Abstract
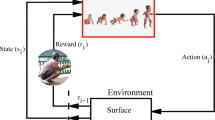
The control of inverted pendulum problem that is one of the classical control problems is important for many areas from autonomous vehicles to robotic. This chapter presents the usage of the deep reinforcement learning algorithms to control the cart-pole balancing problem. The first part of the chapter reviews the theories of deep reinforcement learning methods such as Deep Q Networks (DQN), DQN with Prioritized Experience Replay (DQN+PER), Double DQN (DDQN), Double Dueling Deep-Q Network (D3QN), Reinforce, Asynchronous Advanced Actor Critic Asynchronous (A3C) and Synchronous Advantage Actor-Critic (A2C). Then, the cart-pole balancing problem in OpenAI Gym environment is considered to implement the deep reinforcement learning methods. Finally, the performance of all methods are comparatively given on the cart-pole balancing problem. The results are presented by tables and figures.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Ogata, Y. Yang, Modern Control Engineering, vol. 4 (London, 2002)
A.E. Bryson, Applied Optimal Control: Optimization, Estimation and Control (Routledge, 2018)
M.L. Puterman, Markov Decision Processes: Discrete Stochastic Dynamic Programming (Wiley, 2014
R.S. Sutton, A.G. Barto, Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction (MIT Press, 2018)
K. Vinotha, Bellman equation in dynamic programming. Int. J. Comput. Algorithm 3(3), 277–279 (2014)
C.J. Watkins, P. Dayan, Q-learning. Mach. Learn. 8(3–4), 279–292 (1992)
S.S. Haykin, Neural Networks and Learning Machines (Prentice Hall, New York, 2009)
P. Abbeel, A. Coates, M. Quigley, A.Y. Ng, An application of reinforcement learning to aerobatic helicopter flight, in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2007), pp. 1–8)
Y.C. Wang, J.M. Usher, Application of reinforcement learning for agent-based production scheduling. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 18(1), 73–82 (2005)
L. Peshkin, V. Savova, Reinforcement learning for adaptive routing, in Proceedings of the 2002 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. IJCNN’02 (Cat. No. 02CH37290), vol. 2 (IEEE, 2002), pp. 1825–1830. (2002, May)
X. Dai, C.K. Li, A.B. Rad, An approach to tune fuzzy controllers based on reinforcement learning for autonomous vehicle control. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 6(3), 285–293 (2005)
B.C. Csáji, L. Monostori, B. Kádár, Reinforcement learning in a distributed market-based production control system. Adv. Eng. Inform. 20(3), 279–288 (2006)
W.D. Smart, L.P. Kaelbling, Effective reinforcement learning for mobile robots, in Proceedings 2002 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No. 02CH37292), vol. 4 (IEEE, 2002), pp. 3404–3410. (2002, May)
J.J. Choi, D. Laibson, B.C. Madrian, A. Metrick, Reinforcement learning and savings behavior. J. Financ. 64(6), 2515–2534 (2009)
M. Bowling, M. Veloso, An Analysis of Stochastic Game Theory for Multiagent Reinforcement Learning (No. CMU-CS-00-165). (Carnegie-Mellon University Pittsburgh Pa School of Computer Science, 2000)
D. Silver, A. Huang, C.J. Maddison, A. Guez, L. Sifre, G. Van Den Driessche, J. Schrittwieser, I. Antonoglou, V. Panneershelvam, M. Lanctot, S. Dieleman, Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature, 529(7587), 484 (2016)
V. Mnih, K. Kavukcuoglu, D. Silver, A. Graves, I. Antonoglou, D. Wierstra, M. Riedmiller, Playing atari with deep reinforcement learning (2013). ar**v:1312.5602
V. Mnih, K. Kavukcuoglu, D. Silver, A.A. Rusu, J. Veness, M.G. Bellemare, A. Graves, M. Riedmiller, A.K. Fidjeland, G. Ostrovski, S. Petersen Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 518(7540), 529 (2015)
H.V. Hasselt, Double Q-learning, in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2010), pp. 2613–2621
H. Van Hasselt, A. Guez, D. Silver, Deep reinforcement learning with double q-learning, in Thirtieth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2016, March)
Z. Wang, T. Schaul, M. Hessel, H. Van Hasselt, M. Lanctot, N. De Freitas, Dueling network architectures for deep reinforcement learning (2015). ar**v:1511.06581
J. Sharma, P.A. Andersen, O.C. Granmo, M. Goodwin, Deep q-learning with q-matrix transfer learning for novel fire evacuation environment (2019). ar**v:1905.09673
A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, G.E. Hinton, Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks, in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2012), pp. 1097–1105
A. Karpathy, G. Toderici, S. Shetty, T. Leung, R. Sukthankar, L. Fei-Fei, Large-scale video classification with convolutional neural networks, in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2014), pp. 1725–1732
T.N. Sainath, O. Vinyals, A. Senior, H. Sak, Convolutional, long short-term memory, fully connected deep neural networks, in 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (IEEE, 2015), pp. 4580–4584. (2015, April)
O. Abdel-Hamid, A.R. Mohamed, H. Jiang, G. Penn, Applying convolutional neural networks concepts to hybrid NN-HMM model for speech recognition, in 2012 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech And Signal Processing (ICASSP) (IEEE, 2012), pp. 4277–4280. (2012, March)
A. Uçar, Y. Demir, C. Güzeliş, Moving towards in object recognition with deep learning for autonomous driving applications, in 2016 International Symposium on INnovations in Intelligent SysTems and Applications (INISTA) (IEEE, 2016), pp. 1–5. (2016, August)
H.A. Pierson, M.S. Gashler, Deep learning in robotics: a review of recent research. Adv. Robot. 31(16), 821–835 (2017)
L. Fei-Fei, J. Deng, K. Li, ImageNet: constructing a large-scale image database. J. Vis. 9(8), 1037–1037 (2009)
A.E. Sallab, M. Abdou, E. Perot, S. Yogamani, Deep reinforcement learning framework for autonomous driving. Electron. Imaging 2017(19), 70–76 (2017)
Y. Zhu, R. Mottaghi, E. Kolve, J.J. Lim, A. Gupta, L. Fei-Fei, A. Farhadi, Target-driven visual navigation in indoor scenes using deep reinforcement learning, in 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) (IEEE, 2017), pp. 3357–3364. (2017, May)
S. Levine, C. Finn, T. Darrell, P. Abbeel, End-to-end training of deep visuomotor policies. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 17(1), 1334–1373 (2016)
L. **e, S. Wang, A. Markham, N. Trigoni, Towards monocular vision based obstacle avoidance through deep reinforcement learning (2017). ar**v:1706.09829
X.B. Peng, M. van de Panne, Learning locomotion skills using deeprl: does the choice of action space matter?, in Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation (ACM, 2017), p. 12. (2017, July)
G. Kahn, A. Villaflor, B. Ding, P. Abbeel, S. Levine, Self-supervised deep reinforcement learning with generalized computation graphs for robot navigation, in 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) (IEEE, 2018), pp. 1–8. (2018, May)
T. Hester, M. Vecerik, O. Pietquin, M. Lanctot, T. Schaul, B. Piot, D. Horgan, J. Quan, A. Sendonaris, I. Osband, G. Dulac-Arnold, Deep q-learning from demonstrations, in Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2018, April)
T. Schaul, J. Quan, I. Antonoglou, D. Silver, Prioritized experience replay (2015). ar**v:1511.05952
R.J. Williams, Simple statistical gradient-following algorithms for connectionist reinforcement learning. Mach. Learn. 8(3–4), 229–256 (1992)
V. Mnih, A.P. Badia, M. Mirza, A. Graves, T. Lillicrap, T. Harley, D. Silver, K. Kavukcuoglu, Asynchronous methods for deep reinforcement learning, in International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1928–1937. (2016, June)
A.V. Clemente, H.N. Castejón, A. Chandra, Efficient parallel methods for deep reinforcement learning (2017). ar**v:1705.04862
R.R. Torrado, P. Bontrager, J. Togelius, J. Liu, D. Perez-Liebana, Deep reinforcement learning for general video game AI, in 2018 IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence and Games (CIG) (IEEE, 2018), pp. 1–8. (2018, August)
G. Brockman, V. Cheung, L. Pettersson, J. Schneider, J. Schulman, J. Tang, W. Zaremba, Openai gym (2016). ar**v:1606.01540
Y. Demir, A. Uçar, Modelling and simulation with neural and fuzzy-neural networks of switched circuits. COMPEL Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 22(2), 253–272 (2003)
Ç. Kaymak, A. Uçar, A Brief survey and an application of semantic image segmentation for autonomous driving, in Handbook of Deep Learning Applications (Springer, Cham, 2019), pp. 161–200
A.W. Moore, C.G. Atkeson, Memory-based reinforcement learning: efficient computation with prioritized swee**, in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (1993), pp. 263–270
R. Özalp, C. Kaymak, Ö. Yildirum, A. Uçar, Y. Demir, C. Güzeliş, An implementation of vision based deep reinforcement learning for humanoid robot locomotion, in 2019 IEEE International Symposium on INnovations in Intelligent SysTems and Applications (INISTA) (IEEE, 2019), pp. 1–5 (2019, July)
https://lilianweng.github.io/lil-log/2018/04/08/policy-gradient-algorithms.html. Accessed 9 Sept 2019
C. Knoll, K. Röbenack, Generation of stable limit cycles with prescribed frequency and amplitude via polynomial feedback, in International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices (IEEE, 2012), pp. 1–6. (2012, March)
I. Goodfellow, Y. Bengio, A. Courville, Deep Learning. (MIT Press, 2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) grant numbers 117E589. In addition, GTX Titan X Pascal GPU in this research was donated by the NVIDIA Corporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Özalp, R., Varol, N.K., Taşci, B., Uçar, A. (2020). A Review of Deep Reinforcement Learning Algorithms and Comparative Results on Inverted Pendulum System. In: Tsihrintzis, G., Jain, L. (eds) Machine Learning Paradigms. Learning and Analytics in Intelligent Systems, vol 18. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-49724-8_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-49724-8_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-49723-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-49724-8
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)