Abstract
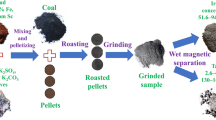
Red mud is a waste material of the Bayer process for alumina production from bauxite ore. Red mud is generally pumped to disposal in an artificial pond which is accompanied by great land occupation and environmental issues. Many researches in different fields have been carried out to evaluate the red mud . Of these, researches on recovering valuable metals from red mud are the most successful. In this study, recovery of iron , which is the most abundant metal in red mud , was investigated. A red mud sample with 34% Fe2O3 was used. Solid state carbothermic reduction followed by wet magnetic separation was performed to recover iron . Reduction was carried out at temperatures 1000–1200 °C. Reduced samples were ground and subjected to wet magnetic separation. The effect of reduction temperature and grinding time were investigated on the metallization of iron and the iron content of the final concentrate.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paramguru RK, Rath PC, Misra VN (2005) Trend in red mud utilization—a review. Miner Process Extr Metall Rev Int J 26:1–29
Mayes W et al (2015) Risks, remediation and recovery: lessons for bauxite rsidue management from Ajka. Paper presented at the bauxite residue valorisation and best practices, Leuven, 5–7 October 2015
Li G, Liu M, Rao M, Jiang T, Zhuang J, Zhang Y (2014) Stepwise extraction of valuable components from red mud based on reductive roasting with sodium salts. J Hazard Mater 280:774–780
Samouhos M, Taxiarchou M, Tsakiridis PE, Potiriadis K (2013) Greek “red mud” residue: a study of microwave reductive roasting followed by magnetic separation for a metallic iron recovery process. J Hazard Mater 254–255:193–205
Zhu D, Chun T, Pan J, He Z (2012) Recovery of iron from high-iron red mud by reduction roasting with adding sodium salt. J Iron Steel Res Int 19(8):1–5
Borra CR, Pontikes Y, Binnemans K, Gerven TV (2015) Leaching of rare earths from bauxite residue (red mud). Miner Eng 76:20–27
Wang W, Pranolo Y, Cheng CY (2013) Recovery of scandium from synthetic red mud leach solutions by solvent extraction with D2EHPA. Sep Purif Technol 108:96–102
Liu Y, Naidu R (2014) Hidden values in bauxite residue (red mud): recovery of metals. Waste Manag 34(12):2662–2673
Liu Z, Li H (2015) Metallurgical process for valuable elements recovery from red mud—a review. Hydrometallurgy 155:29–43
Piga L, Pochetti F, Stoppa L (1993) Recovering metals from red mud generated during alumina production. JOM 45(11):54–59
Acknowledgements
The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TÜBİTAK) is greatly acknowledged for the financial support under the project no: 117M185.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society
About this paper
Cite this paper
Eray, S., Keskinkilic, E., Varol, M., Topkaya, Y.A., Geveci, A. (2020). A Study on Recovery of Iron from Red Mud by Solid State Reduction Followed by Magnetic Separation. In: Peng, Z., et al. 11th International Symposium on High-Temperature Metallurgical Processing. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36540-0_35
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36540-0_35
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-36539-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-36540-0
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)