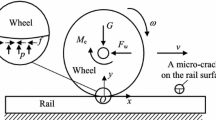
Abstract
In this study, we present a method for predicting the initiation of fatigue cracks at insulated rail joints (IRJs). The method includes (1) FE simulation of dynamic wheel/rail interaction at IRJs; (2) analysis on the evolution of wheel/rail contact behavior, and (3) numerical prediction on the initiation life and position of fatigue cracks. To demonstrate the method, we analyzed the crack initiation for a series of rail end intervals. The results indicate that shear loads in the material affects more on the initiation of fatigue cracks at both the surface and subsurface of rail head. Fatigue cracks have a higher likelihood to take place at 0–2 mm below the rail surface of IRJs, with the most dangerous region being at 1 mm below the rail surface. The variation of the rail end interval seldom affects the crack initiation life at the leading rail end of IRJs, whereas it can significantly influence the crack initiation life at the rear rail end.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Esveld, C.: Modern Railway Track, 2nd edn. MRT-Productions, The Netherlands (2001)
Dukkipati, R., Dong, R.: The dynamic effects of conventional freight car running over a dipped-joint. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 31(2), 95–111 (1999)
Mandal, N., Dhanasekar, M., Sun, Y.: Impact forces at dipped rail joints. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F: J. Rail Rapid Transit 230, 271–282 (2014)
Ringsberg, J.W.: Life prediction of rolling contact fatigue crack initiation. Int. J. Fatigue 23(7), 575–586 (2001)
Liu, Y., Stratman, B., Mahadevan, S.: Fatigue crack initiation life prediction of railroad wheels. Int. J. Fatigue 28(7), 747–756 (2006)
Nejad, R., Shariati, M., Farhangdoost, K.: Effect of wear on rolling contact fatigue crack growth in rails. Tribol. Int. 94, 118–125 (2016)
Mohammadzadeh, S., Sharavi, M., Keshavarzian, H.: Reliability analysis of fatigue crack initiation of railhead in bolted rail joint. Eng. Fail. Anal. 29, 132–148 (2013)
Yang, Z., Boogaard, A., Chen, R., Dollevoet, R., Li, Z.: Numerical and experimental study of wheel-rail impact vibration and noise generated at an insulated rail joint. Int. J. Impact Eng. 113, 29–39 (2018)
Yang, Z., Boogaard, A., Wei, Z., Liu, J., Dollevoet, R., Li, Z.: Numerical study of wheel-rail impact contact solutions at an insulated rail joint. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 138–139, 310–322 (2018)
Zhao, X., Zhao, X., Liu, C., Wen, Z., **, X.: A study on dynamic stress intensity factors of rail cracks at high speeds by a 3D explicit finite element model of rolling contact. Wear 366, 60–70 (2016)
Jiang, Y., Sehitoglu, H.: A model for rolling contact failure. Wear 224, 38–49 (1999)
Wang, J., Xu, Y., Lian, S., Wang, L.: Probabilistic prediction model for initiation of RCF cracks in heavy-haul railway. Int. J. Fatigue 33, 212–216 (2011)
Zhou, Y., Han, Y., Mu, D., Zhang, C., Huang, X.: Prediction of the coexistence of rail head check initiation and wear growth. Int. J. Fatigue 112, 289–300 (2018)
Akama, M., Matsuda, H., Doi, H., Tsujie, M.: Fatigue crack initiation life prediction of rails using theory of critical distance and critical plane approach. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 6, 54–69 (2012)
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank the support of Science and Technology Research and Development Plan of China Academy of Railway Sciences No. 2018YJ300 and 2018YJ146.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wei, Z., Liu, X., Zhou, Y., Jia, X., Li, G. (2020). Study on the Initiation of Fatigue Cracks Due to Wheel-Rail Impact at Insulated Rail Joints. In: Klomp, M., Bruzelius, F., Nielsen, J., Hillemyr, A. (eds) Advances in Dynamics of Vehicles on Roads and Tracks. IAVSD 2019. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-38077-9_86
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-38077-9_86
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-38076-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-38077-9
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)