Abstract
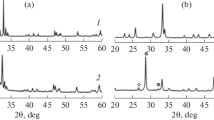
A set of transition metal oxides was prepared via a sol-gel synthesis using different metal (Mn, Cu, and Fe) nitrates to ensure a proper manganese to metal ratio in the final product. Specifically, three pure metal oxides (Mn2O3, CuO, and Fe2O3) and mixed oxides (MnCu15, MnFe15, and MnCu7.5Fe7.5) were synthesized and characterized by means of XRD, N2-physisorption at −196 °C, H2-TPR, FESEM, and XPS techniques. The catalysts were tested for the catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) using two probe molecules, namely ethylene and propylene. As a result, the best reaction rates were observed for the MnCu7.5Fe7.5 powder sample and were attributed to the synergistic interactions occurring between the Mn, Cu, and Fe species in the crystalline structure. Similarly, Mn2O3 showed a good catalytic performance. The excellent catalytic activity of the oxides was correlated with the high amount of reactive chemisorbed oxygen species located on the surface, since these species are useful for the oxidation of VOCs. As well, the improvement of the catalytic activity corresponded to the enhanced reducibility of the catalysts at lower temperatures (i.e., better lattice-oxygen mobility) observed during the temperature-programmed reduction studies.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Koppmann, Volatile Organic Compounds in the Atmosphere (Blackwell, Hoboken, 2007)
R. Atkinson, J. Arey, Atmospheric degradation of volatile organic compounds. Chem. Rev. 103, 4605–4638 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr0206420
B.J. Finlayson-Pitts, J.N. Pitts Jr., Tropospheric air pollution: ozone, airborne toxics, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and particles. Science 276(5315), 1045–1051 (1979)
N. Ramírez, A. Cuadras, E. Rovira, et al., Chronic risk assessment of exposure to volatile organic compounds in the atmosphere near the largest Mediterranean industrial site. Environ. Int. 39, 200–209 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVINT.2011.11.002
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Office of Air and Radiation. Control Techniques for Volatile Organic Compound Emissions from Stationary Sources. (1992)
D. Duprez, F. Cavani, Handbook of Advanced Methods and Processes in Oxidation Catalysis: From Laboratory to Industry (Imperial College Press, London, 2014)
E.C. Moretti, American Institute of Chemical Engineers. Center for Waste Reduction Technologies, Practical Solutions for Reducing Volatile Organic Compounds and Hazardous Air Pollutants (Center for Waste Reduction Technologies, American Institute of Chemical Engineers, New York, NY, 2001)
L.F. Liotta, Catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds on supported noble metals. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 100, 403–412 (2010)
H. Huang, Y. Xu, Q. Feng, D.Y.C. Leung, Low temperature catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds: a review. Cat. Sci. Technol. 5, 2649–2669 (2015)
M.S. Kamal, S.A. Razzak, M.M. Hossain, Catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs)—a review. Atmos. Environ. 140, 117–134 (2016) https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ATMOSENV.2016.05.031
H.C. Genuino, S. Dharmarathna, E.C. Njagi, et al., Gas-phase total oxidation of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylenes using shape-selective manganese oxide and copper manganese oxide catalysts. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp301342f
D.A. Aguilera, A. Perez, R. Molina, S. Moreno, Cu-Mn and Co-Mn catalysts synthesized from hydrotalcites and their use in the oxidation of VOCs. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 104, 144–150 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.02.019
M. Piumetti, S. Bensaid, T. Andana, et al., Cerium-copper oxides prepared by solution combustion synthesis for total oxidation reactions: from powder catalysts to structured reactors. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 205, 455–468 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.12.054
D. Delimaris, T. Ioannides, VOC oxidation over MnOx-CeO2 catalysts prepared by a combustion method. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 84, 303–312 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.02.003
D. Delimaris, T. Ioannides, VOC oxidation over CuO-CeO2 catalysts prepared by a combustion method. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 89, 295–302 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.02.003
H. Lu, X. Kong, H. Huang, et al., Cu–Mn–Ce ternary mixed-oxide catalysts for catalytic combustion of toluene. J. Environ. Sci. 32, 102–107 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JES.2014.11.015
M. Piumetti, D. Fino, N. Russo, Mesoporous manganese oxides prepared by solution combustion synthesis as catalysts for the total oxidation of VOCs. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 163, 277–287 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.08.012
M.J. Marin Figueredo, T. Andana, S. Bensaid, et al., Cerium–copper–manganese oxides synthesized via solution combustion synthesis (SCS) for total oxidation of VOCs. Catal. Letters. 150, 1821–1840 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-019-03094-x
W.M. Haynes, CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics: A Ready-Reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data, 95th edn. (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2014)
C. Julien, M. Massot, R. Baddour-Hadjean, et al., Raman spectra of birnessite manganese dioxides. Solid State Ionics 159, 345–356 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(03)00035-3
S. Bach, M. Henry, N. Baffier, J. Livage, Sol-gel synthesis of manganese oxides. J. Solid State Chem. 88, 325–333 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-4596(90)90228-P
X. Tang, Y. Li, X. Huang, et al., MnOx-CeO2 mixed oxide catalysts for complete oxidation of formaldehyde: effect of preparation method and calcination temperature. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 62, 265–273 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2005.08.004
A. Pintar, J. Batista, S. Hočevar, TPR, TPO, and TPD examinations of Cu0.15Ce0.85O 2-y mixed oxides prepared by co-precipitation, by the sol-gel peroxide route, and by citric acid-assisted synthesis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 285, 218–231 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.11.049
S.E. Shirsath, D. Wang, S.S. Jadhav, et al., Ferrites Obtained by Sol–Gel Method, in Handbook of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, (Springer International Publishing, New York, 2018), pp. 1–41
R.D. Shannon, Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta. Crystallogr. Sect. A. 32, 751–767 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0567739476001551
F. Kapteijn, L. Singoredjo, A. Andreini, J.A. Moulijn, Activity and selectivity of pure manganese oxides in the selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide with ammonia. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 3, 173–189 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0926-3373(93)E0034-9
G. Avgouropoulos, T. Ioannides, H. Matralis, Influence of the preparation method on the performance of CuO-CeO 2 catalysts for the selective oxidation of CO. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 56, 87–93 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2004.07.017
G. Munteanu, L. Ilieva, D. Andreeva, Kinetic parameters obtained from TPR data for α-Fe2O3 and Au/α-Fe2O3 systems. Thermochim. Acta 291, 171–177 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6031(96)03097-3
J. Zieliński, I. Zglinicka, L. Znak, Z. Kaszkur, Reduction of Fe2O3 with hydrogen. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 381, 191–196 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2010.04.003
A. Wöllner, F. Lange, H. Schmelz, H. Knözinger, Characterization of mixed copper-manganese oxides supported on titania catalysts for selective oxidation of ammonia. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 94, 181–203 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0926-860X(93)85007-C
T. Li, Y. Yang, C. Zhang, et al., Effect of manganese incorporation manner on an iron-based catalyst for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 16, 244–251 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-9953(07)60055-3
I.R. Leith, M.G. Howden, Temperature-programmed reduction of mixed iron-manganese oxide catalysts in hydrogen and carbon monoxide. Appl. Catal. 37, 75–92 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-9834(00)80752-6
L. Kundakovic, M. Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, Reduction characteristics of copper oxide in cerium and zirconium oxide systems. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 171, 13–29 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-860X(98)00056-8
J.F. Moulder, W.F. Stickle, P.E. Sobol, K.D. Bomben, Handbook of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (Perkin-Elmer Corporation, Physical Electronics Division, Eden Prairie, 1992)
V.P. Santos, M.F.R. Pereira, J.J.M. Órfão, J.L. Figueiredo, The role of lattice oxygen on the activity of manganese oxides towards the oxidation of volatile organic compounds. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 99, 353–363 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.07.007
S.C. Kim, W.G. Shim, Catalytic combustion of VOCs over a series of manganese oxide catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 98, 180–185 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.05.027
M.C. Biesinger, B.P. Payne, A.P. Grosvenor, et al., Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 2717–2730 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.10.051
M.C. Biesinger, L.W.M. Lau, A.R. Gerson, R.S.C. Smart, Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Sc, Ti, V, Cu and Zn. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 887–898 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.10.051
W. Liu, M. Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, Total oxidation of carbon monoxide and methane over transition metal-fluorite oxide composite catalysts.pdf. J. Catal. 153, 317–332 (1995)
T. Yamashita, P. Hayes, Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe 2+ and Fe 3+ ions in oxide materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 2441–2449 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.09.063
M. Piumetti, N. Russo, Notes on Catalysis for Environment and Energy (CLUT-Politecnico di Torino, Torino, 2017)
E.C. Njagi, H.C. Genuino, C.K. King, et al., Applied catalysis A: general catalytic oxidation of ethylene at low temperatures using porous copper manganese oxides. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 421-422, 154–160 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2012.02.011
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Marin Figueredo, M.J., Piumetti, M., Bensaid, S., Fino, D., Nunzio, R. (2021). Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds over Porous Manganese Oxides Prepared via Sol-Gel Method. In: Piumetti, M., Bensaid, S. (eds) Nanostructured Catalysts for Environmental Applications. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58934-9_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58934-9_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-58933-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-58934-9
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)