Abstract
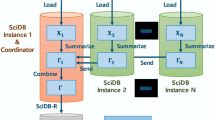
Machine learning requires scalable processing. An important acceleration mechanism is data summarization, which is accurate for many models and whose summary requires a small amount of RAM. In this paper, we generalize a data summarization matrix to produce one or multiple summaries, which benefits a broader class of models, compared to previous work. Our solution works well in popular languages, like R and Python, on a shared-nothing architecture, the standard in big data analytics. We introduce an algorithm which computes machine learning models in three phases: Phase 0 pre-processes and transfers the data set to the parallel processing nodes; Phase 1 computes one or multiple data summaries in parallel and Phase 2 computes a model in one machine based on such data set summaries. A key innovation is evaluating a demanding vector-vector outer product in C++ code, in a simple function call from a high-level programming language. We show Phase 1 is fully parallel, requiring a simple barrier synchronization at the end. Phase 2 is a sequential bottleneck, but contributes very little to overall time. We present an experimental evaluation with a prototype in the R language, with our summarization algorithm programmed in C++. We first show R is faster and simpler than competing big data analytic systems computing the same models, including Spark (using MLlib, calling Scala functions) and a parallel DBMS (computing data summaries with SQL queries calling UDFs). We then show our parallel solution becomes better than single-node processing as data set size grows.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Jarrah, O.Y., Yoo, P.D., Muhaidat, S., Karagiannidis, G.K., Taha, K.: Efficient machine learning for big data: a review. Big Data Res. 2(3), 87–93 (2015)
Arthur, D., Vassilvitskii, S.: k-means++: the advantages of careful seeding. In: Proceedings of the Eighteenth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, SODA, pp. 1027–1035 (2007)
Behm, A., et al.: ASTERIX: towards a scalable, semistructured data platform for evolving-world models. Distrib. Parallel Databases (DAPD) 29(3), 185–216 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10619-011-7082-y
Bradley, P., Fayyad, U., Reina, C.: Scaling clustering algorithms to large databases. In: Proceedings of the ACM KDD Conference, pp. 9–15 (1998)
Chebolu, S.U.S., Ordonez, C., Al-Amin, S.T.: Scalable machine learning in the R language using a summarization matrix. In: Hartmann, S., Küng, J., Chakravarthy, S., Anderst-Kotsis, G., Tjoa, A.M., Khalil, I. (eds.) DEXA 2019. LNCS, vol. 11707, pp. 247–262. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-27618-8_19
Dean, J., et al.: Large scale distributed deep networks. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1232–1240 (2012)
Eddelbuettel, D.: Seamless R and C++ Integration with Rcpp. Springer, New York (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-6868-4
Gemulla, R., Nijkamp, E., Haas, P., Sismanis, Y.: Large-scale matrix factorization with distributed stochastic gradient descent. In: Proceedings of the KDD, pp. 69–77 (2011)
Hellerstein, J., et al.: The MADlib analytics library or MAD skills, the SQL. Proc. VLDB 5(12), 1700–1711 (2012)
Hu, H., Wen, Y., Chua, T., Li, X.: Toward scalable systems for big data analytics: a technology tutorial. IEEE Access 2, 652–687 (2014)
Lang, D.T., Lang, M.D.T.: Package ‘RCurl’ (2012)
Li, F., Nath, S.: Scalable data summarization on big data. Distrib. Parallel Databases 32(3), 313–314 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10619-014-7145-y
Ordonez, C., Cabrera, W., Gurram, A.: Comparing columnar, row and array DBMSS to process recursive queries on graphs. Inf. Systems 63, 66–79 (2016)
Ordonez, C., Omiecinski, E.: Accelerating EM clustering to find high-quality solutions. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 7(2), 135–157 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-003-0141-6
Ordonez, C., Zhang, Y., Cabrera, W.: The Gamma matrix to summarize dense and sparse data sets for big data analytics. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. (TKDE) 28(7), 1906–1918 (2016)
Ostrouchov, G., Chen, W.C., Schmidt, D., Patel, P.: Programming with big data in R (2012). http://r-pbd.org/
Rickert, J.: Big data analysis with revolution R enterprise. Revolution Analytics (2011)
Schmidberger, M., Morgan, M., Eddelbuettel, D., Yu, H., Tierney, L., Mansmann, U.: State-of-the-art in parallel computing with R. J. Stat. Softw. 47 (2009)
Stonebraker, M., et al.: MapReduce and parallel DBMSs: friends or foes? Commun. ACM 53(1), 64–71 (2010)
**ng, E.P., et al.: Petuum: a new platform for distributed machine learning on big data. IEEE Trans. Big Data 1(2), 49–67 (2015)
Zaharia, M., Chowdhury, M., Franklin, M., Shenker, S., Stoica, I.: Spark: cluster computing with working sets. In: HotCloud USENIX Workshop (2010)
Zhang, T., Ramakrishnan, R., Livny, M.: BIRCH: an efficient data clustering method for very large databases. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGMOD Conference, pp. 103–114 (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Al-Amin, S.T., Ordonez, C. (2020). Scalable Machine Learning on Popular Analytic Languages with Parallel Data Summarization. In: Song, M., Song, IY., Kotsis, G., Tjoa, A.M., Khalil, I. (eds) Big Data Analytics and Knowledge Discovery. DaWaK 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12393. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59065-9_22
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59065-9_22
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-59064-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-59065-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)