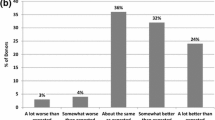
Abstract
The psychosocial evaluation for living kidney donation is the starting point in a process designed to both promote optimal care for prospective donors and protect donors from adverse psychosocial outcomes after donation. The evaluation and the process of conducting it are informed by research evidence on the nature of postdonation psychosocial outcomes, including physical, emotional, and social functioning components of health-related quality of life, as well as other elements such as financial burdens associated with donation. In this chapter, we delineate the domains to be examined in the psychosocial evaluation, and discuss the processes and procedures to be used to conduct the evaluation and report its findings. We consider implications of psychosocial evaluation findings for the care of both individuals who donate and those who do not donate. Additionally, we discuss donors’ postdonation psychosocial care needs and the ways in which such care, when combined with the collection of postdonation follow-up data, can inform the education and preparation of donor candidates during the predonation evaluation process. Finally, we review both qualitative and quantitative research evidence on the nature of psychosocial outcomes in living donors, risk factors for adverse outcomes, and implications of these data for clinical care and for intervention development.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abecassis M, Adams M, Adams P, Arnold RM, Atkins CR, Barr ML, et al. Consensus statement on the live organ donor. JAMA. 2000;284(22):2919–26. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.284.22.2919.
Adams PL, Cohen D, Danovitch G, Edington RM, Gaston RS, Jacobs CL, et al. The nondirected live-kidney donor: ethical considerations and practice guidelines: a national conference report. Transplantation. 2002;74:582–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007890-200208270-00030.
Barr ML, Belghiti J, Villamil FG, Pomfret EA, Sutherland DS, Gruessner RW, et al. A report of the Vancouver Forum on the care of the live organ donor: lung, liver, pancreas, and intestine data and medical guidelines. Transplantation. 2006;81(10):1373–85. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.tp.0000216825.56841.cd.
Canadian Council for Donation and Transplantation. Enhancing living donation: a Canadian forum. Edmonton, AB: The Council; 2006.
Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). 42 CFR Parts 405, 482, 488, and 498 Medicare Program; Hospital Conditions of Participation: Requirements for Approval and Re-Approval of Transplant Centers to Perform Organ Transplants; Final Rule. Available at: https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Provider-Enrollment-and-Certification/GuidanceforLawsAndRegulations/Downloads/TransplantFinalLawandReg.pdf. Accessed: 7 Sept 2020.
Delmonico F, Council of the Transplantation Society. A report of the Amsterdam Forum on the care of the live kidney donor: data and medical guidelines. Transplantation. 2005;79(6 Suppl):S53–66. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15785361/.
Dew MA, Jacobs CL, Jowsey SG, Hanto R, Miller C, Delmonico FL, et al. Guidelines for the psychosocial evaluation of living unrelated kidney donors in the United States. Am J Transplant. 2007;7(5):1047–54. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2007.01751.x.
Ethics Committee of the Transplantation Society. The consensus statement of the Amsterdam Forum on the care of the live kidney donor. Transplantation. 2004;78(4):491–2. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.tp.0000136654.85459.1e.
Kanellis J, CARI (Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment) Group. The CARI guidelines: justification of living donor kidney transplantation. Nephrology. 2010;15(Suppl 1):S72–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1797.2009.01212.x.
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Living Kidney Donor Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline on the evaluation and care of living kidney donors. Transplantation. 2017;101(Suppl 8S):S1–109. https://kdigo.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/2017-KDIGO-LD-GL.pdf.
LaPointe Rudow D, Hays R, Baliga P, Cohen DJ, Cooper M, Danovitch GM, et al. Consensus conference on best practices in live kidney donation: recommendations to optimize education, access, and care. Am J Transplant. 2015;15(4):914–22. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.13173.
Living Kidney Donor Follow-Up Conference Writing Group, Leichtman A, Abecassis M, Barr M, Charlton M, Cohen D, et al. Living kidney donor follow-up: state-of-the-art and future directions, conference summary and recommendations. Am J Transplant. 2011;11(12):2561–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03816.x.
Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN) / United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS). Policy 14: Living Donation. Available at: https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/governance/policies/. Accessed: 7 Sept 2020.
Lentine KL, Segev DL. Understanding and communicating medical risks for living kidney donors: a matter of perspective. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28(1):12–24. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2016050571.
Tong A, Chapman JR, Wong G, de Bruijn J, Craig JC. Screening and follow-up of living kidney donors: a systematic review of clinical practice guidelines. Transplantation. 2011;92:962–72. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e3182328276.
Dew MA, Switzer GE, DiMartini AF, Myaskovsky L, Crowley-Matoka M. Psychosocial aspects of living organ donation. In: Tan HP, Marcos A, Shapiro R, editors. Living donor organ transplantation. New York: Taylor and Francis; 2007. p. 7–26.
Matas AJ, Hays RE, Ibrahim HN. Long-term non-end-stage renal disease risks after living kidney donation. Am J Transplant. 2017;17(4):893–900. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.14011.
Lentine KL, Lam NN, Segev DL. Risks of living kidney donation: current state of knowledge on outcomes important to donors. Clin J Am Soc Nephol. 2019;14(4):597–608. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.11220918.
Dew MA, Boneysteele G, DiMartini AF. Unrelated donors. In: Steel JL, editor. Living donor advocacy: an evolving role within transplantation. New York: Springer; 2014. p. 149–67.
DiMartini AF, Shenoy A, Dew MA. Organ transplantation. In: Levenson JL, editor. The American Psychiatric Publishing Textbook of psychosomatic medicine and consultation-liaison psychiatry. 3rd ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc; 2019. p. 859–906.
DiMartini AF, Dew MA, Crone C. Organ transplantation. In: Sadock BJ, Sadock VA, Ruiz P, editors. Kaplan and Sadock’s Comprehensive textbook of psychiatry. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2017. p. 2357–73.
Jowsey SG, Schneekloth TD. Psychosocial factors in living organ donation: clinical and ethical challenges. Transplant Rev. 2008;22(3):192–5.
LaPointe Rudow D, Swartz K, Phillips C, Hollenberger J, Smith T, Steel JL. The psychosocial and independent living donor advocate evaluation and post-surgery care of living donors. J Clin Psychol Med Settings. 2015;22(2–3):136–49.
Olbrisch ME, Benedict SM, Haller DL, Levenson JL. Psychosocial assessment of living organ donors: clinical and ethical considerations. Prog Transplant. 2001;11(1):40–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trre.2008.04.008.
Shenoy A. The psychosocial evaluation of live donors. In: Sher Y, Maldonado J, editors. The psychosocial care of end-stage disease and transplant patients. New York: Springer; 2019. p. 49–59.
Duerinckx N, Timmerman L, Van Gogh J, van Busschbach J, Ismail SY, Massey EK, et al. Predonation psychosocial evaluation of living kidney and liver donor candidates: a systematic literature review. Transpl Int. 2014;27(1):2–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.12154.
Fisher MS Sr. Psychosocial evaluation interview protocol for living related and living unrelated kidney donors. Soc Work Health Care. 2003;38(1):39–61. https://doi.org/10.1300/j010v38n01_03.
Iacoviello BM, Shenoy A, Braoude J, Jennings T, Vaidya S, Brouwer J, et al. The Live Donor Assessment Tool: a psychosocial assessment tool for live organ donors. Psychosomatics. 2015;56(3):254–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psym.2015.02.001.
Leo RL, Smith BA, Mori DL. Guidelines for conducting a psychiatric evaluation of the unrelated kidney donor. Psychosomatics. 2003;44(6):452–60. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.psy.44.6.452.
Massey EK, Timmerman L, Ismail SY, Duerinckx N, Lopes A, Maple H, et al. The ELPAT living organ donor Psychosocial Assessment Tool (EPAT): from ‘what’ to ‘how’ of psychosocial screening-a pilot study. Transpl Int. 2018;31(1):56–70. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.13041.
Schroder NM, McDonald LA, Etringer G, Snyders M. Consideration of psychosocial factors in the evaluation of living donors. Prog Transplant. 2008;18:41–9. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18429581/.
van Hardeveld E, Tong A, CARI Group. The CARI guidelines: psychosocial care of living kidney donors. Nephrology. 2010;15(suppl 1):S80–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1797.2009.01213.x.
Hanson CS, Ralph AF, Manera KE, Gill JS, Kanellis J, Wong G, et al. The lived experience of “being evaluated” for organ donation: focus groups with living kidney donors. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;12(11):1852–61. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.03550417.
Ralph AF, Butow P, Hanson CS, Chadban SJ, Chapman JR, Craig JC, et al. Donor and recipient views on their relationship in living kidney donation: thematic synthesis of qualitative studies. Am J Kidney Dis. 2017;69(5):602–16. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.09.017.
Tong A, Chapman JR, Wong G, Kanellis J, McCarthy G, Craig JC. The motivations and experiences of living kidney donors: a thematic synthesis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012;60:15–26. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2011.11.043.
Crowley-Matoka M, Siegler M, Cronin DC 2nd. Long-term quality of life issues among adult-to-pediatric living liver donors: a qualitative exploration. Am J Transplant. 2004;4(5):744–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2004.00377.x.
Iacoviello BM, Shenoy A, Hunt J, Filipovic-Jewell Z, Haydel B, LaPointe Rudow D. A prospective study of the reliability and validity of the Live Donor Assessment Tool. Psychosomatics. 2017;58(5):519–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psym.2017.03.012.
Kook YWA, Shenoy A, Hunt J, Desrosiers F, Gordon-Elliott JS, Jowsey-Gregoire S, et al. Multicenter investigation of the reliability and validity of the Live Donor Assessment Tool as an enhancement to the psychosocial evaluation of living donors. Am J Transplant. 2019;19(4):1119–28. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.15170.
Rodrigue JR, Guenther R, Kaplan B, Mandelbrot DA, Pavlakis M, Howard RJ. Measuring the expectations of kidney donors: initial psychometric properties of the Living Donation Expectancies Questionnaire. Transplantation. 2008;85(9):1230–4. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e31816c5ab0.
Wirken L, van Middendorp H, Hooghof CW, Sanders JSF, Dam RE, van der Pant KAMI, et al. Pre-donation cognitions of potential living organ donors: the development of the Donation Cognition Instrument in potential kidney donors. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017;32:573–80. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfw421.
Reese PP, Allen MB, Carney C, Leidy D, Levsky S, Pendse R, et al. Outcomes for individuals turned down for living kidney donation. Clin Transpl. 2018;32:e13408. https://doi.org/10.1111/ctr.13408.
Allen MB, Abt PL, Reese PP. What are the harms of refusing to allow living kidney donation? An expanded view of risks and benefits. Am J Transplant. 2014;14(3):531–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.12599.
Dew MA, DiMartini AF, DeVito Dabbs AJ, Zuckoff A, Tan HP, McNulty ML, et al. Preventive intervention for living donor psychosocial outcomes: feasibility and efficacy in a randomized controlled trial. Am J Transplant. 2013;13(10):2672–84. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.12393.
Lentine KL, Schnitzler MA, **ao H, Axelrod D, Davis CL, McCabe M, et al. Depression diagnoses after living kidney donation: linking U.S. Registry data and administrative claims. Transplantation. 2012;94:77–83. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e318253f1bc.
National Council for Behavioral Health. Center for Integrated Health Solutions. Screening tools. https://www.integration.samhsa.gov/clinical-practice/screening-tools#anxiety. Accessed: 7 Sept 2020.
Rush AJ Jr, First MB, Blacker D, editors. Handbook of psychiatric measures. 2nd ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association Press; 2008.
Tan JC, Gordon EJ, Dew MA, LaPointe Rudow D, Steiner RW, Woodle ES, et al. Living donor kidney transplantation: facilitating education about live kidney donation-recommendations from a consensus conference. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;10(9):1670–7. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.01030115.
Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN). Procedures to collect postdonation follow-up data from living donors. Available at: https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/resources/guidance/procedures-to-collect-post-donation-follow-up-data-from-living-donors/. Accessed: 7 Sept 2020.
Dew MA, Jacobs CL. Psychosocial and socioeconomic issues facing the living kidney donor. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2012;19(4):237–43. https://dx.doi.org/10.1053%2Fj.ackd.2012.04.006.
Kasiske BL, Asrani SK, Dew MA, Henderson ML, Henrich C, Humar A, et al. The Living Donor Collective: a scientific registry for living donors. Am J Transplant. 2017;17(12):3040–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.14365.
Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN) / United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS). Policy 18: Data Submission Requirements. Available at: https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/governance/policies/. Accessed: 7 Sept 2020.
Dew MA, Zuckoff A, DiMartini AF, DeVito Dabbs AJ, McNulty ML, Fox KR, et al. Prevention of poor psychosocial outcomes in living organ donors: from description to theory-driven intervention development and initial feasibility testing. Prog Transplant. 2012;22(3):280–93. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ackd.2012.04.006.
Jacobs CL, Gross CR, Messersmith EE, Hong BA, Gillespie BW, Hill-Callahan P, et al. Emotional and financial experiences of kidney donors over the past 50 years: the RELIVE Study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;10(12):2221–31. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.07120714.
Fellner CH, Marshall JR. Twelve kidney donors. JAMA. 1968;206(12):2703–7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4880430/.
Simmons RG, Klein SD, Simmons RL. Gift of life: the social and psychological impact of organ transplantation. Brunswick, NJ: Transaction Books; 1987. http://hdl.handle.net/10822/1034762.
Kisch AM, Forsberg A, Fridh I, Almgren M, Lundmark M, Lovén C, et al. The meaning of being a living kidney, liver or stem cell donor-a meta-ethnography. Transplantation. 2018;102:744–56. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000002073.
Slinin Y, Brasure M, Eidman K, Bydash J, Maripuri S, Carlyle M, et al. Long-term outcomes of living kidney donation. Transplantation. 2016;100(6):1371–86. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000001252.
Wirken L, van Middendorp H, Hooghof CW, Rovers MM, Hoitsma AJ, Hilbrands LB, et al. The course and predictors of health-related quality of life in living kidney donors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Transplant. 2015;15:3041–54. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.13453.
Gross CR, Messersmith EE, Hong BA, Jowsey SG, Jacobs C, Gillespie BW, et al. Health-related quality of life in kidney donors from the last five decades: results from the RELIVE study. Am J Transplant. 2013;13:2924–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.12434.
Dew MA, Switzer GE. Listening to living donors. Transplantation. 2018;102(5):718–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000002074.
Ralph AF, Butow P, Hanson CS, Chadban SJ, Chapman JR, Craig JC, et al. Donor and recipient views on their relationship in living kidney donation: thematic synthesis of qualitative studies. Am J Kidney Dis. 2017;69:602–16. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.09.017.
Thys K, Schwering KL, Siebelink M, Dobbels F, Borry P, Schotsmans P, et al. Psychosocial impact of pediatric living-donor kidney and liver transplantation on recipients, donors, and the family: a systematic review. Transpl Int. 2015;28:270–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.12481.
Franklin PM, Crombie AK. Live related renal transplantation: psychological, social, and cultural issues. Transplantation. 2003;76(8):1247–52. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.TP.0000087833.48999.3D.
Andersen MH, Mathisen L, Øyen O, Wahl AK, Hanestad BR, Fosse E. Living donors’ experiences 1 wk after donating a kidney. Clin Transpl. 2005;19(1):90–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-0012.2004.00304.x.
Clarke A, Mitchell A, Abraham C. Understanding donation experiences of unspecified (altruistic) kidney donors. Br J Health Psychol. 2014;19(2):393–408. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjhp.12048.
Ralph AF, Butow P, Craig JC, Wong G, Chadban SJ, Luxton G, et al. Living kidney donor and recipient perspectives on their relationship: longitudinal semi-structured interviews. BMJ Open. 2019;9(4):e026629. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-026629.
Garcia MC, Chapman JR, Shaw PJ, Gottlieb DJ, Ralph A, Craig JC, et al. Motivations, experiences, and perspectives of bone marrow and peripheral blood stem cell donors: thematic synthesis of qualitative studies. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013;19(7):1046–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2013.04.012.
Sharma VK, Enoch MD. Psychological sequelae of kidney donation: a 5-10 year follow up study. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1987;75(3):264–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0447.1987.tb02787.x.
Duffy MA. Intrafamilial kidney transplants: the impact on the sibling relationship among donors, recipients and volunteers. 2009. Available from ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global-305174960. http://pitt.idm.oclc.org/login?url=https://search-proquest-com.pitt.idm.oclc.org/docview/305174960?accountid=14709. Accessed: 7 Sept 2020.
Andersen MH, Bruserud F, Mathisen L, Wahl AK, Hanestad BR, Fosse E. Follow-up interviews of 12 living kidney donors one yr after open donor nephrectomy. Clin Transpl. 2007;21(6):702–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-0012.2007.00726.x.
Shaw RM. Rethinking elements of informed consent for living kidney donation: findings from a New Zealand study. Health Sociol Rev. 2015;24(1):109–22.
Hanson CS, Chapman JR, Gill JS, Kanellis J, Wong G, Craig JC, et al. Identifying outcomes that are important to living kidney donors: a nominal group technique study. Clin J Am Soc Nephol. 2018;13(6):916–26. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.13441217.
Lunsford SL, Shilling LM, Chavin KD, Martin MS, Miles LG, Norman ML, et al. Racial differences in the living kidney donation experience and implications for education. Prog Transplant. 2007;17(3):234–40.
Williams AM, Colefax L, O’Driscoll CT, Dawson S. An exploration of experiences of living renal donors following donation. Nephrol Nurs J. 2009;36(4):423–7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19715110/.
Shaw RM, Bell LJM. ‘Because you can’t live on love’: living kidney donors’ perspectives on compensation and payment for organ donation. Health Expect. 2015;18(6):3201–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/hex.12310.
Hildebrand L, Melchert TP, Anderson RC. Impression management during evaluation and psychological reactions post-donation of living kidney donors. Clin Transpl. 2014;28(8):855–61. https://doi.org/10.1111/ctr.12390.
Tushla L, LaPointe RD, Milton J, Rodrigue JR, Schold JD, Hays RE, et al. Reducing financial barriers to live kidney donation: resources available and policy changes needed to improve access. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;10(9):1696–702. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.01000115.
Barnieh L, Kanellis J, McDonald S, Arnold J, Sontrop JM, Cuerden M, et al. Direct and indirect costs incurred by Australian living kidney donors. Nephrology. 2018;23(12):1145–51. https://doi.org/10.1111/nep.13205.
Przech S, Garg AX, Arnold JB, Barnieh L, Cuerden MS, Dipchand C, et al. Financial costs incurred by living kidney donors: a prospective cohort study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;29(12):2847–57. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2018040398.
Rodrigue JR, Schold JD, Morrissey P, Whiting J, Vella J, Kayler LK, et al. Direct and indirect costs following living kidney donation: findings from the KDOC study. Am J Transplant. 2016;16(3):869–76. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.13591.
Hanson CS, Tong A. Outcomes of interest to living kidney donors. Curr Transplant Rep. 2019;6:177–83.
Benzing C, Hau HM, Kurtz G, Schmelzle M, Tautenhahn HM, Morgül MH, et al. Long-term health-related quality of life of living kidney donors: a single-center experience. Qual Life Res. 2015;24(12):2833–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-015-1027-2.
Clemens K, Boudville N, Dew MA, Geddes C, Gill JS, Jassal V, et al. The long-term quality of life of living kidney donors: a multicenter cohort study. Am J Transplant. 2011;11(3):463–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2010.03424.x.
de Groot IB, Stiggelbout AM, van der Boog PJM, Baranski AG, Marang-van de Mheen PJ, PARTNER-study group. Reduced quality of life in living kidney donors: association with fatigue, societal participation and pre-donation variables. Transpl Int. 2012;25(9):967–75. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-2277.2012.01524.x.
Dols LFC, IJzermans JNM, Wentink N, Tran TCK, Zuidema WC, Dooper IM, et al. Long-term follow-up of a randomized trial comparing laparoscopic and mini-incision open live donor nephrectomy. Am J Transplant. 2010;10:2481–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2010.03281.x.
Ibrahim HN, Foley R, Tan L, Rogers T, Bailey RF, Guo H, et al. Long-term consequences of kidney donation. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:459–69. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0804883.
Janki S, Klop KWJ, Dooper IMM, Weimar W, Ijzermans JNM, Kok NFM. More than a decade after live donor nephrectomy: a prospective cohort study. Transpl Int. 2015;28(11):1268–75. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.12589.
Mjøen G, Stavem K, Westlie L, Midtvedt K, Fauchald P, Norby G, et al. Quality of life in kidney donors. Am J Transplant. 2011;11(6):1315–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03517.x.
Meyer K, Wahl AK, Bjørk IT, Wisløff T, Hartmann A, Andersen MH. Long-term, self-reported health outcomes in kidney donors. BMC Nephrol. 2016;17:8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-016-0221-y.
Sommerer C, Feuerstein D, Dikow R, Rauch G, Hartmann M, Schaier M, et al. Psychosocial and physical outcome following kidney donation-a retrospective analysis. Transpl Int. 2015;28(4):416–28. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.12509.
Messersmith EE, Gross CR, Beil CA, Gillespie BW, Jacobs C, Taler SJ, et al. Satisfaction with life among living kidney donors: a RELIVE Study of long-term donor outcomes. Transplantation. 2014;98(12):1294–300. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000000360.
Jowsey SG, Jacobs C, Gross CR, Hong BA, Messersmith EE, Gillespie BW, et al. Emotional well-being of living kidney donors: findings from the RELIVE Study. Am J Transplant. 2014;14(11):2535–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.12906.
Rodrigue JR, Schold JD, Morrissey P, Whiting J, Vella J, Kayler LK, et al. Mood, body image, fear of kidney failure, life satisfaction, and decisional stability following living kidney donation: findings from the KDOC study. Am J Transplant. 2018;18(6):1397–407. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.14618.
Rodrigue JR, Fleishman A, Schold JD, Morrissey P, Whiting J, Vella J, et al. Patterns and predictors of fatigue following living donor nephrectomy: findings from the KDOC Study. Am J Transplant. 2020;20(1):181–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.15519.
Holscher CM, Leanza J, Thomas AG, Waldram MM, Haugen CE, Jackson KR, et al. Anxiety, depression, and regret of donation in living kidney donors. BMC Nephrol. 2018;19(1):218. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-018-1024-0.
Weidebusch S, Reiermann C, Steinke FA, Muthny HJ, Pavenstaedt B, Schoene-Seifert N, et al. Quality of life, co**, and mental health status after living kidney donation. Transplant Proc. 2009;41(5):1483–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2009.02.102.
Lopes A, Frade IC, Teixeira L, Oliveira C, Almeida M, Dias L, et al. Depression and anxiety in living kidney donation: evaluation of donors and recipients. Transplant Proc. 2011;43(1):131–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2010.12.028.
Kroencke S. The relevance of donor satisfaction after living kidney donation-a plea for a routine psychosocial follow-up. Transpl Int. 2018;31(12):1330–1. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.13355.
Menjivar A, Torres X, Paredes D, Avinyo N, Peri JM, De Sousa-Amorim E, et al. Assessment of donor satisfaction as an essential part of living donor kidney transplantation: an eleven-year retrospective study. Transpl Int. 2018;31(12):1332–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.13334.
Gill JS, Gill J, Barnieh L, Dong J, Rose C, Johnston O, et al. Income of living kidney donors and the income difference between living kidney donors and their recipients in the United States. Am J Transplant. 2012;12(11):3111–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.04211.x.
Lentine KL, Mannon RB. The Advancing American Kidney Health (AAKH) Executive Order: Promise and Caveats for Expanding Access to Kidney Transplantation. Kidney360. 2020;1(6):557–560. https://doi.org/10.34067/KID.0001172020.
Dew MA, Butt Z, Liu Q, Simpson MA, Zee J, Ladner DP, et al. Prevalence and predictors of patient-reported long-term mental and physical health after donation in the Adult-to-Adult Living-Donor Liver Transplantation Cohort Study. Transplantation. 2018;102(1):105–18. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000001942.
Watson JM, Behnke MK, Fabrizio MD, McCune TR. Recipient graft failure or death impact on living kidney donor quality of life based on the living organ donor network database. J Endourol. 2013;27(12):1525–9. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2013.0189.
Rodrigue JR, Schutzer ME, Paek M, Morrissey P. Altruistic kidney donation to a stranger: psychosocial and functional outcomes at two US transplant centers. Transplantation. 2011;91(7):772–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e31820dd2bd.
Maple H, Chilcot J, Burnapp L, Gibbs P, Santhouse A, Norton S, et al. Motivations, outcomes, and characteristics of unspecified (nondirected altruistic) kidney donors in the United Kingdom. Transplantation. 2014;98(11):1182–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000000340.
Massey EK, Kranenburg LW, Zuidema WC, Hak G, Erdman RAM, Hilhorst M, et al. Encouraging psychological outcomes after altruistic donation to a stranger. Am J Transplant. 2010;10:1445–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2010.03115.x.
Jacobs C, Berglund DM, Wiseman JF, Garvey C, Larson DB, Voges M, et al. Long-term psychosocial outcomes after nondirected donation: a single-center experience. Am J Transplant. 2019;19(5):1498–506. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.15179.
Kranenburg L, Zuidema W, Vanderkroft P, Duivenvoorden H, Weimar W, Passchier J, et al. The implementation of a kidney exchange program does not induce a need for additional psychosocial support. Transpl Int. 2007;20(5):432–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-2277.2007.00461.x.
Serur D, Charlton M, Lawton M, Sinacore J, Gordon-Elliot J. Donors in chains: psychosocial outcomes of kidney donors in paired exchange. Prog Transplant. 2014;24(4):371–4. https://doi.org/10.7182/pit2014222.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Dew, M.A., DiMartini, A.F., Steel, J.L., Jowsey-Gregoire, S.G. (2021). Psychosocial Evaluation, Care and Quality of Life in Living Kidney Donation. In: Lentine, K.L., Concepcion, B.P., Lerma, E.V. (eds) Living Kidney Donation. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-53618-3_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-53618-3_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-53617-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-53618-3
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)