Abstract
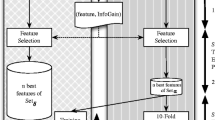
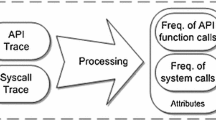
As the most widely used operating system for smartphones, Android is still growing, with many applications deployed in the mobile space, as well as other Android-based Internet-of-Things devices. A major side effect of the unprotected usage of such apps is the security loophole allowing app developers to access users’ critical data on their devices. Hence, the lack of modern, precise validation of Android apps necessitates a new technique for malware detection. Proposed is a new smart mechanism that utilizes several machine learning models to analyze Android app behavior. More than 100 thousand Android application packages (APKs) containing more than 80,000 malware variants from 179 different families (in addition to benign Android apps) were collected. For added robustness, the model was trained with various malware found between 2006 and 2018. In consideration of the utilized app-dataset size, our smart model is poised as a very fast processing method for vast amounts of apps, unimplemented by other works in the field. The proposed smart Android malware detector obtained a very encouraging accuracy, ranging between 95% and 97%, on average for around 100 thousand analyzed APKs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou, Y., Wang, Z., Zhou, W., Jiang, X.: Hey, you, get off of my market: detecting malicious apps in official and alternative Android markets. In: Proceedings of the 19th Annual Network & Distributed System Security Symposium, February 2012
Zhou, Y., Jiang, X.: Dissecting android Malware: characterization and evolution security and privacy (SP). In: 2012 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (2012)
Cheng, J., Wong, S.H., Yang, H., Lu, S.: SmartSiren: virus detection and alert for smartphones. In: International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services (MobiSys) (2007)
Sanz, B., Santos, I., Laorden, C., Ugarte-Pedrero, X., Bringas, P.G., Alvarez, G.: PUMA: permission usage to detect Malware in Android. In: Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing (AISC) (2012)
Wang, J., Deng, P., Fan, Y., Jaw, L., Liu, Y.: Virus detection using data mining techniques. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (2003)
Android-Apktool, a tool for reverse engineering Android APK files. https://code.google.com/p/android-apktool/
MARVIN: efficient and comprehensive mobile app classification through static and dynamic analysis
Android Platform Architecture. https://developer.android.com/guide/platform/
Chen, X., Andersen, J., Mao, Z., Bailey, M., Nazario, J.: Towards an understanding of anti-virtualization and anti-debugging behavior in modern malware. In: DSN (2008)
Jidigam, R.K., Austin, T.H., Stamp, M.: Singular value decomposition and metamorphic detection. J. Comput. Virol. Hacking Tech. 11(4), 203–216 (2014)
Fredrikson, M., Jha, S., Christodorescu, M., Sailer, R., Yan, X.: Synthesizing near-optimal malware specifications from suspicious behaviors. In: SP 2010 Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, pp. 45–60 (2010)
Kolbitsch, C., Comparetti, P.M., Kruegel, C., Kirda, E., Zhou, X., Wang, X.: Effective and efficient malware detection at the end host. In: USENIX Security (2009)
Lanzi, A., Balzarotti, D., Kruegel, C., Christodorescu, M., Kirda, E.: AccessMiner: using system-centric models for malware protection. In: CCS (2010)
Palahan, S., Babic, D., Chaudhuri, S., Kifer, D.: Extraction of statistically significant malware behaviors. In: ACSAC (2013)
Paleari, R., Martignoni, L., Roglia, G.F., Bruschi, D.: A fistful of red-pills: How to automatically generate procedures to detect CPU emulators. In: USENIX WOOT (2009)
Rieck, K., Trinius, P., Willems, C., Holz, T.: Automatic analysis of malware behavior using machine learning. J. Comput. Secur. 19(4), 639–668 (2011)
Singh, T., Di Troia, F., Corrado, V.A., et al.: J. Comput. Virol. Hack. Tech. 12, 203 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11416-015-0252-0
Zhu, D.Y., Jung, J., Song, D., Kohno, T., Wetherall, D.: TaintEraser: protecting sensitive data leaks using application-level taint tracking. SIGOPS Oper. Syst. Rev. 45(1), 142–154 (2011)
Peiravian, N., Zhu, X.: Machine learning for Android malware detection using permission and API calls. In: 2013 IEEE 25th International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (2013)
Li, X., Liu, J., Huo, Y., Zhang, R., Yao, Y.: An Android malware detection method based on Android Manifest file. In: International Conference on Cloud Computing and Intelligence Systems (CCIS), pp. 239–243 (2016)
Talha, K.A., Alper, D.I., Aydin, C.: APK Auditor: permission-based Android malware detection system. Digit. Invest. 13, 1–14 (2015)
Arasavalli, S., Sravya, Y., Venuturumilli, S., Tottempudi, P., Ramakoteswarrao, G.: Securing Android devices from snoo** apps. ICOEI 2018 (2018)
Virus Total. https://www.virustotal.com/gui/graph-overview
Arp, D., Spreitzenbarth, M., Hubner, M., Gascon, H., Rieck, K: Drebin: efficient and explainable detection of Android Malware in your pocket. In: 21th Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium (NDSS), February 2014
Spreitzenbarth, M., Echtler, F., Schreck, T., Freling, F.C., Hoffmann, J.: MobileSandbox: looking deeper into Android applications. In: 28th International ACM Symposium on Applied Computing (SAC), March 2013
Zheng, M., Sun, M., Lui, J.C.S.: Droid analytics: a signature based analytic system to collect, extract, analyze and associate Android malware. In: 2013 12th IEEE International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications (2013)
Choudhary, M., Kishore, B.: HAAMD: hybrid analysis for Android malware detection. In: 2018 International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI) (2018)
https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/permissions/overview
Cassel, M., Lima, F.: Evaluating one-hot encoding finite state machines for SEU reliability in SRAM-based FPGAs. In: 12th IEEE International On-Line Testing Symposium (IOLTS 2006) (2006)
Hearst, M.A., Dumais, S.T., Osuna, E., Platt, J., Scholkopf, B.: Support vector machines. IEEE Intell. Syst. Appl. 13(4), 18–28 (1998)
Breiman, L.: Mach. Learn. 45, 5 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Liao, Y., Vemuri, V.R.: Use of K-nearest neighbor classifier for intrusion detection. Comput. Secur. 21(5), 439–448 (2002)
Li, M., Yuan, B.: 2D-LDA: a statistical linear discriminant analysis for image matrix. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 26(5), 527–532 (2005)
Haifley, T.: Linear logistic regression: an introduction. In: IEEE International Integrated Reliability Workshop Final Report (2002)
Navada, A., Ansari, A.N., Patil, S., Sonkamble, B.A.: Overview of use of decision tree algorithms in machine learning. In: 2011 IEEE Control and System Graduate Research Colloquium (2011)
Wu, D.-J., Mao, C.-H., Wei, T.-E., Lee, H.-M., Wu, K.-P.: DroidMat: Android malware detection through manifest and API Calls tracing. In: 2012 Seventh Asia Joint Conference on Information Security (2012)
Seshardi, V., Ramzan, Z., Satish, S., Kalle, C.: Using machine infection characteristics for behavior-based detection of malware. https://patents.google.com/patent/US8266698B1/en
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Alahy, Q.E., Chowdhury, M.NUR., Soliman, H., Chaity, M.S., Haque, A. (2020). Android Malware Detection in Large Dataset: Smart Approach. In: Arai, K., Kapoor, S., Bhatia, R. (eds) Advances in Information and Communication. FICC 2020. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1129. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-39445-5_58
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-39445-5_58
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-39444-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-39445-5
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)