuous location data release. The proposed method replaces PIM with SM, whose implementation is simple and efficient. Furthermore, SM can achieve the same privacy budget with less noise addition, so it can maintain higher quality of services in LBS. Comprehensive experiments conducted on real location data demonstrate that the proposed method is efficient and can maintain high data utility compared with the method based on PIM.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Primault, V., Boutet, A., Mokhtar, S.B., Brunie, L.: The long road to computational location privacy: a survey. IEEE Commun, Surv. Tutorials 21(3), 2772–2793 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2018.2873950
Tan, Z., Wang, C., Yan, C., Zhou, M., Jiang, C.: Protecting privacy of location-based services in road networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transport. Syst. 14 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2020.2992232
Chatzikokolakis, K., Elsalamouny, E., Palamidessi, C., Pazii, A.: Methods for location privacy: a comparative overview. Found. Trends® Privacy Secur. 1(4), 199–257 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1561/3300000017
Wei, J., Lin, Y., Yao, X., Zhang, J.: Differential privacy-based location protection in spatial crowdsourcing. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 1 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSC.2019.2920643
Dwork, C.: Differential privacy. In: Bugliesi, M., Preneel, B., Sassone, V., Wegener, I. (eds.) ICALP 2006. LNCS, vol. 4052, pp. 1–12. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/11787006_1
**ao, Y., **ong, L.: Protecting locations with differential privacy under temporal correlations. In: Proceedings of the 22Nd ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, New York, NY, USA, pp. 1298–1309 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1145/2810103.2813640
Machanavajjhala, A., Kifer, D., Abowd, J., Gehrke, J., Vilhuber, L.: Privacy: theory meets practice on the map. In: 2008 IEEE 24th International Conference on Data Engineering, pp. 277–286, April 2008. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDE.2008.4497436
Andrés, M.E., Bordenabe, N.E., Chatzikokolakis, K., Palamidessi, C.: Geo-indistinguishability: differential privacy for location-based systems. In: Proceedings of the 2013 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer & Communications Security, pp. 901–914, New York, NY, USA (2013). https://doi.org/10.1145/2508859.2516735
Bordenabe, N.E., Chatzikokolakis, K., Palamidessi, C.: Optimal geo-indistinguishable mechanisms for location privacy. In: Proceedings of the 2014 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security - CCS 2014, Scottsdale, Arizona, USA, pp. 251–262 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1145/2660267.2660345
Niu, B., Chen, Y., Wang, Z., Li, F., Wang, B., Li, H.: Eclipse: preserving differential location privacy against long-term observation attacks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 1 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMC.2020.3000730
Gursoy, M.E., Liu, L., Truex, S., Yu, L.: Differentially private and utility preserving publication of trajectory data. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 18(10), 2315–2329 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMC.2018.2874008
Zhu, T., **ong, P., Li, G., Zhou, W.: Correlated differential privacy: hiding information in non-IID data set. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 10(2), 229–242 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2014.2368363
Liu, C., Chakraborty, S., Mittal, P.: Dependence Makes You Vulnerable: Differential Privacy Under Dependent Tuples. In: 23rd Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, NDSS 2016, p. 15. CA, USA, San Diego (Feb. 2016)
Yang, B., Sato, I., Nakagawa, H.: Bayesian differential privacy on correlated data. In: Proceedings of the 2015 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, New York, NY, USA, May 2015, pp. 747–762 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1145/2723372.2747643
Cao, Y., Yoshikawa, M., **ao, Y., **ong, L.: Quantifying differential privacy in continuous data release under temporal correlations. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 31(7), 1281–1295 (Jul. 2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2018.2824328
Cao, Y., Yoshikawa, M., **ao, Y., **ong, L.: Quantifying differential privacy under temporal correlations. In: 2017 IEEE 33rd International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), San Diego, CA, USA, April 2017, pp. 821–832 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDE.2017.132
Dwork, C., Naor, M., Pitassi, T., et al.: Differential privacy under continual observation. Stoc 715–724 (2010)
Geng, Q., Kairouz, P., Oh, S., Viswanath, P.: The staircase mechanism in differential privacy. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Sig. Process. 9(7), 1176–1184 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2425831
Geng, Q., Viswanath, P.: The optimal mechanism in differential privacy. In: International Symposium on Information Theory, pp. 2371–2375 (2014)
Chen, R., Fung, B.C.M., Desai, B.C.: Differentially private trajectory data publication. ar**v Preprint, ar**v: 1112.2020 (2011)
Yu, Z., Zhang, L., **e, X., Ma, W.-Y.: Mining interesting locations and travel sequences from GPS trajectories. In: Proceedings of International Conference on World Wild Web (WWW 2009), Madrid, Spain, pp. 791–800. ACM Press (2009)
Acknowledgment
The authors would also like to appreciate the anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions, which lead to a substantial improvement of this paper. This research has been funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61672468, 61702148).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fang, R., Han, J., Yu, J., Yao, X., Peng, H., Lu, J. (2021). Differentially Private Location Preservation with Staircase Mechanism Under Temporal Correlations. In: Gao, H., Wang, X., Iqbal, M., Yin, Y., Yin, J., Gu, N. (eds) Collaborative Computing: Networking, Applications and Worksharing. CollaborateCom 2020. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 350. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67540-0_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67540-0_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-67539-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-67540-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)