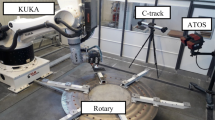
Abstract
Complex structures and a high level of customization in architecture and construction industries require the usage of industrial robots for milling or additive manufacturing applications. Due to economic aspects and the intensive research on robot machining, conventional machine tools are increasingly superseded for specific tasks by industrial robots. However, assembling errors during the manufacturing process and low structural stiffness of industrial robots are still main reasons for inaccuracies of robotic based machining. This paper presents a comparison between industrial robots and cnc machine tools and evaluates their strength and weaknesses. Furthermore, recently published works considering robot calibration and offline compensation strategies in order to increase the absolute and machining accuracy are presented. Finally, the adaption of an existing robot machining process chain with additional components underlines the potential of robots for machining tasks.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ji, W., Wang, L.: Industrial robotic machining: a review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 103(1–4), 1239–1255 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03403-z
Klimchik, A.: Enhanced stiffness modeling of serial and parallel manipulators for robotic-based processing of high performance materials, p. 161 (2012)
Andrew Liou, Y.H., Lin, P.P., Lindeke, R.R., Chiang, H.D.: Tolerance specification of robot kinematic parameters using an experimental design technique—the Taguchi method. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 10(3), 199–207 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0736-5845(93)90055-o
Karan, B., Vukobratović, M.: Calibration and accuracy of manipulation robot models. Mech. Mach. Theory 29, 479–500 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0094-114X(94)90130-9
Nubiola, A., Bonev, I.A.: Absolute calibration of an ABB IRB 1600 robot using a laser tracker. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 29(1), 236–245 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2012.06.004
Nguyen, H.-N., Le, P.-N., Kang, H.-J.: A new calibration method for enhancing robot position accuracy by combining a robot model–based identification approach and an artificial neural network–based error compensation technique. Adv. Mech. Eng. 11(1), 168781401882293 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1177/1687814018822935
Newman, W.S., Birkhimer, C.E., Horning, R.J., Wilkey, A.T.: Calibration of a Motoman P8 robot based on laser tracking. In: Proceedings 2000 ICRA Millennium Conference on IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Symposia Proceedings (Cat. No.00CH37065), vol. 4, pp. 3597–3602, April 2000. Bd.4, https://doi.org/10.1109/robot.2000.845292
Brutscheck, T., Bücker, M.: Modellierung von Roboterkinematiken nach Denavit und Hartenberg. In: Bandow, G., Holzmüller, H.H. (eds.) Das ist gar kein Modell!: Unterschiedliche Modelle und Modellierungen in Betriebswirtschaftslehre und Ingenieurwissenschaften, pp. 149–165. Gabler, Wiesbaden (2009)
Mooring, B., Roth, Z.S., Driels, M.R.: Fundamentals of Manipulator Calibration. Wiley, New York (1991)
Martinelli, A., Tomatis, N., Tapus, A., Siegwart, R.: Simultaneous localization and odometry calibration for mobile robot. In: Proceedings 2003 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2003) (Cat. No.03CH37453), vol. 2, pp. 1499–1504, Okt. 2003. https://doi.org/10.1109/iros.2003.1248856
Jiang, Z., Zhou, W., Li, H., Mo, Y., Ni, W., Huang, Q.: A New kind of accurate calibration method for robotic kinematic parameters based on the extended Kalman and particle filter algorithm. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. 65(4), 3337–3345 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2017.2748058
Song, Y., Zhang, J., Lian, B., Sun, T.: Kinematic calibration of a 5-DoF parallel kinematic machine. Precision Eng. 45, 242–261 (2016) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2016.03.002
Ginani, L., Motta, J.: Theoretical and practical aspects of robot calibration with experimental verification. J. Brazilian Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 33, 15–21 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1590/s1678-58782011000100003
Ye, S.H., Wang, Y., Ren, Y.J., Li, D.K.: Robot calibration using iteration and differential kinematics. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 48, 1–6 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/48/1/001
Lightcap, C., Hamner, S., Schmitz, T., Banks, S.: Improved positioning accuracy of the PA10-6CE robot with geometric and flexibility calibration. IEEE Trans. Rob. 24(2), 452–456 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2007.914003
ABB. Absolute Accuracy, February 2005. https://library.e.abb.com/public/0f879113235a0e1dc1257b130056d133/Absolute%20Accuracy%20EN_R4%20US%2002_05.pdf (zugegriffen Mai 18, 2020)
Altintas, Y., Ber, A.A.: Manufacturing automation: metal cutting mechanics, machine tool vibrations, and CNC design. Appl. Mech. Rev. 54(5), B84–B84 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1399383
Wang, J., Zhang, H., Pan, Z.: Machining with Flexible Manipulators: Critical Issues and Solutions (2006)
Cen, L., Melkote, S.N.: CCT-based mode coupling chatter avoidance in robotic milling. J. Manuf. Process. 29, 50–61 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2017.06.010
Klimchik, A., Ambiehl, A., Garnier, S., Furet, B., Pashkevich, A.: Efficiency evaluation of robots in machining applications using industrial performance measure. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 48,. 12–29 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2016.12.005
Engin, S., Altintas, Y.: Mechanics and dynamics of general milling cutters. Part I: helical end mills, p. 18
Diaz Posada, R.J., Schneider, U., Sridhar, A., Verl, A.: Automatic motion generation for robotic milling optimizing stiffness with sample-based planning. Machines 5(1) (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/machines5010003
Diaz Posada, J.R., Schneider, U., Pidan, S., Geravand, M., Stelzer, P., Verl, A.: High accurate robotic drilling with external sensor and compliance model-based compensation. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 3901–3907, Mai 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/icra.2016.7487579
**e, H., Li, W., Yin, Z.: Posture optimization based on both joint parameter error and stiffness for robotic milling. In: Intelligent Robotics and Applications, pp. 277–286. Cham (2018)
Lin, Y., Zhao, H., Ding, H.: Spindle configuration analysis and optimization considering the deformation in robotic machining applications. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 54, 83–95 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2018.05.005
Cvitanic, T., Nguyen, V., Melkote, S.N.: Pose optimization in robotic machining using static and dynamic stiffness models. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 66, 101992 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2020.101992
Cordes, M., Hintze, W.: Offline simulation of path deviation due to joint compliance and hysteresis for robot machining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 90, April 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9461-z
Tyapin, I., Kaldestad, K.B., Hovland, G.: Off-line path correction of robotic face milling using static tool force and robot stiffness. In: 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 5506–5511, Okt. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/iros.2015.7354157
Schneider, U.: Improving robotic machining accuracy through experimental error investigation and modular compensation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 85, 1–13 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6021-2
Klimchik, A., Bondarenko, D., Pashkevich, A., Briot, S., Furet, B.: Compliance error compensation in robotic-based milling. Inf. Control Autom. Robot. 283, September 2014. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-03500-0_13
Caro, S., Dumas, C., Garnier, S., Furet, B.: Workpiece placement optimization for machining operations with a KUKA KR270-2 robot. In: 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 2921–2926, Mai 2013. https://doi.org/10.1109/icra.2013.6630982
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kainrath, M., Aburaia, M., Stuja, K., Lackner, M., Markl, E. (2021). Accuracy Improvement and Process Flow Adaption for Robot Machining. In: Durakbasa, N.M., Gençyılmaz, M.G. (eds) Digital Conversion on the Way to Industry 4.0. ISPR 2020. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-62784-3_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-62784-3_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-62783-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-62784-3
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)